The document discusses using PHP to summarize documents in 3 sentences or less that provide the key information. It discusses two main ways to pass variables and values to a PHP script - using hidden HTML inputs or appending values to the PHP script's URL. It also discusses updating an example script to provide edit and delete links that pass a user's ID to the handling pages.

![Pengaturcaraan PHP
The second method is to append a value to the PHP script's URL:
This technique emulates the GET method of an HTML form. With this
specific example, page.php receives a variable called $_GET['name'] with a
value of Brian.
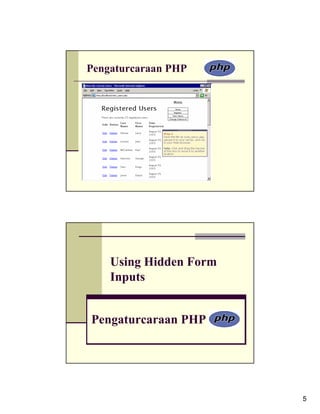
To demonstrate this GET method trick, a new version of the view_users.php
script will be written. This one will provide links to edit or delete an existing
user. The links will pass the user's ID to the handling pages, both of which
will be written subsequently.
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/developingwebapplications-121217020057-phpapp01/85/Developing-web-applications-2-320.jpg)

![Pengaturcaraan PHP
Step 4
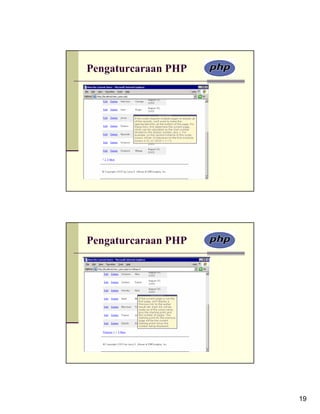
Change the echo statement within
the while loop to match the table's
new structure.
For each record returned from
the database, this line will print
out a row with five columns. The
last three columns are obvious
and easy to create: just refer to
the returned column name.
Pengaturcaraan PHP
For the first two columns,
which provide links to edit or
delete the user, the syntax is
slightly more complicated. The
desired end result is HTML
code like <a
href="edit_user.php?id=X">Edi
t</a>, where X is the user's ID.
Having established this, all we
have to do is print
$row['user_id'] for X, being
mindful of the quotation marks
to avoid parse errors.
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/developingwebapplications-121217020057-phpapp01/85/Developing-web-applications-4-320.jpg)




















![Pengaturcaraan PHP
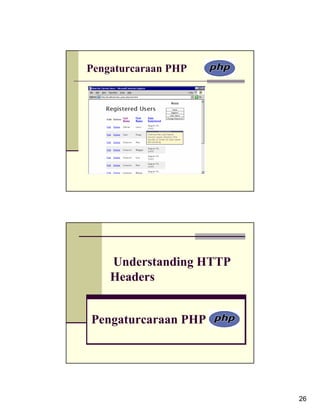
Step 6
Dynamically determine the redirection URL and then call the header() function.
header ('Location: http://' . $_SERVER['HTTP_HOST'] .
dirname($_SERVER['PHP_SELF']) . '/newpage.php');
Pengaturcaraan PHP
Passing values
You can add name=value pairs to the URL in a header() call to pass
values to the target page. In this example, if you added this line to the
script, prior to redirection:
$url .= '?name=' . urlencode ("$fn $ln");
then the thanks.php page could greet the user by $_GET['name'].
29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/developingwebapplications-121217020057-phpapp01/85/Developing-web-applications-29-320.jpg)
