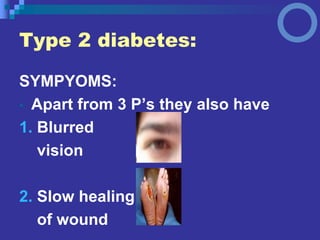
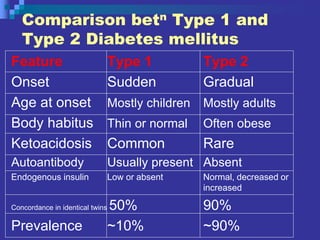
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder where the body has too much glucose in the blood due to either not producing enough insulin or cells not responding to insulin. There are four main types of diabetes: Type 1 is characterized by insulin deficiency due to loss of beta cells in the pancreas and accounts for 10% of cases. Type 2 is characterized by insulin resistance and accounts for 90% of cases. Type 3 covers specific genetic defects affecting insulin action. Gestational diabetes occurs in 2-5% of pregnancies and may improve after delivery but increases risk of later Type 2 diabetes. Diabetes increases risks of heart disease, stroke, nerve damage, foot ulcers, blindness, and kidney failure. Treatment focuses on blood glucose control through lifestyle changes