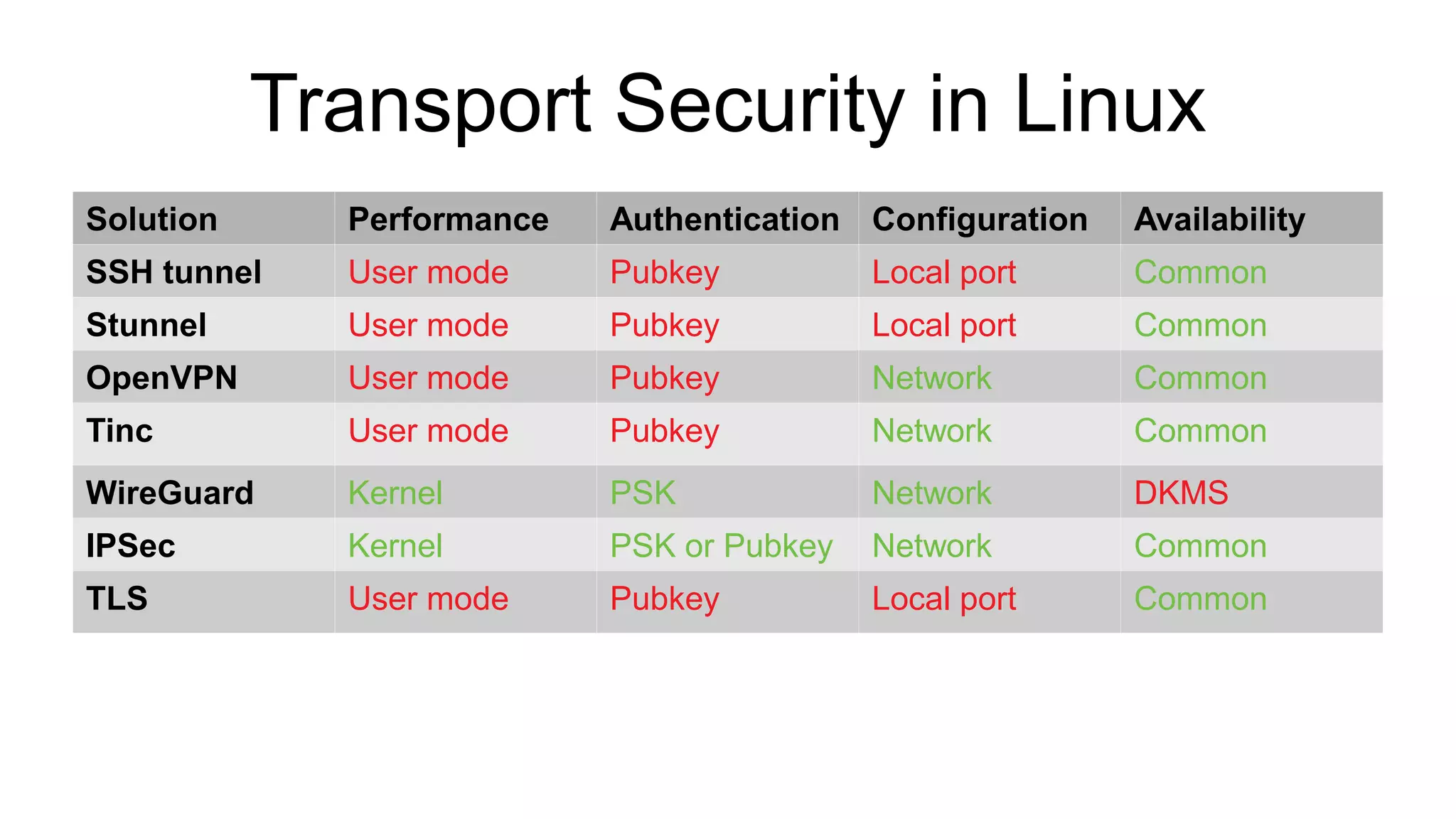
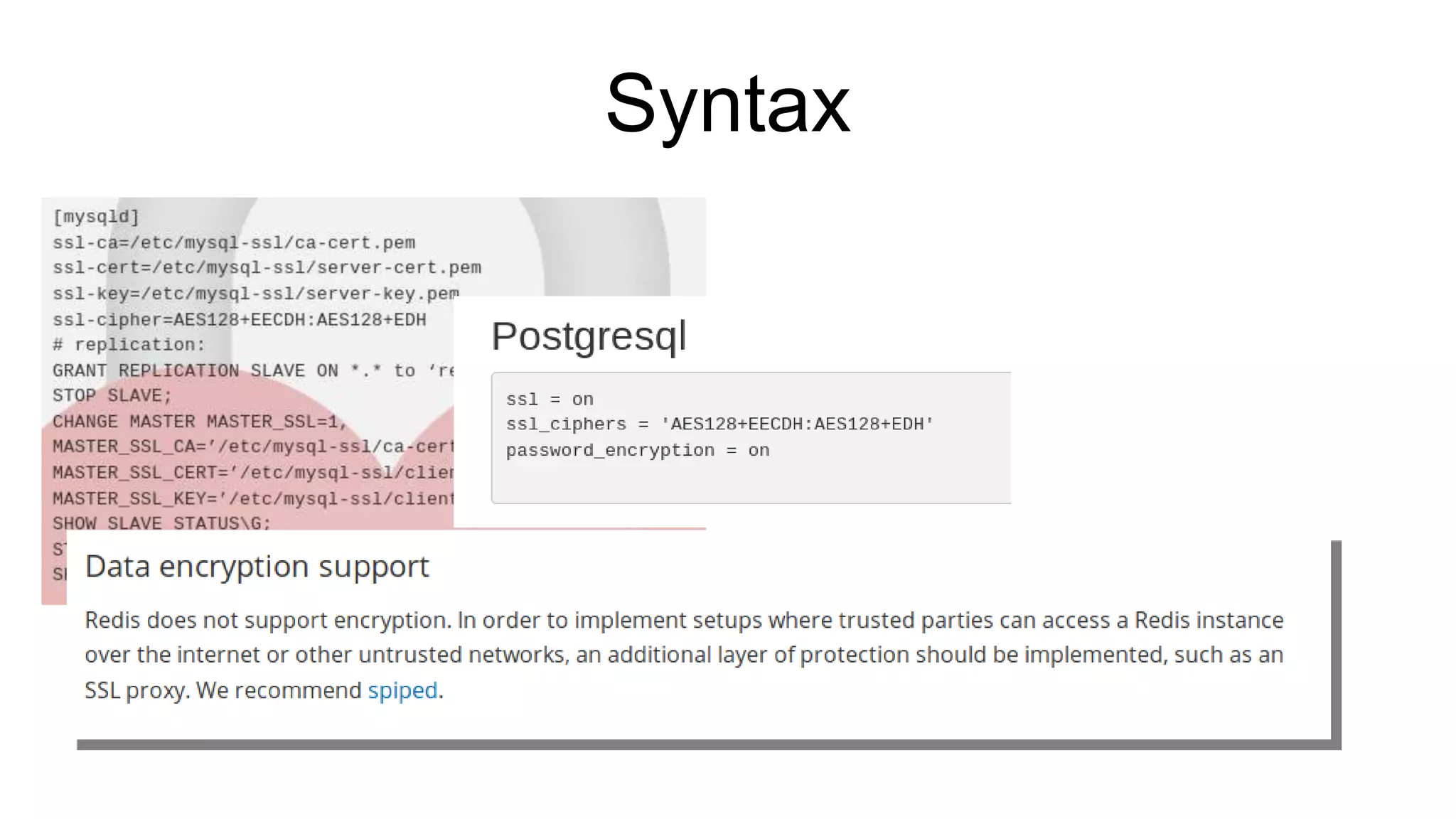
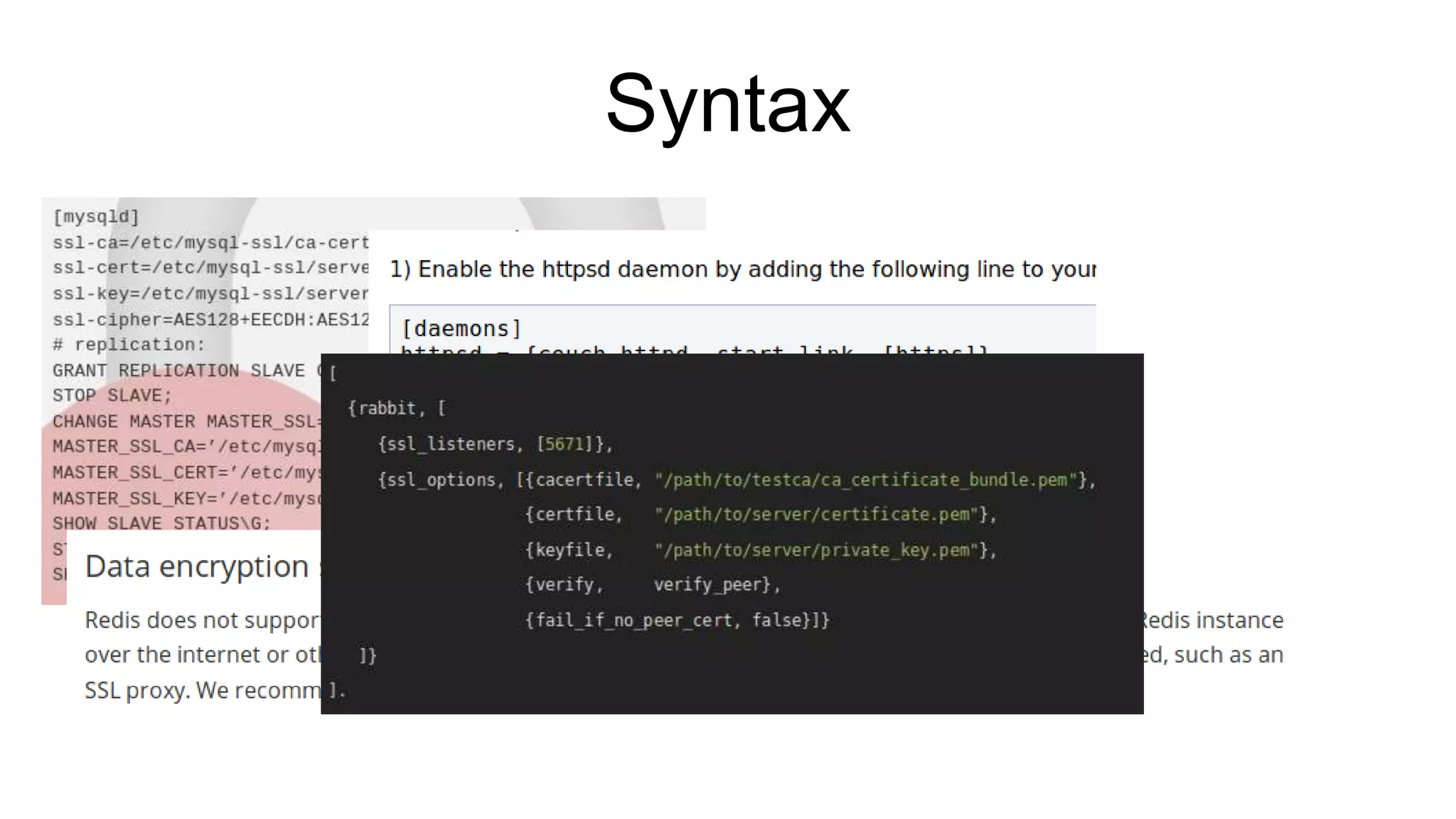
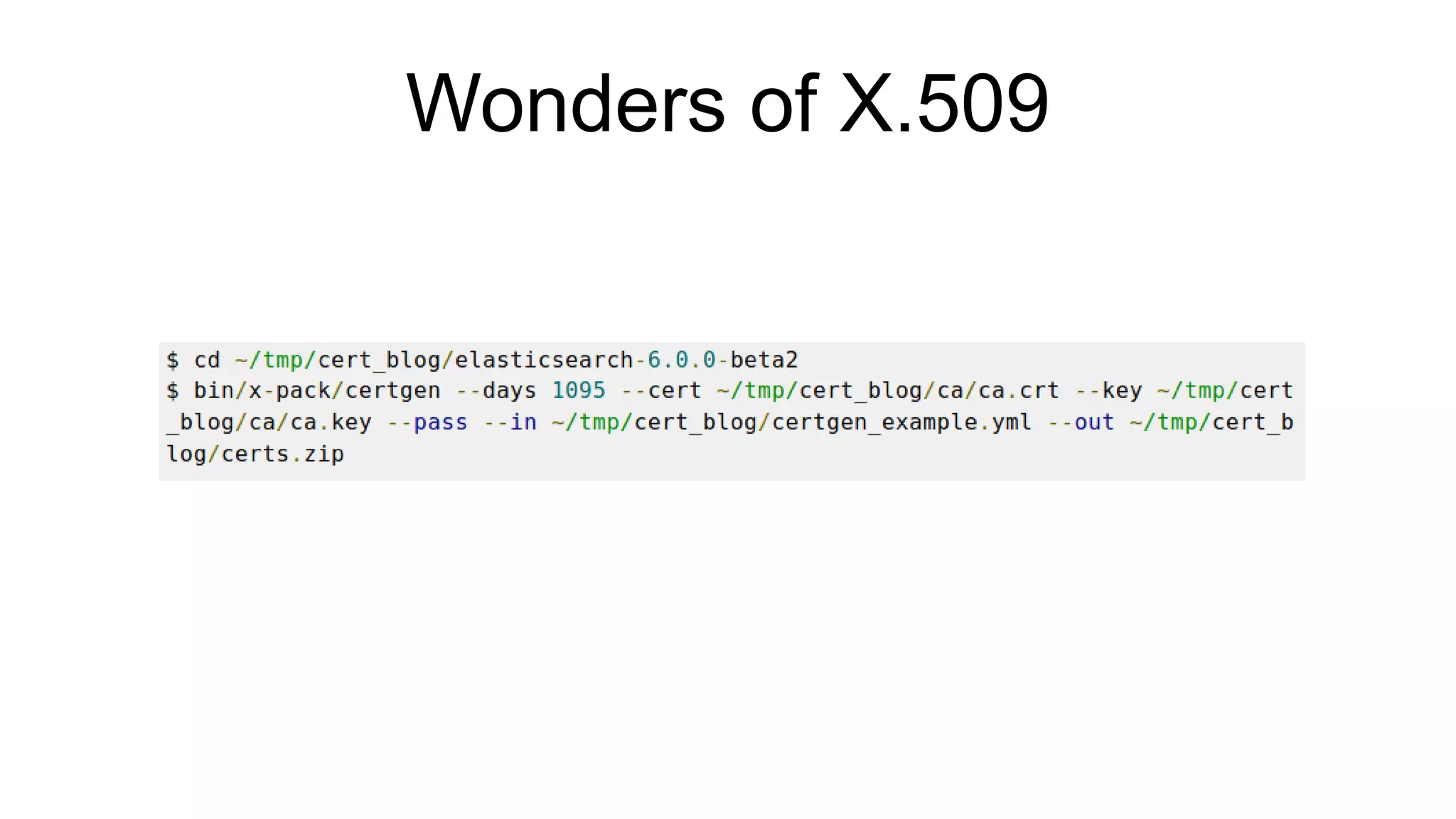
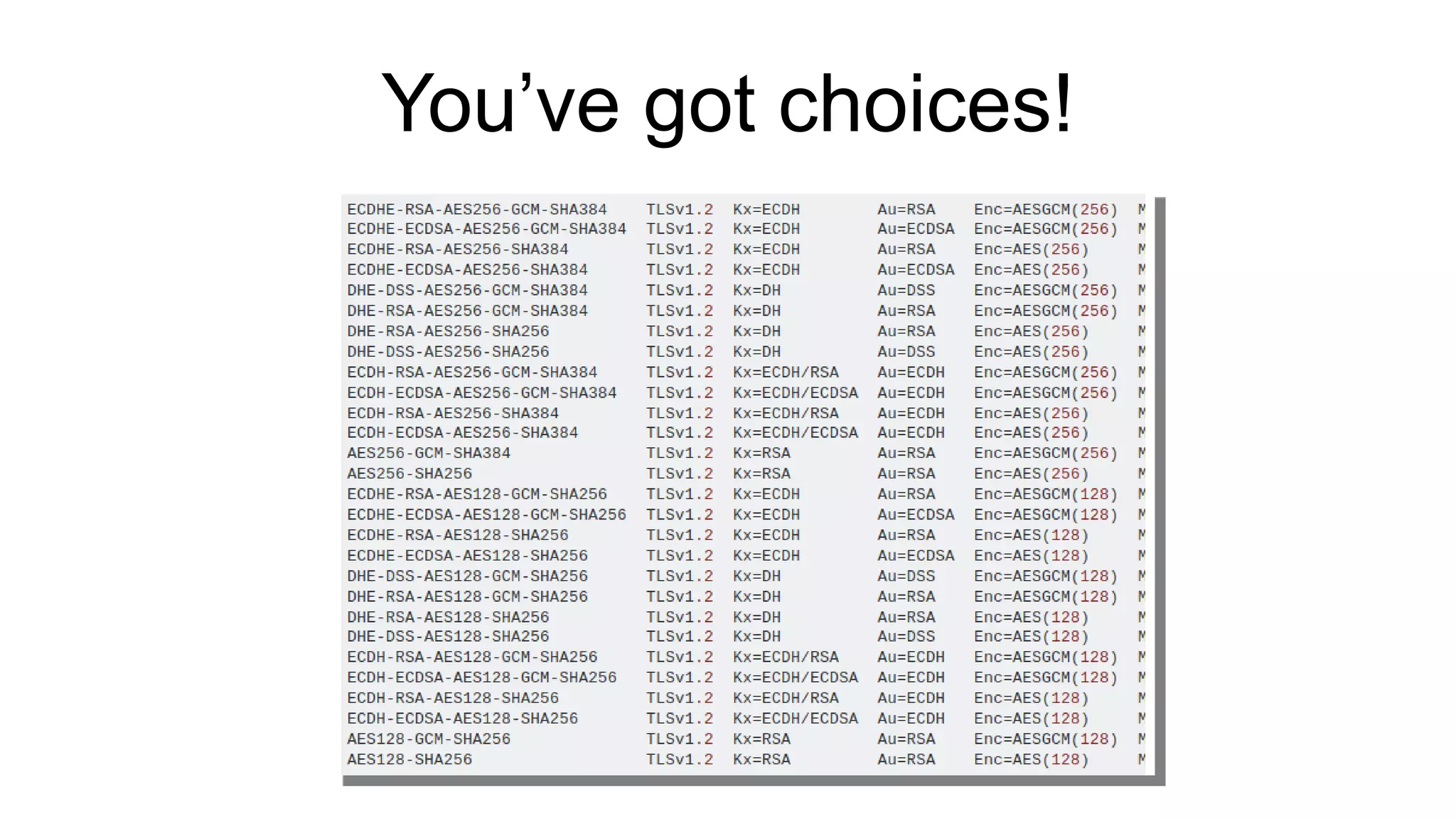
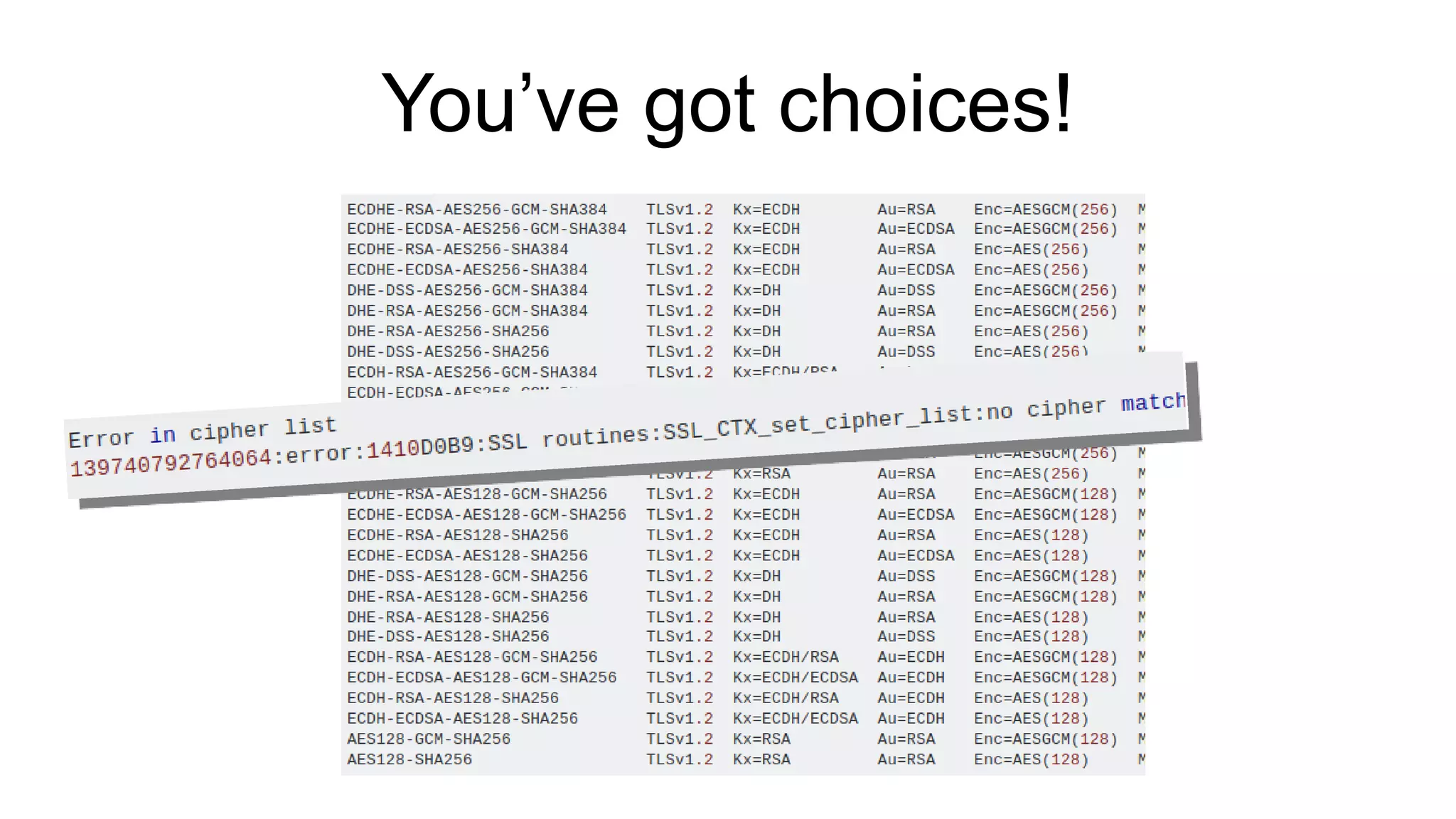
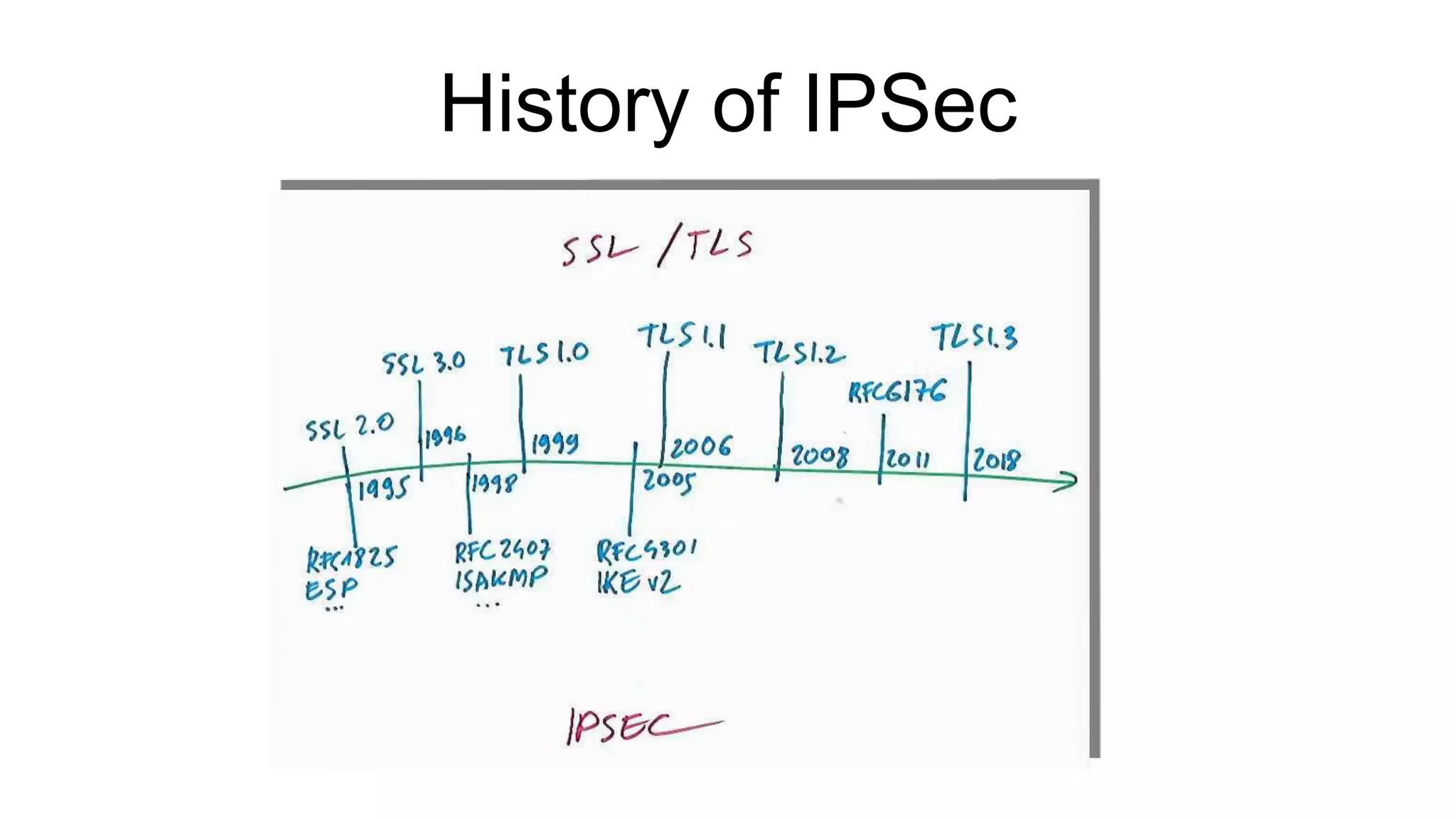
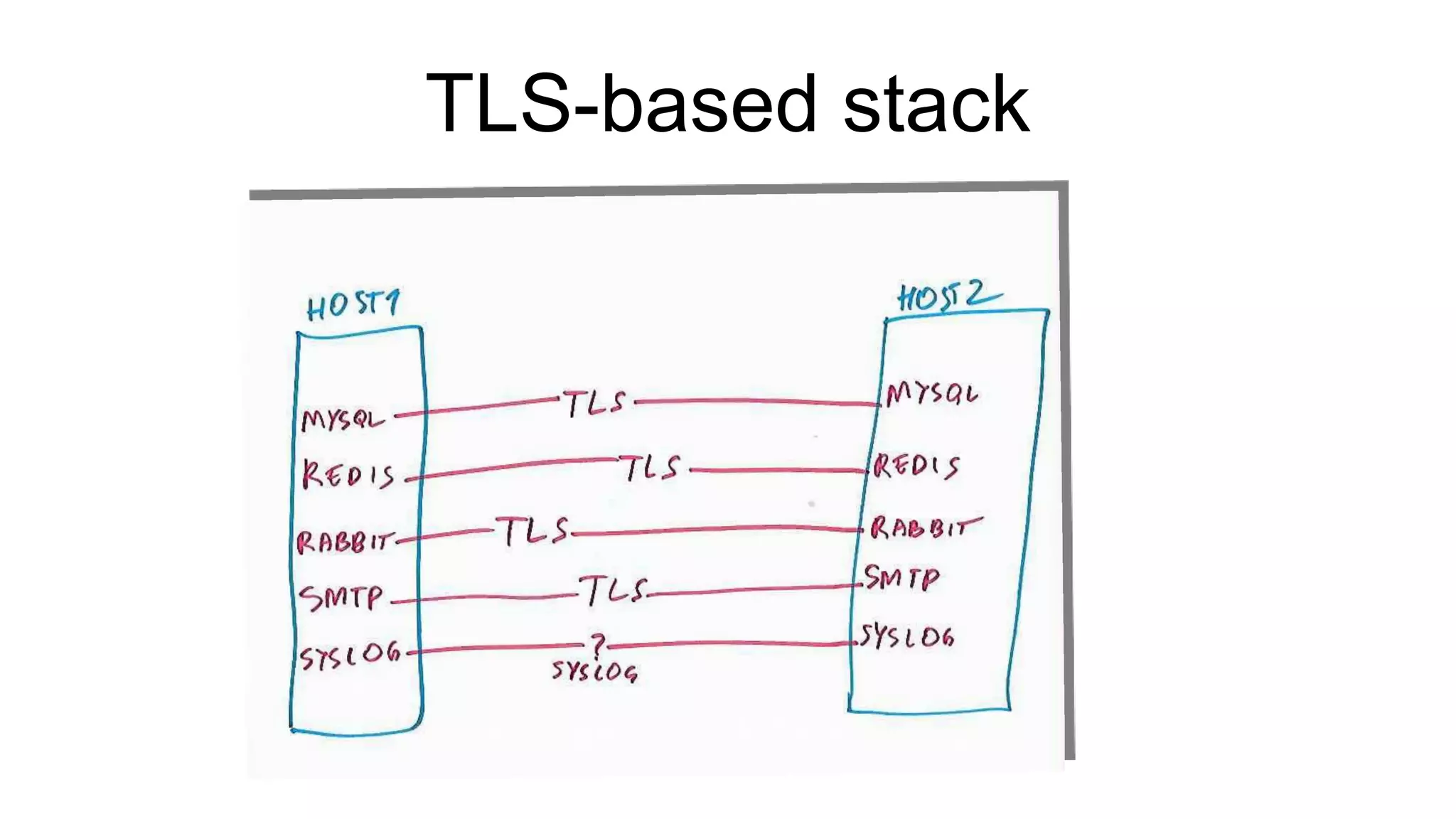
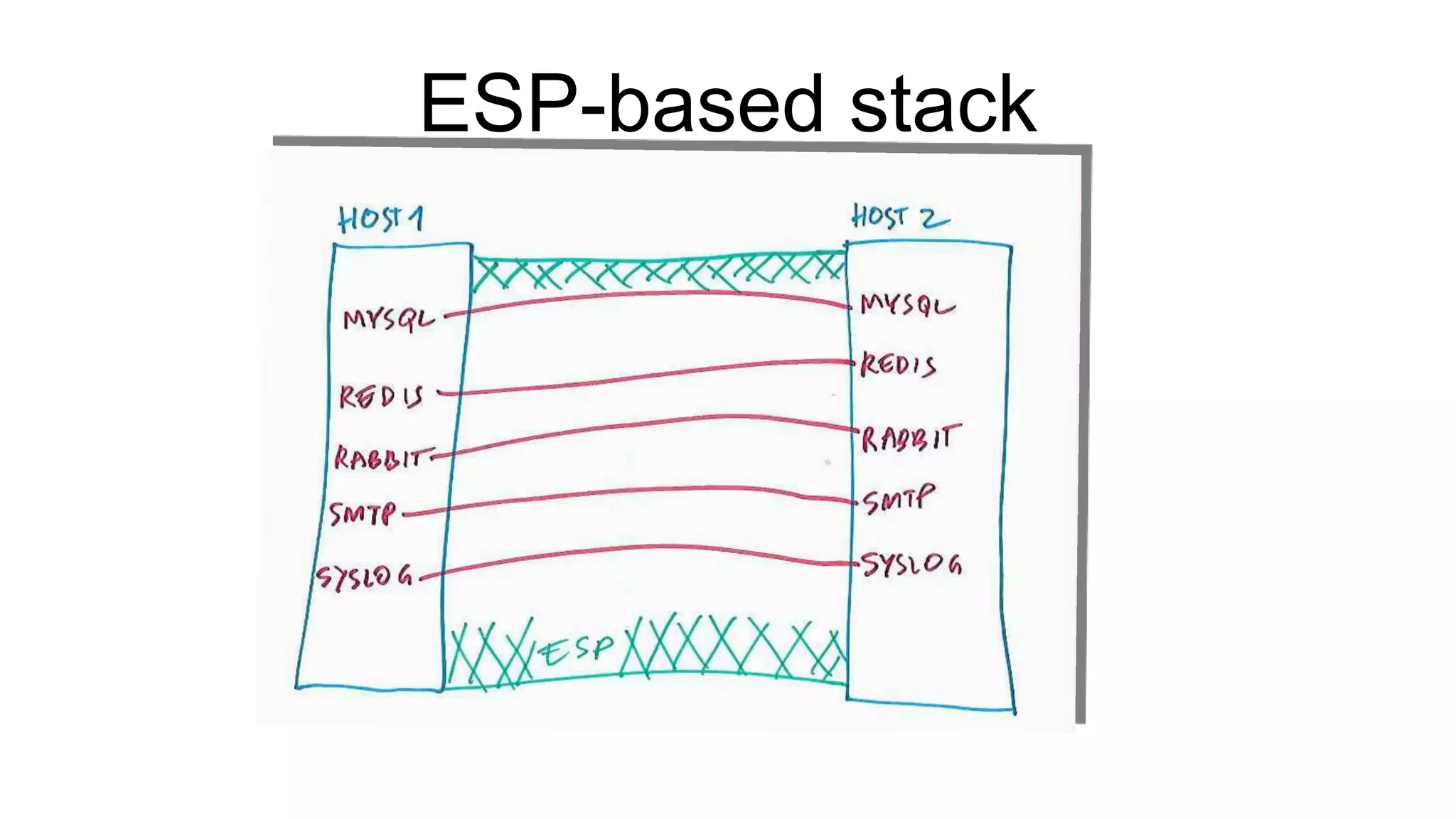
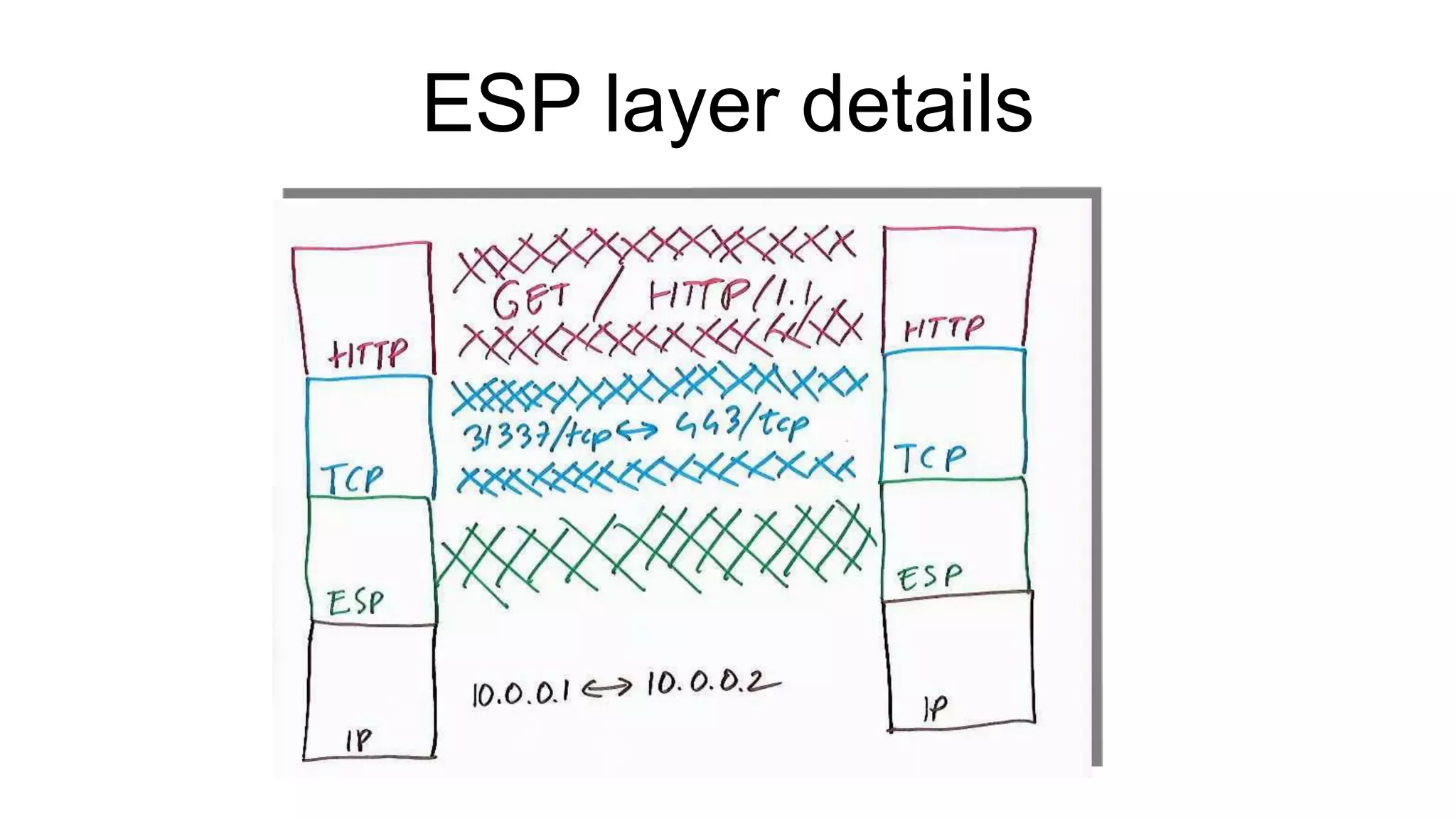
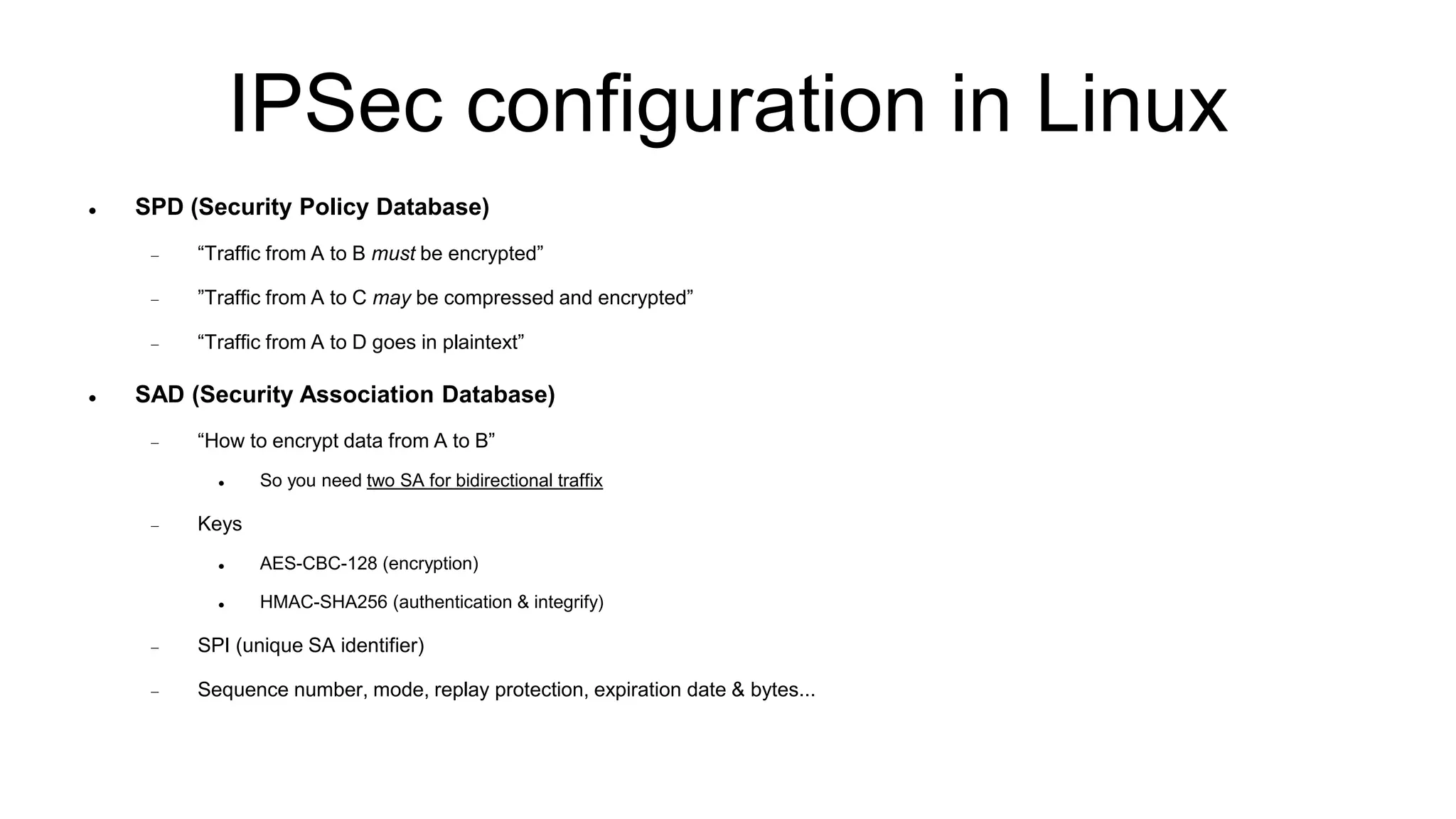
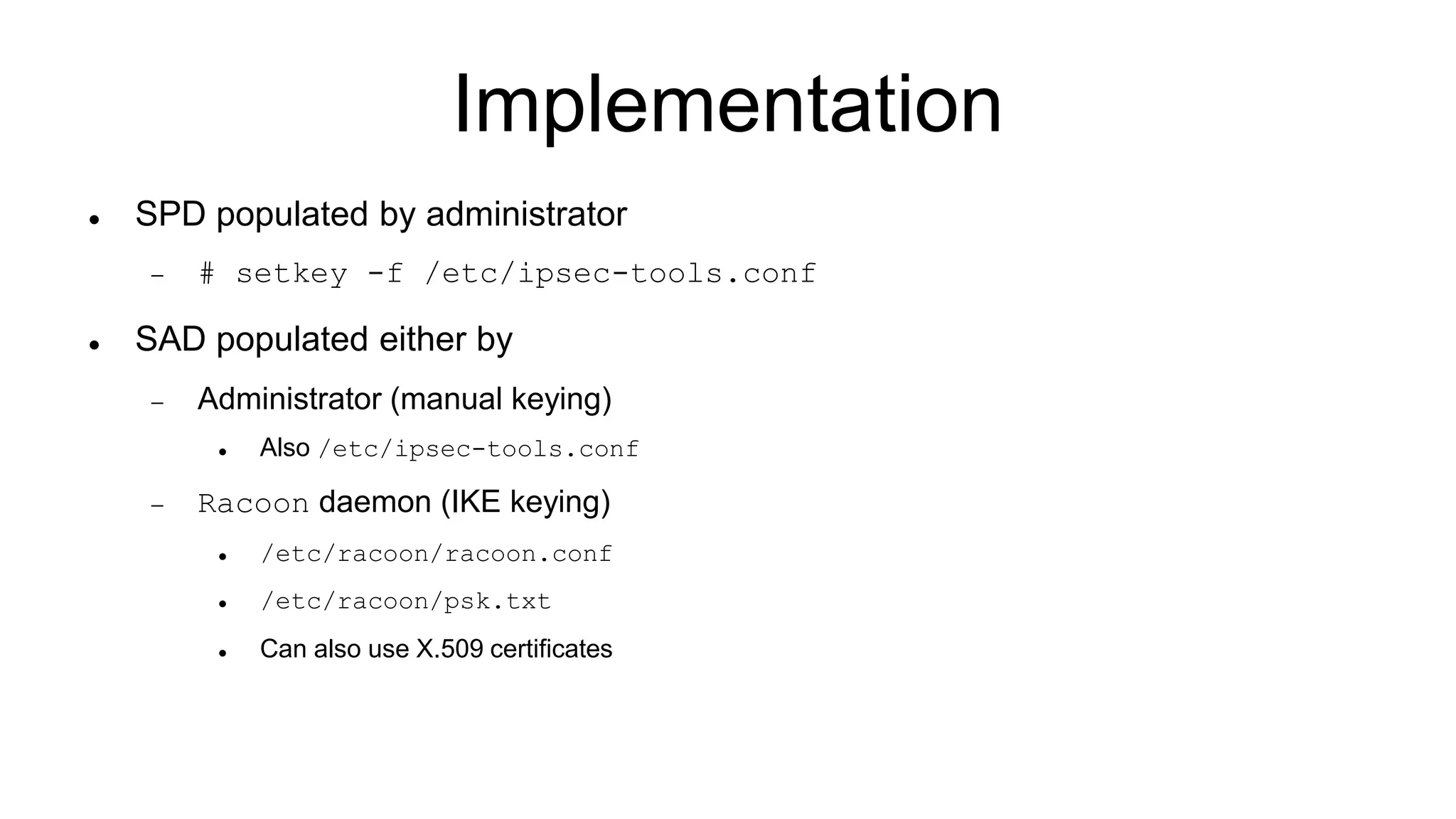
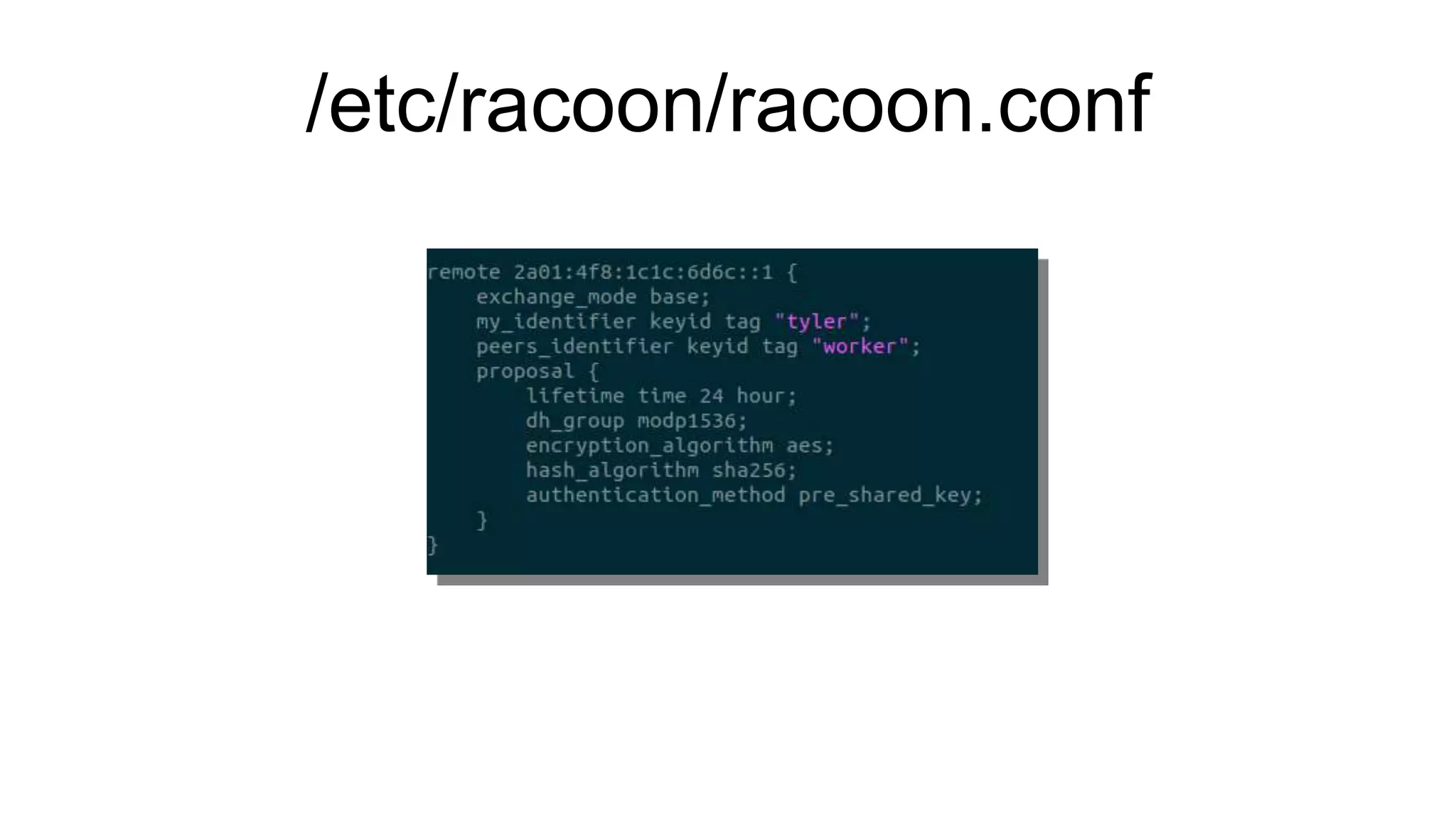
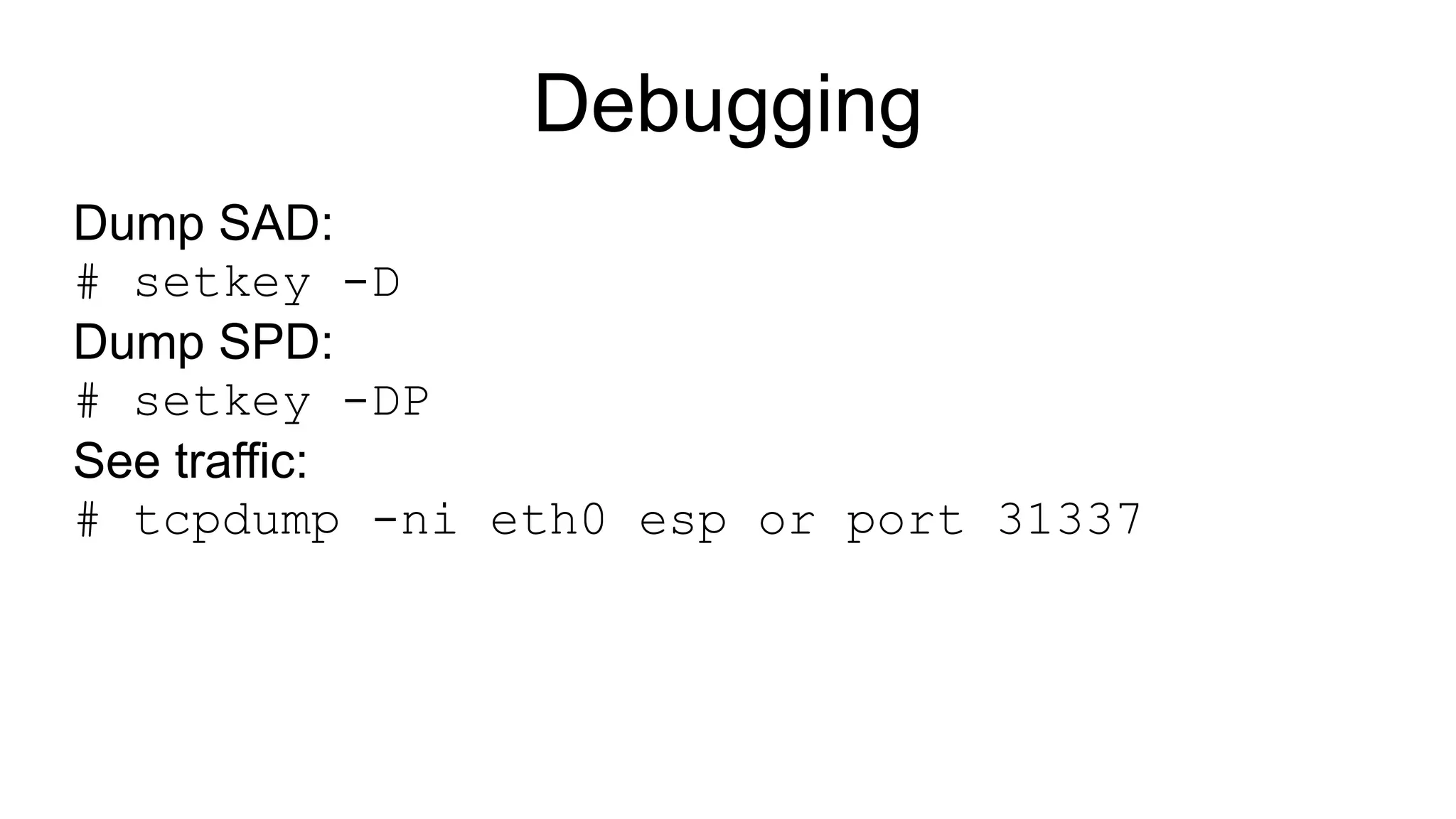
The document discusses various aspects of implementing and managing IPsec in Linux, covering Security Policy Database (SPD) and Security Association Database (SAD). It provides detailed explanations of configurations, troubleshooting, and automating IPsec setups using Ansible. Additionally, it highlights the importance of key management and the role of the racoon daemon in maintaining IPsec connections.