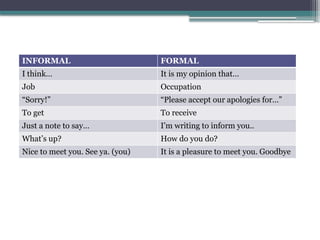
The document discusses the concept of diction, emphasizing the importance of word choice in writing and speaking. It differentiates between formal, informal, colloquial, and slang diction, highlighting their unique characteristics and appropriate contexts. Additionally, it explores the significance of diction in conveying meaning and emotional impact, along with specific examples and a quiz to test comprehension.