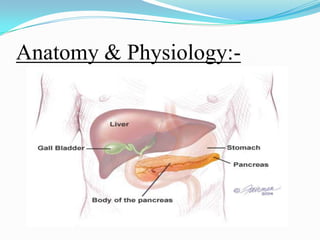
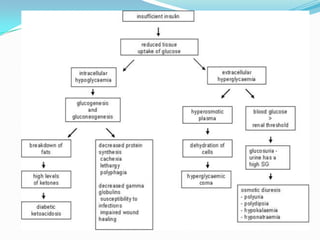
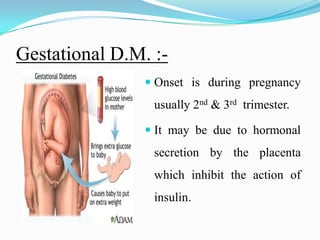
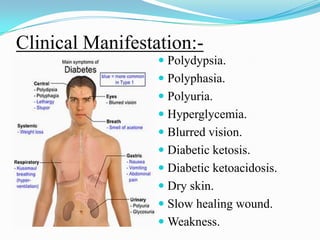
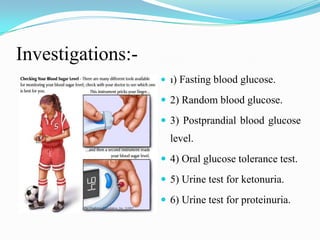
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease characterized by high blood glucose levels due to either insufficient insulin production or the body's inability to use insulin properly. There are several types of diabetes including type 1 caused by autoimmune destruction of insulin-producing beta cells, and type 2 typically associated with obesity and aging and initially managed through lifestyle changes and oral medications. Complications of diabetes can be acute like ketoacidosis or hypoglycemia, or chronic through damage to blood vessels and nerves over many years.