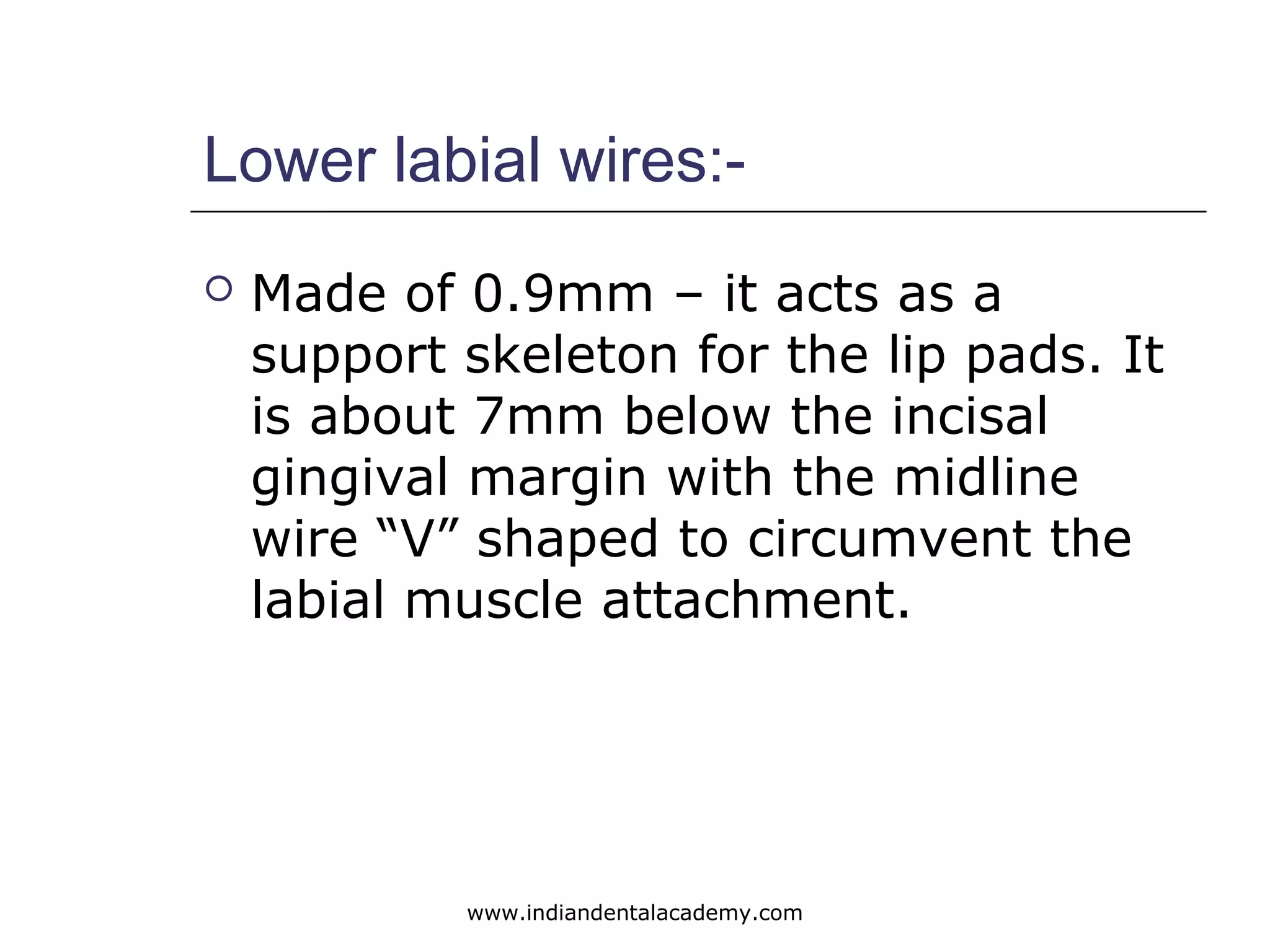
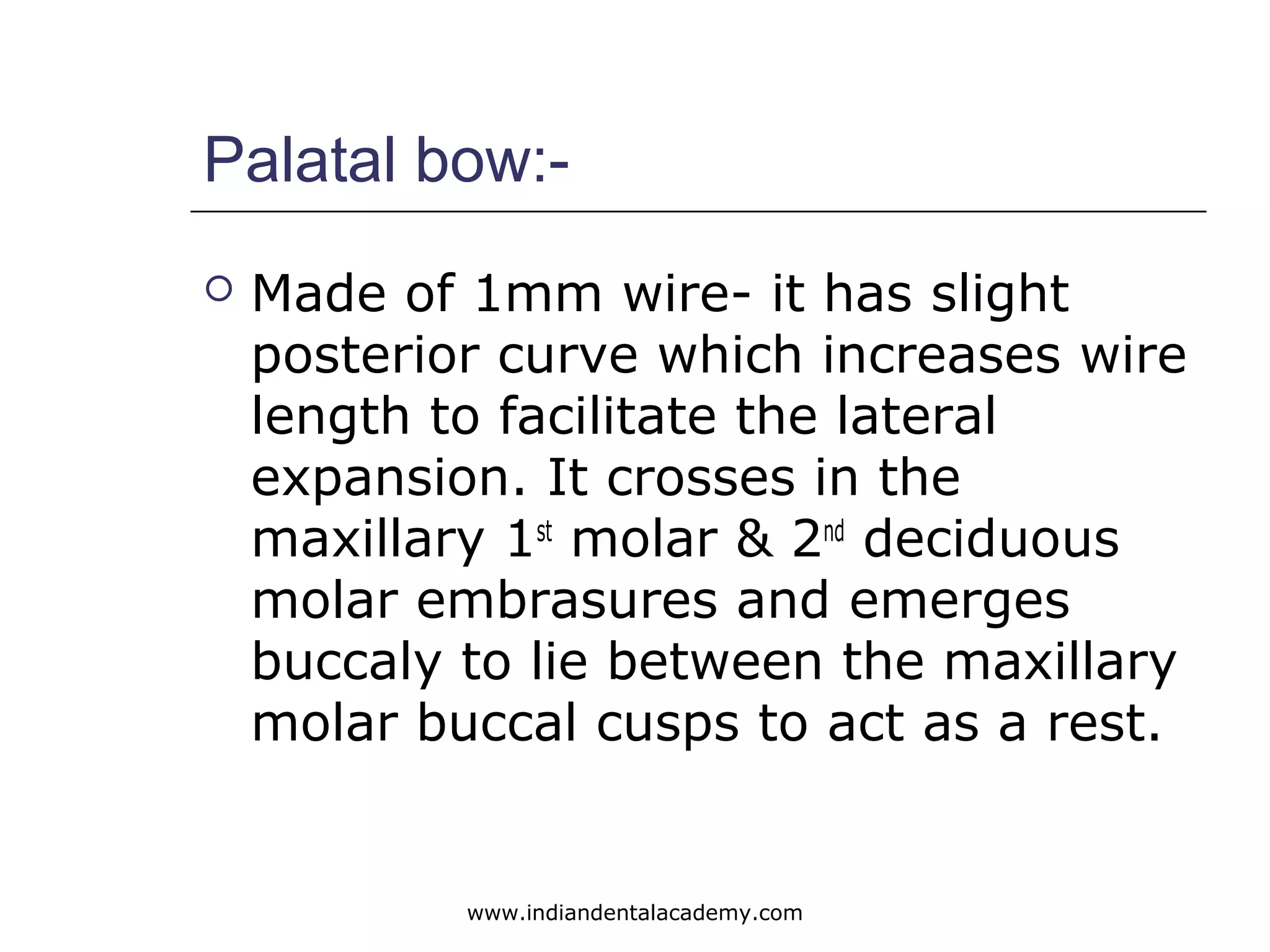
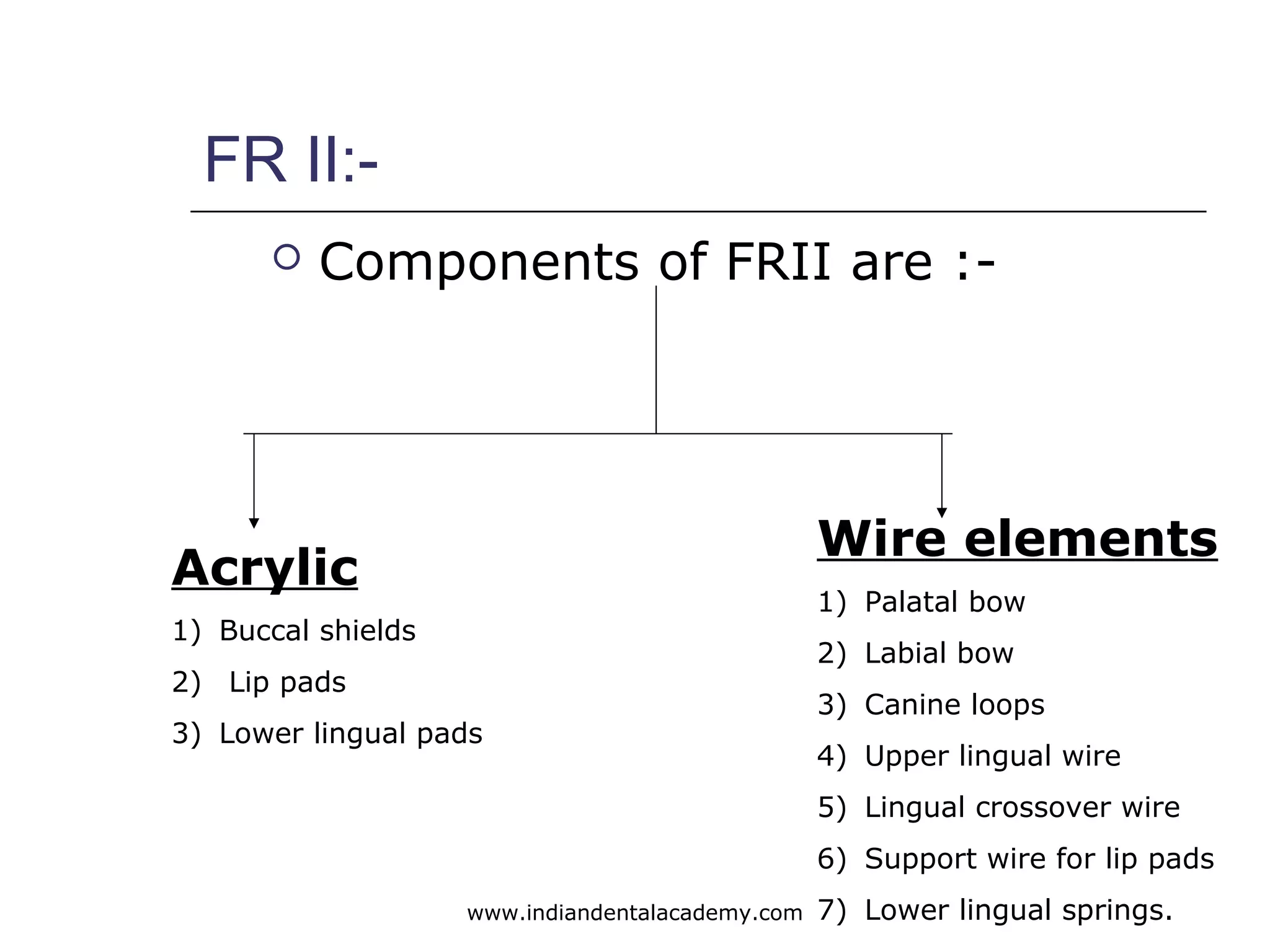
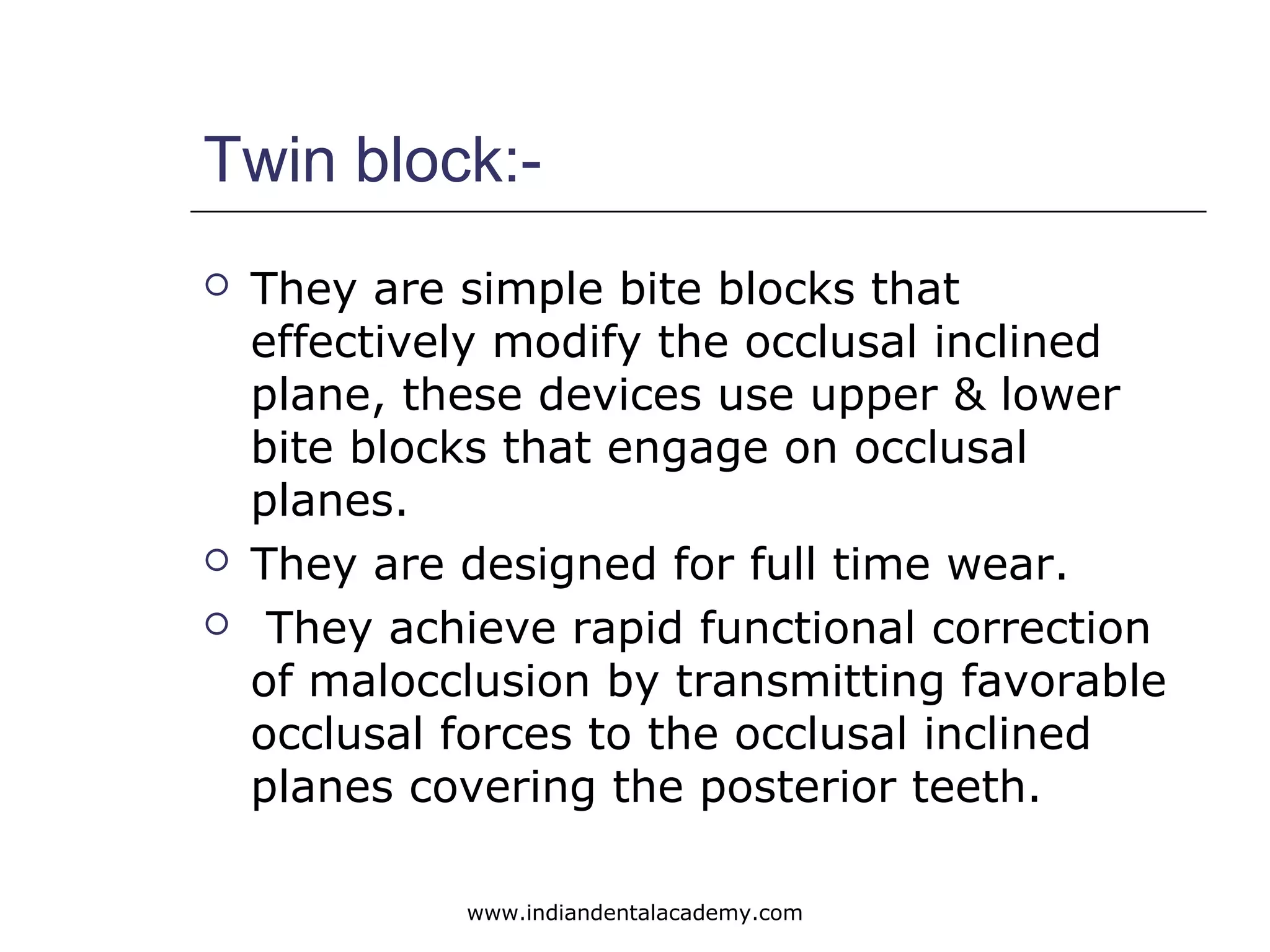
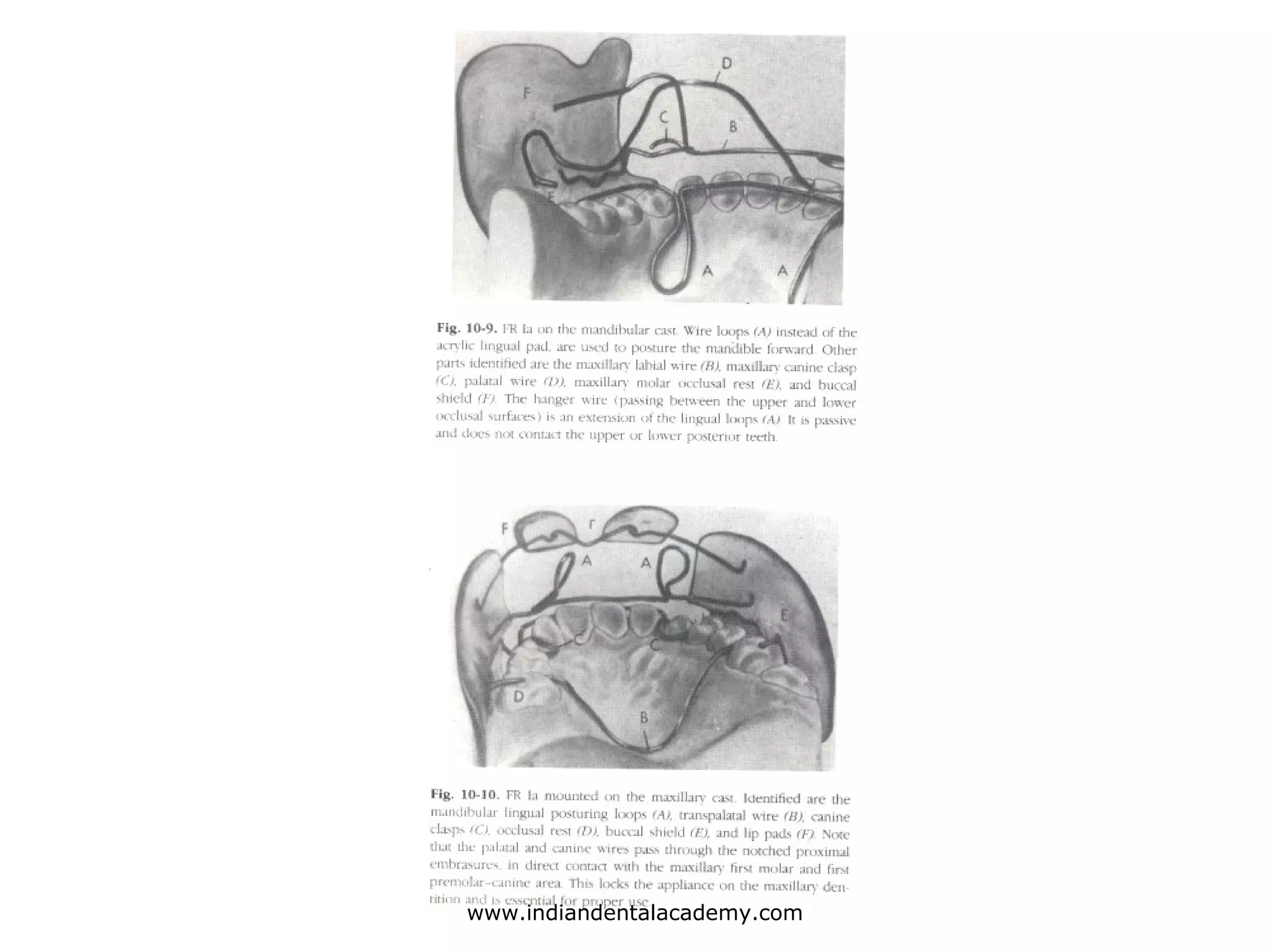
The document discusses myofunctional appliances and their role in orthodontic treatment, focusing on cephalometric and functional analysis. It details the use of the bionator and frankel appliance for correcting various malocclusions, including Class II and III, through functional stimuli and proper tongue positioning. Key concepts include the importance of lip seal, the appliance's structural design, and their therapeutic effects on the dentofacial complex.