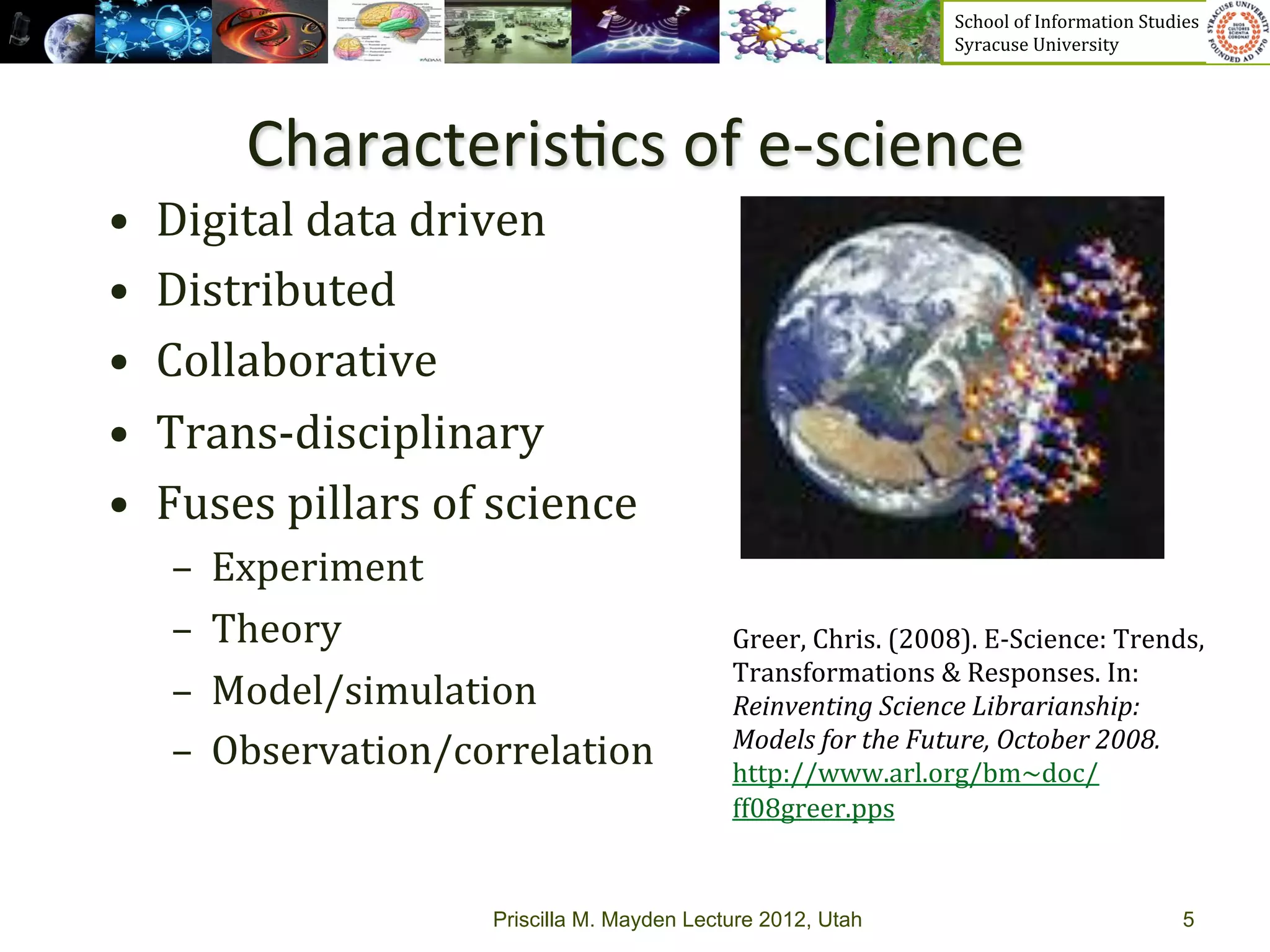
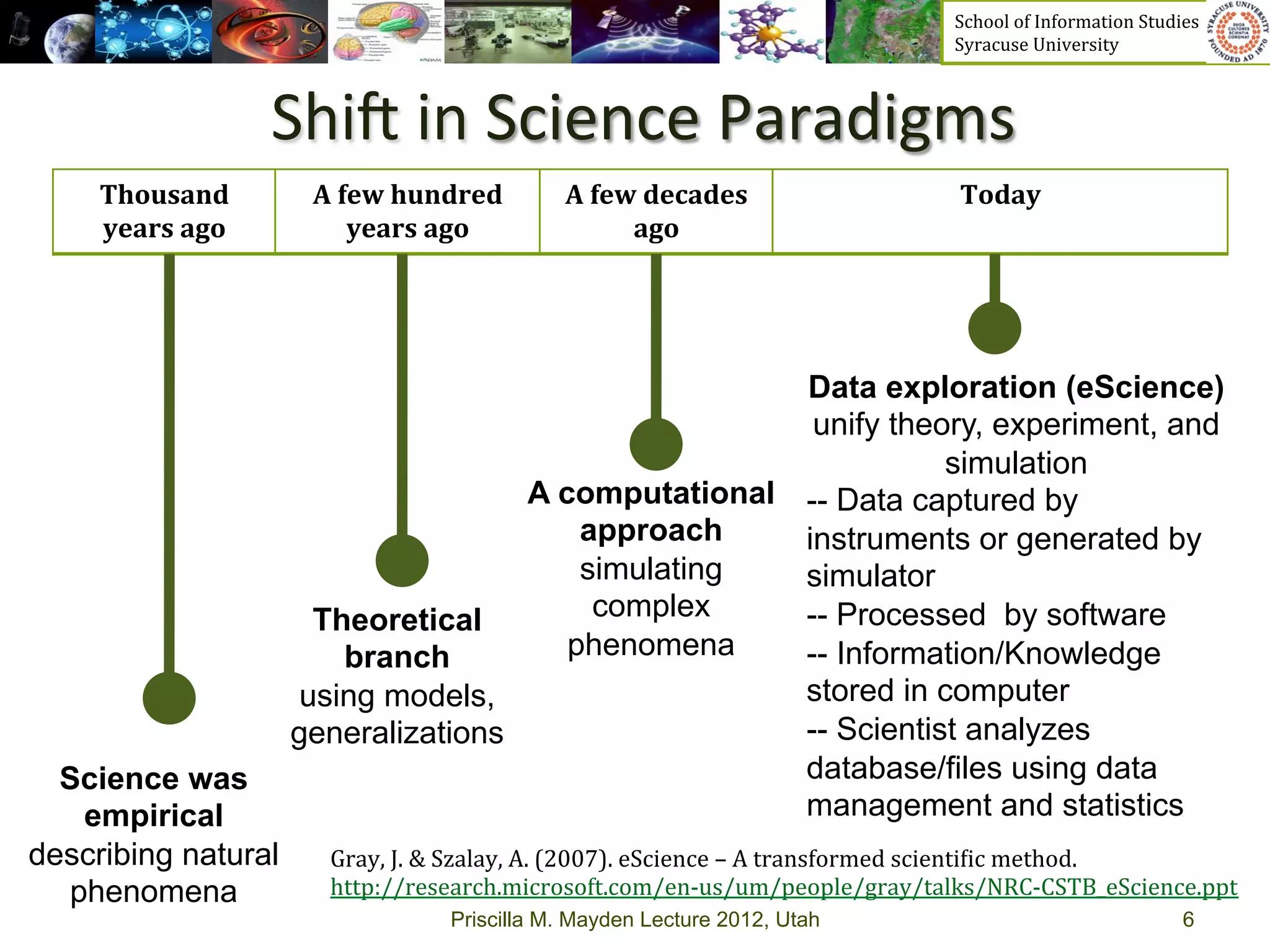
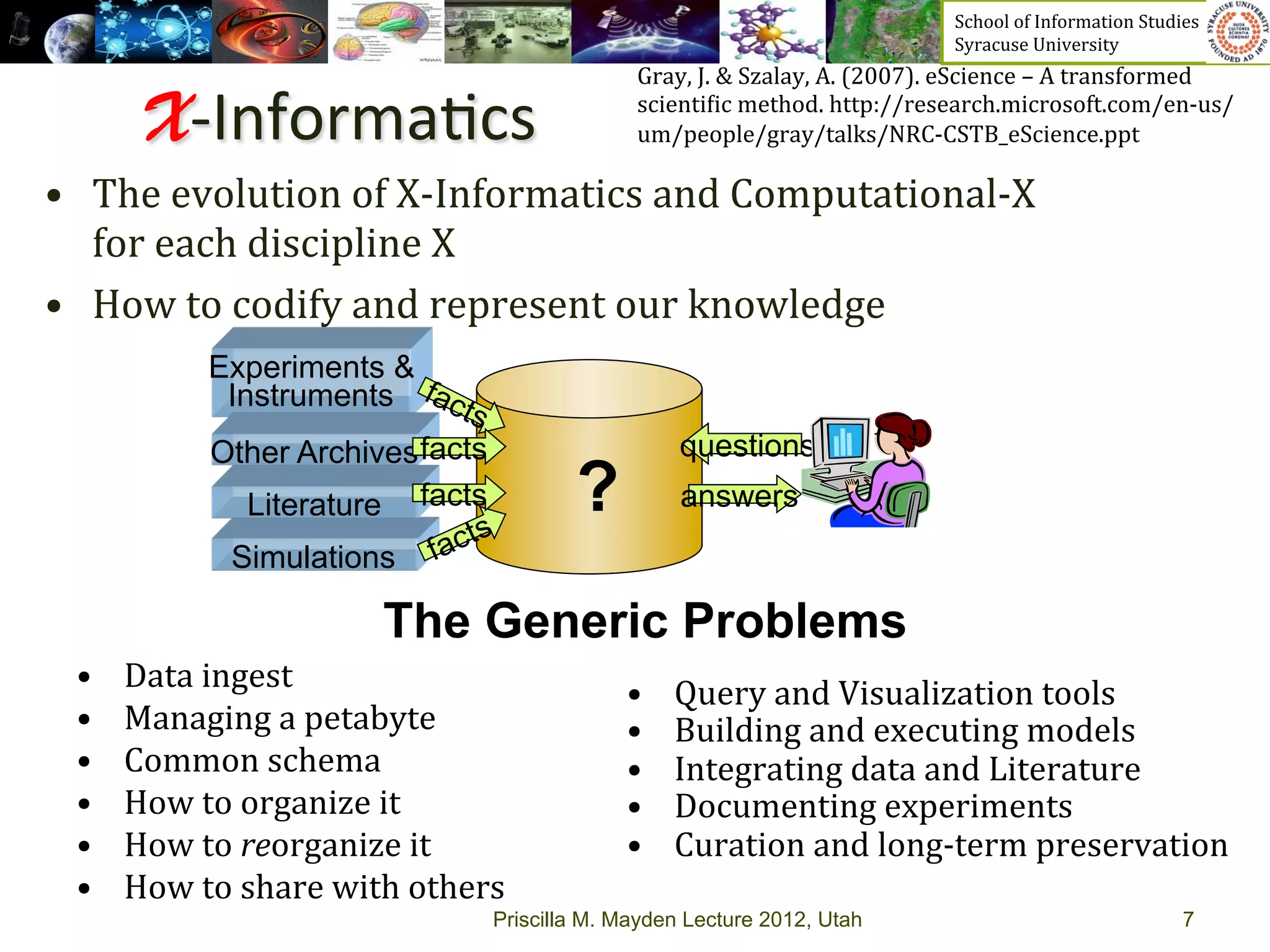
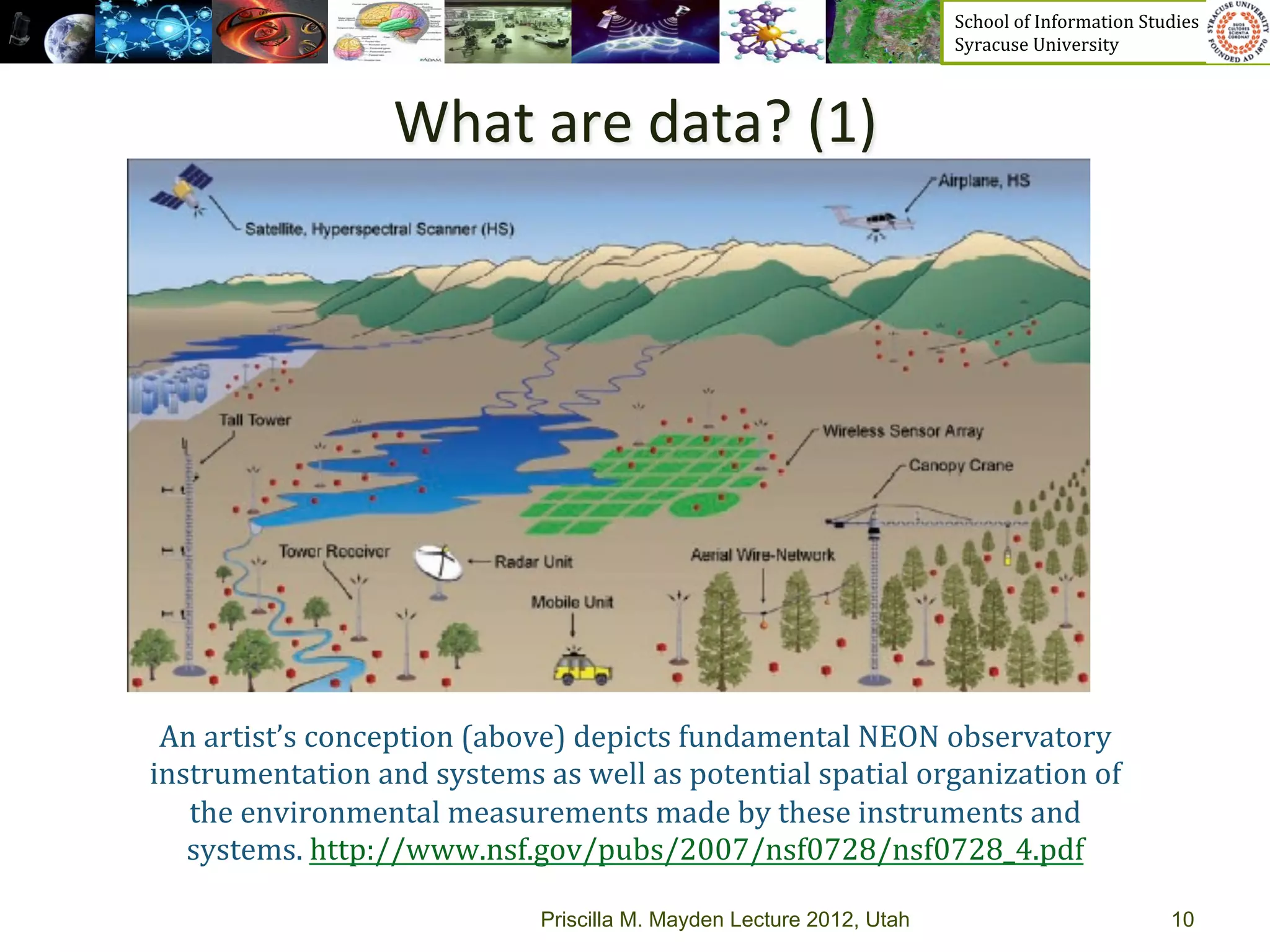
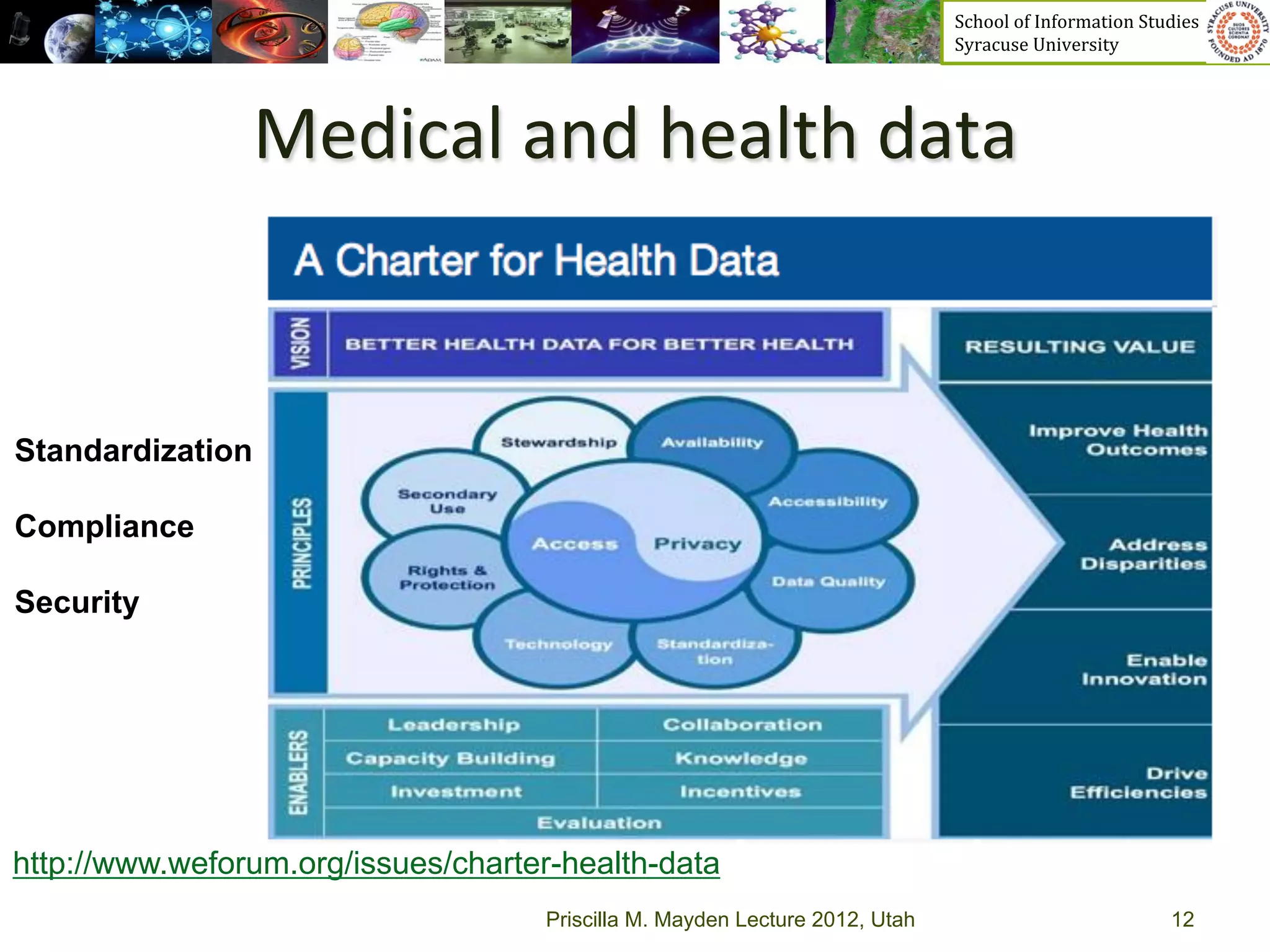
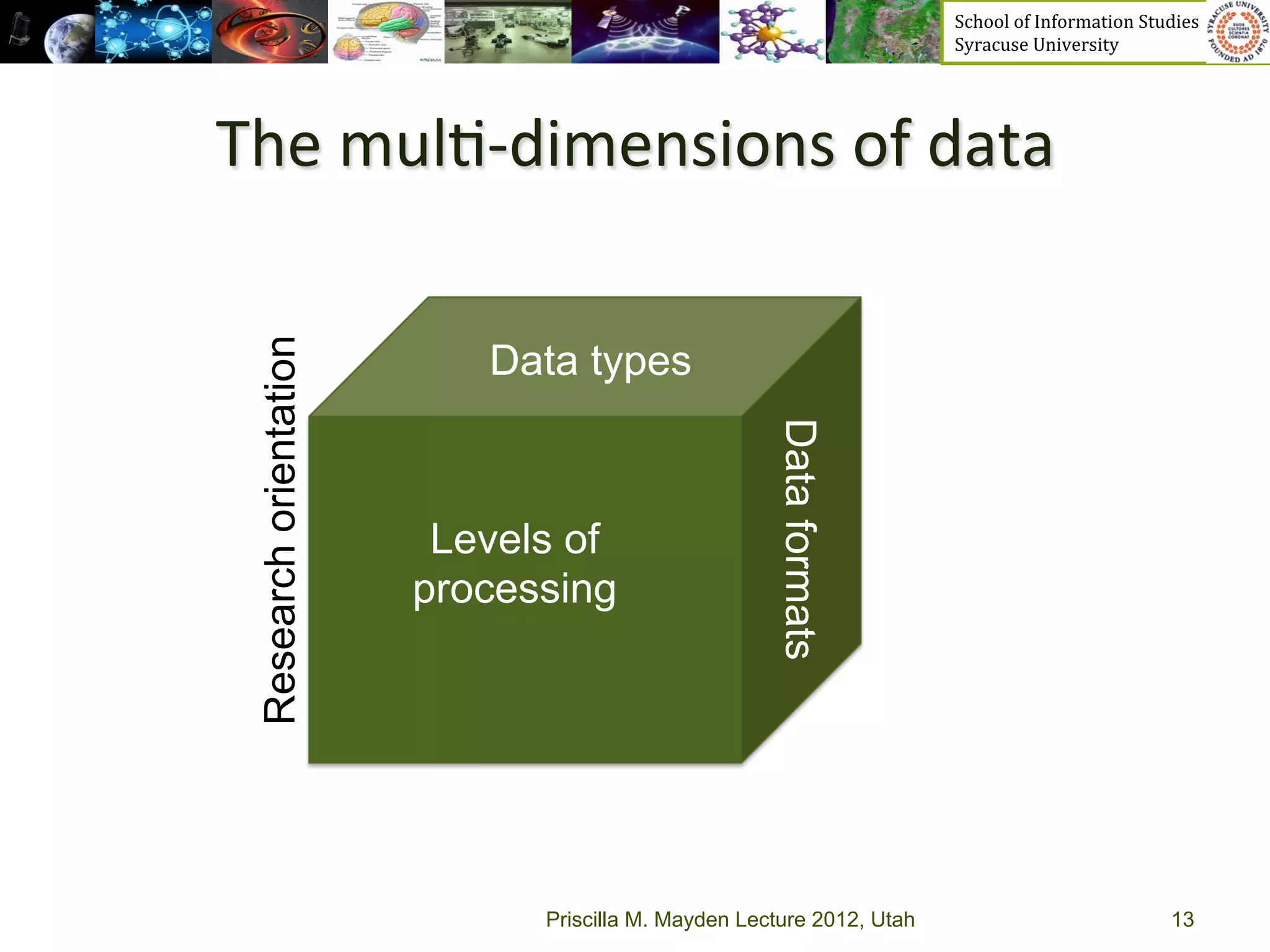
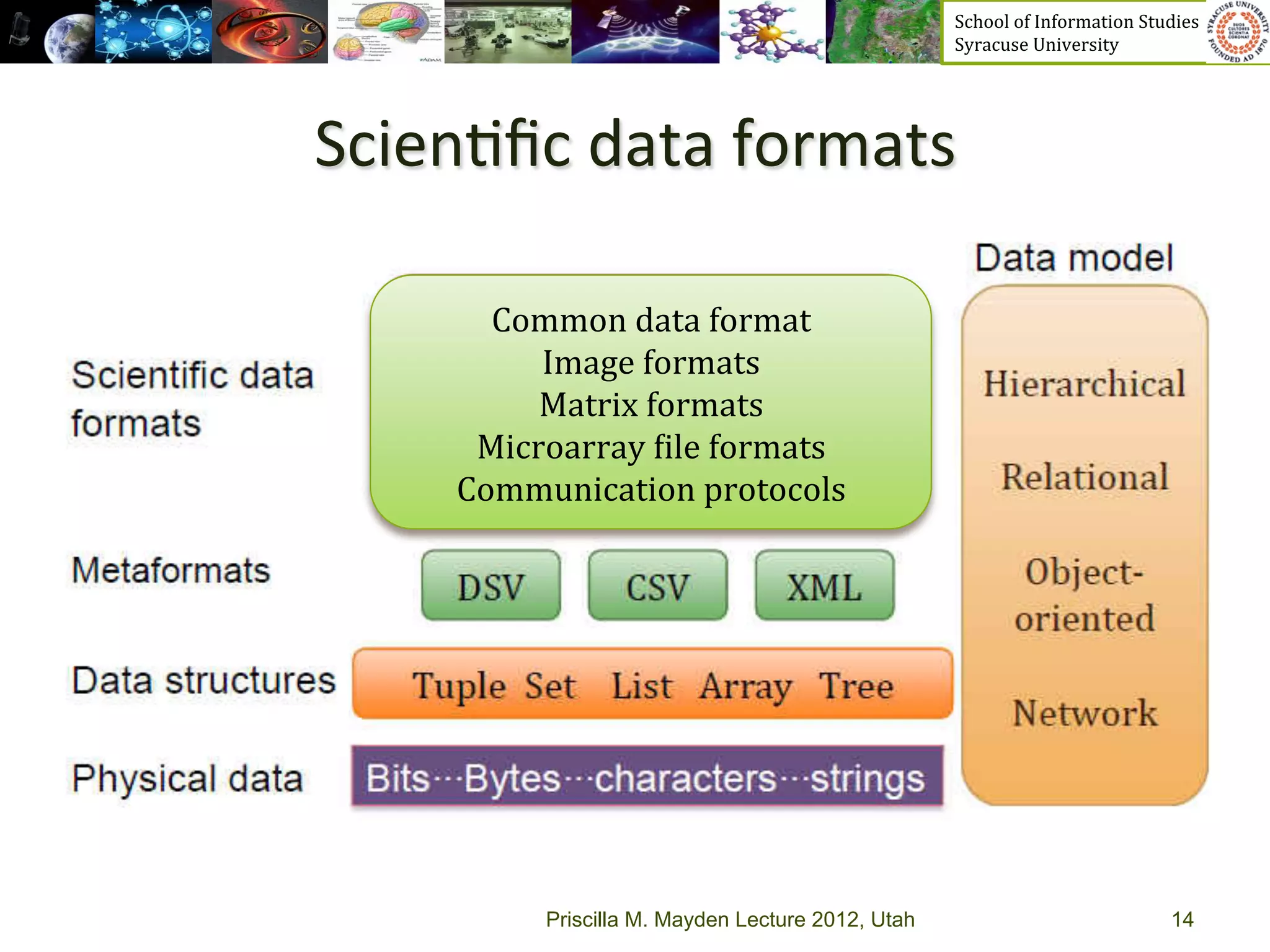
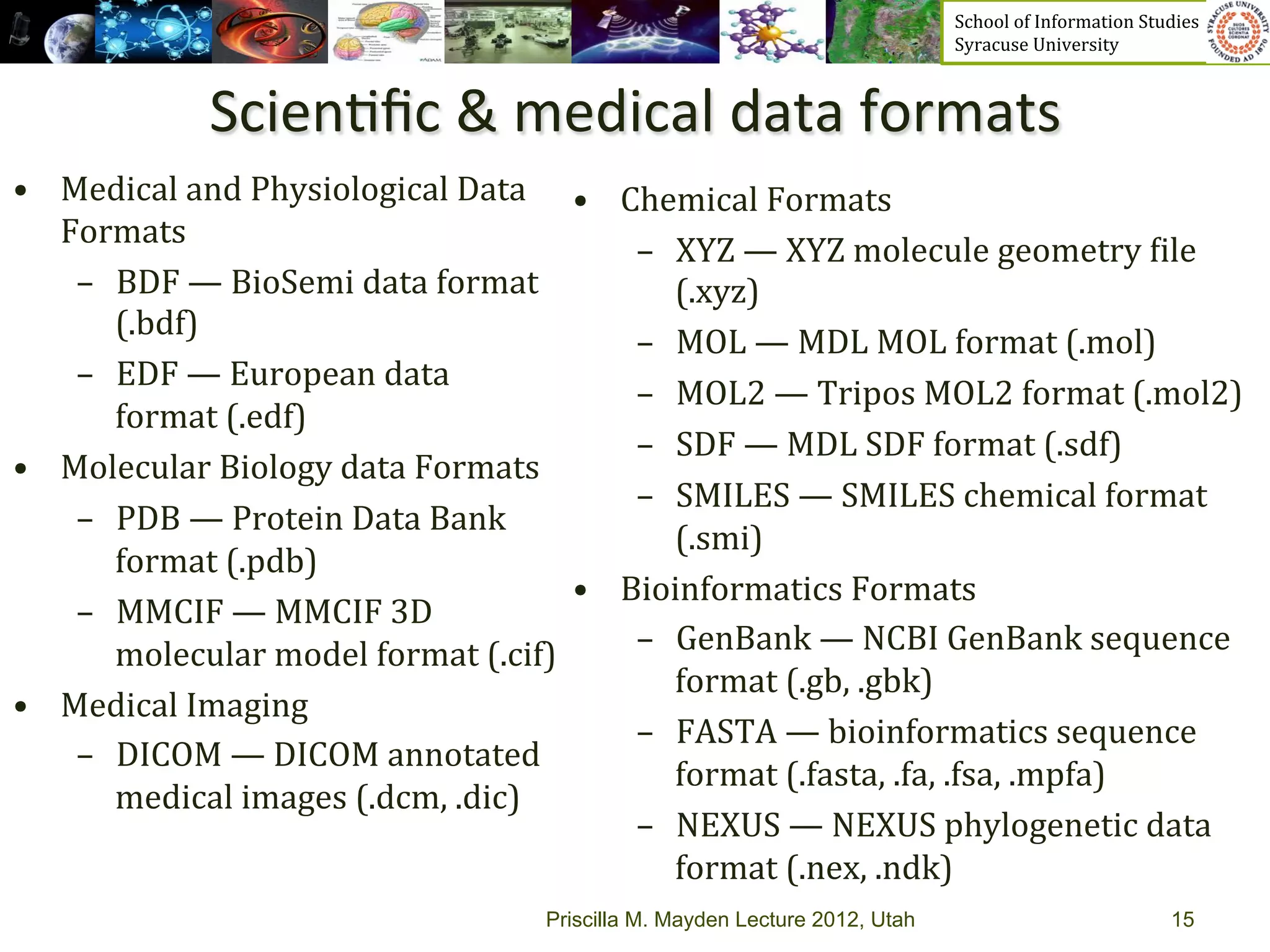
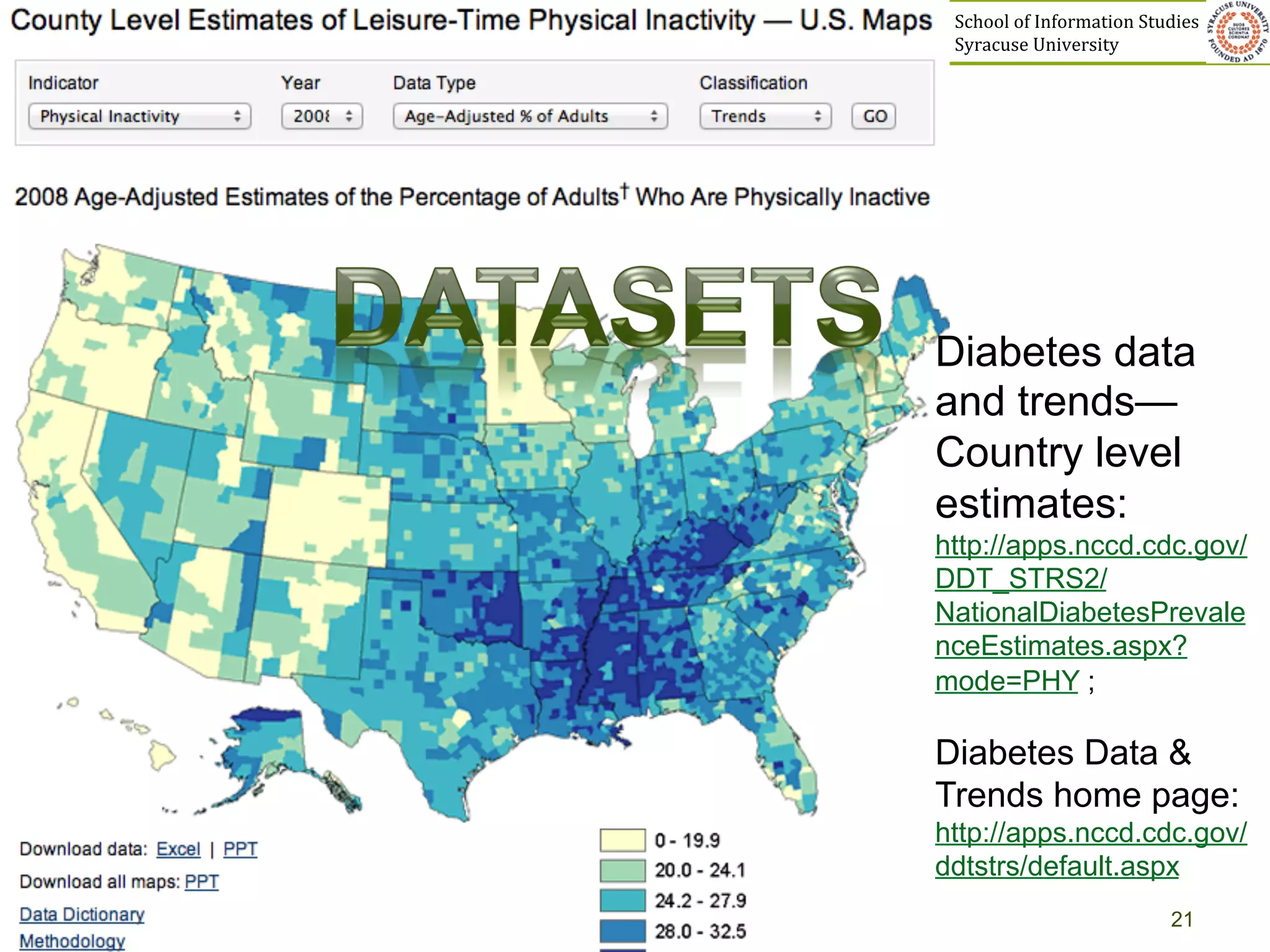
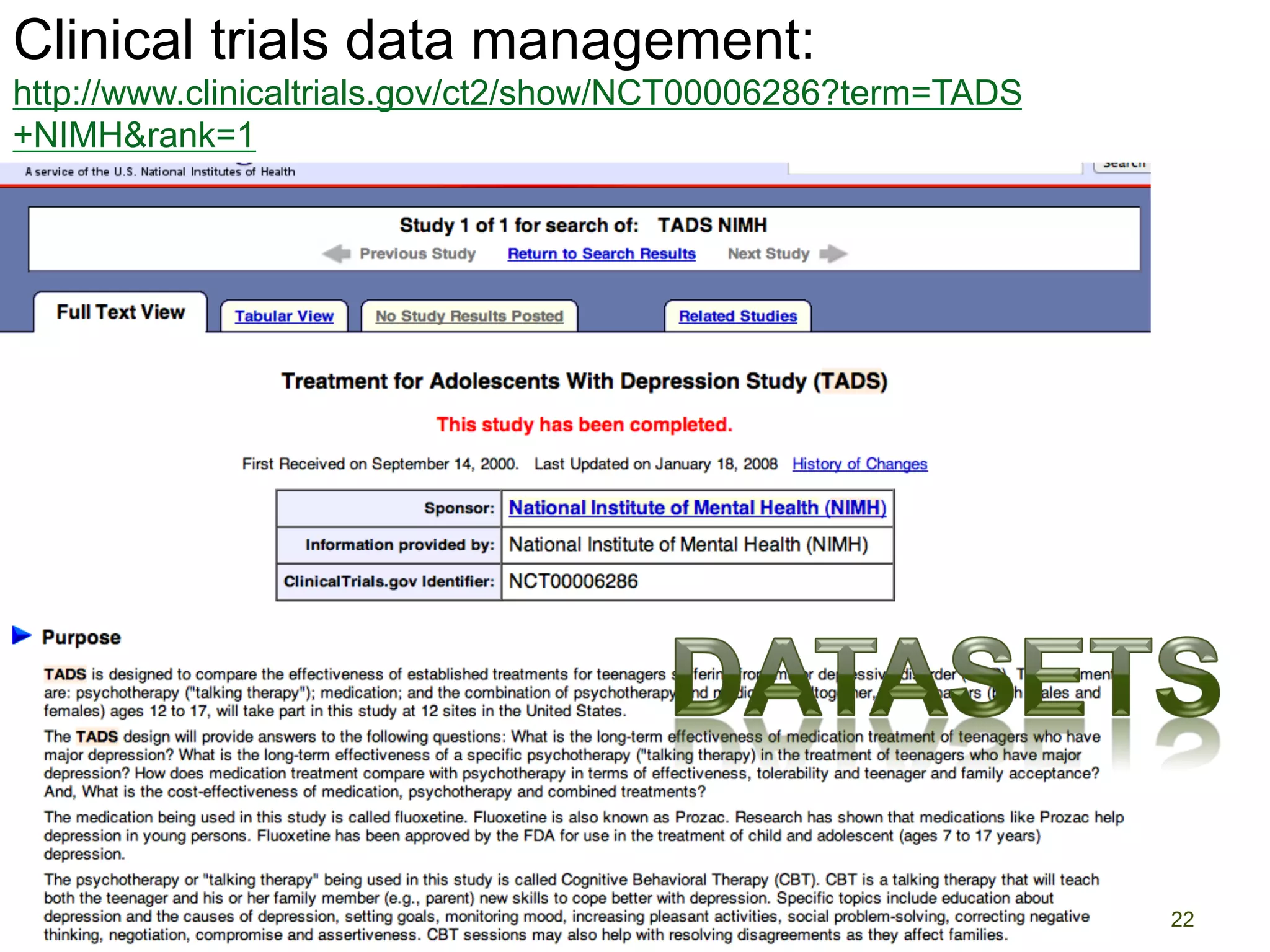
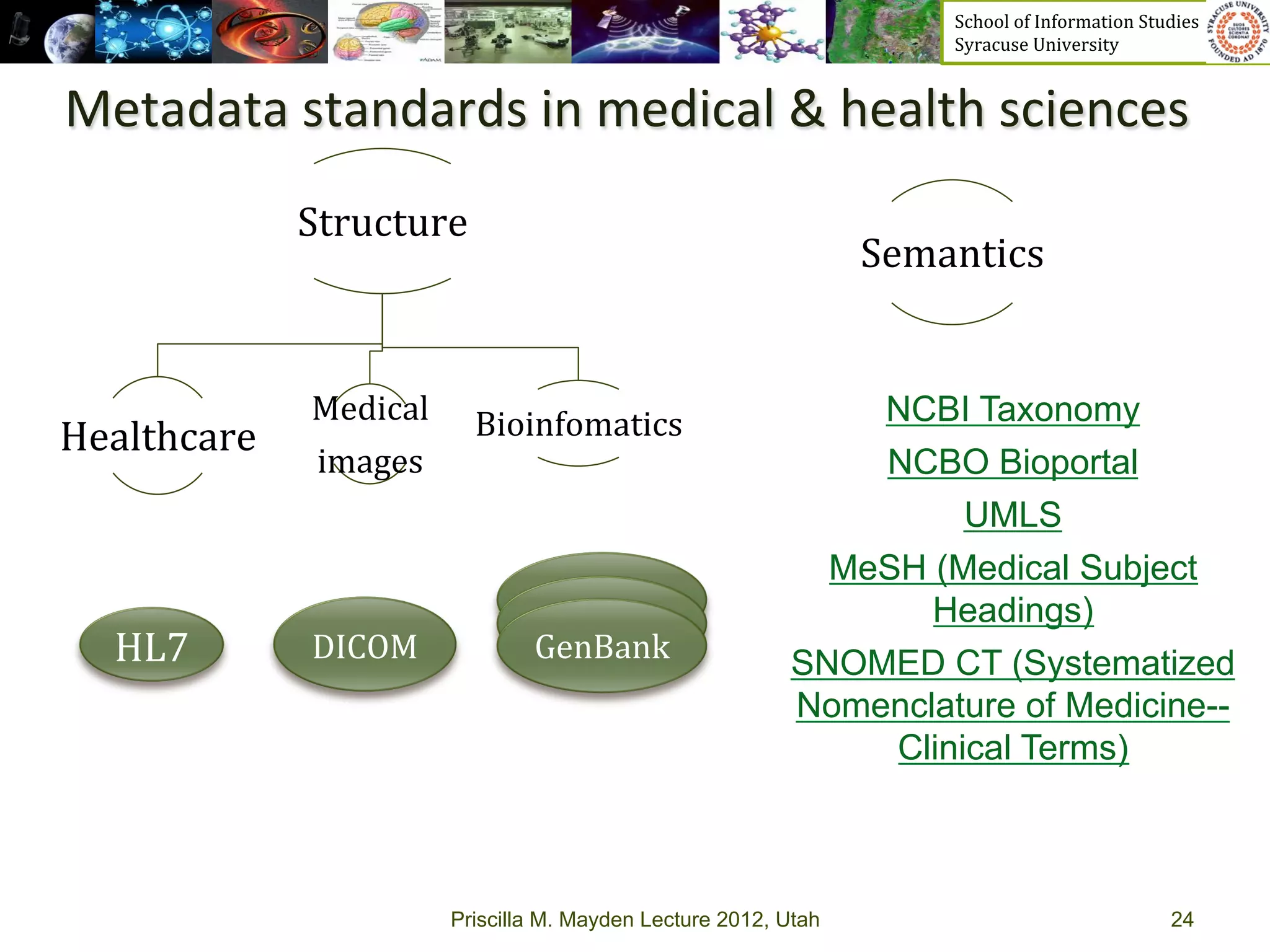
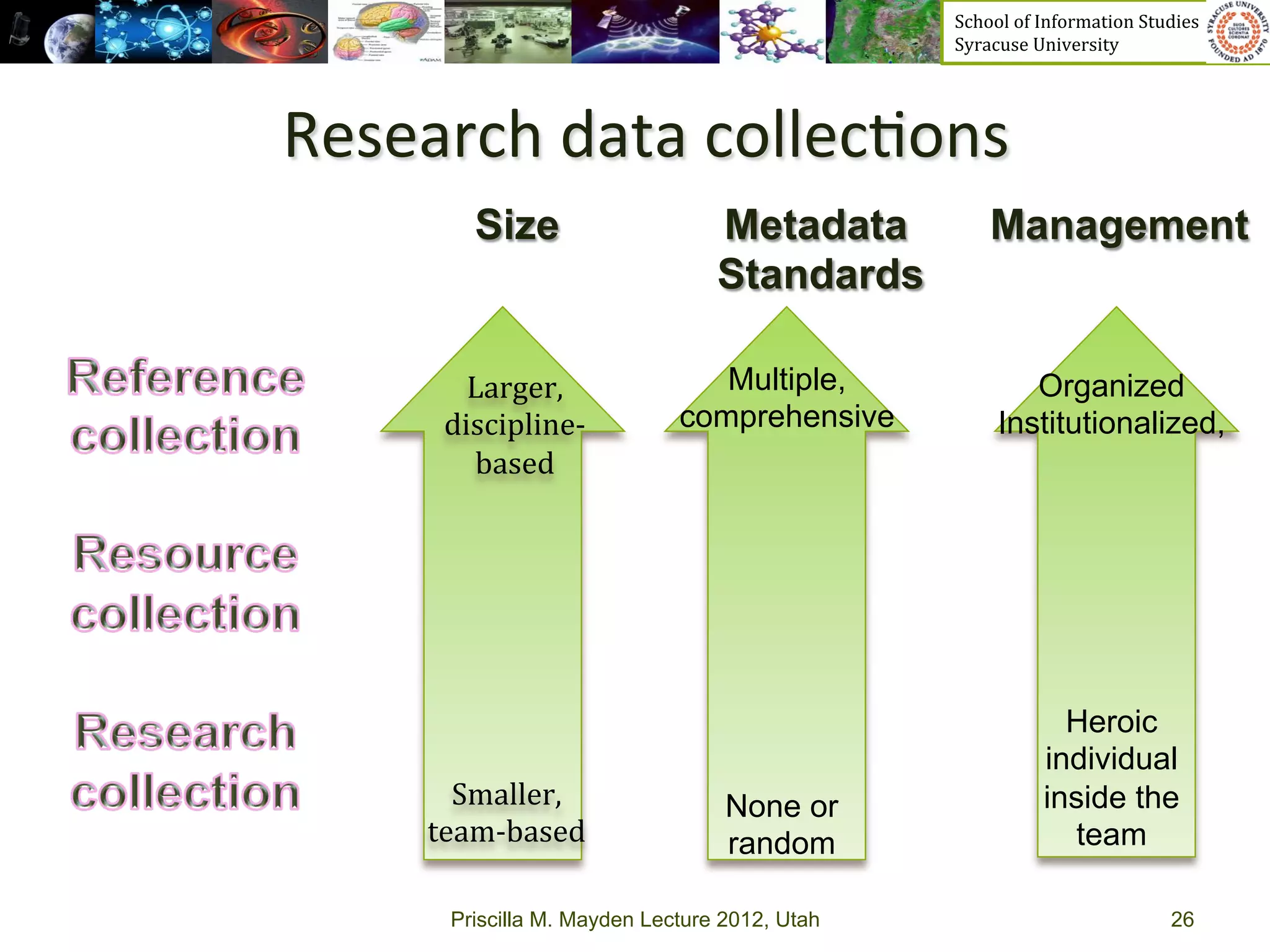
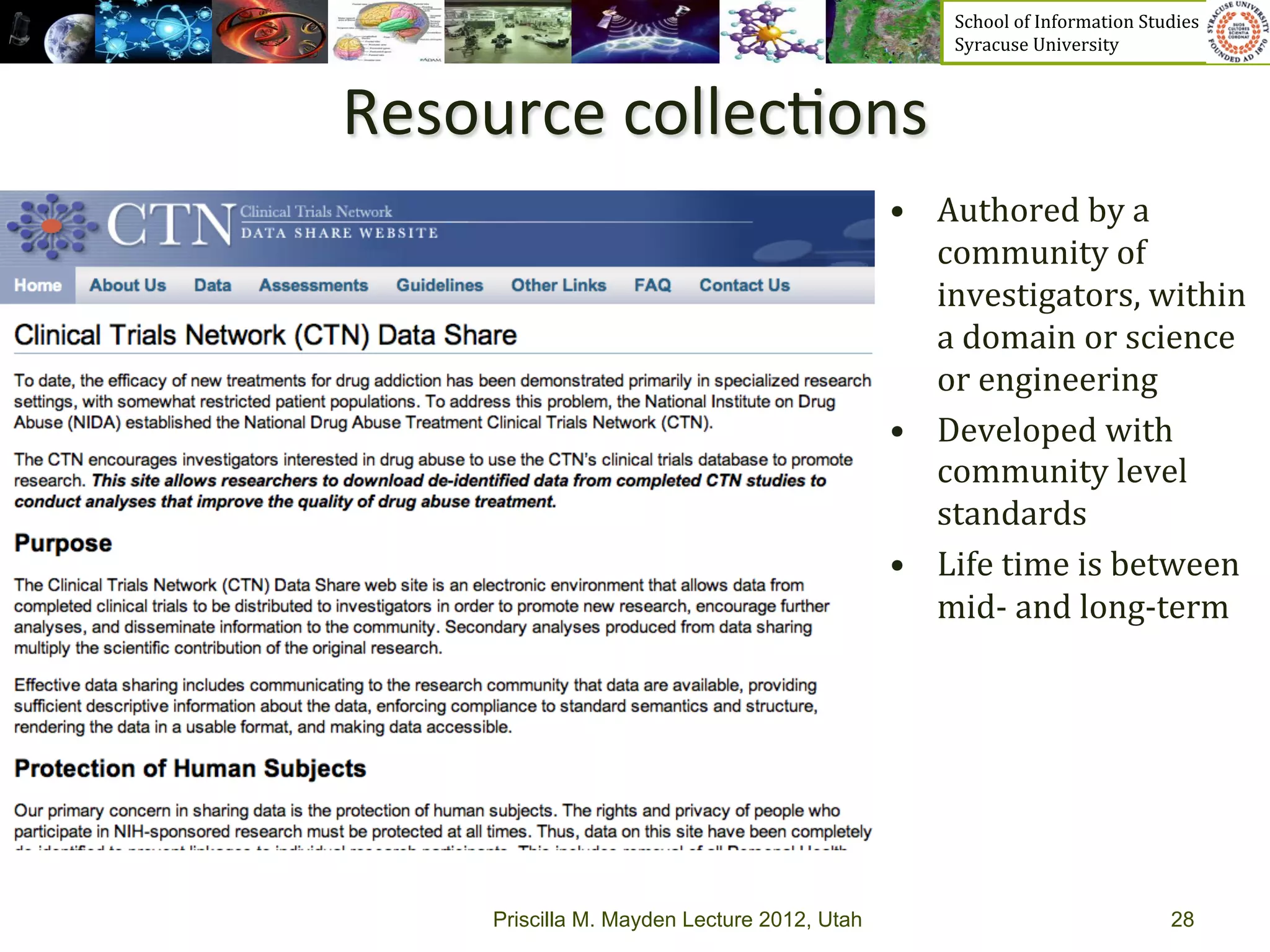
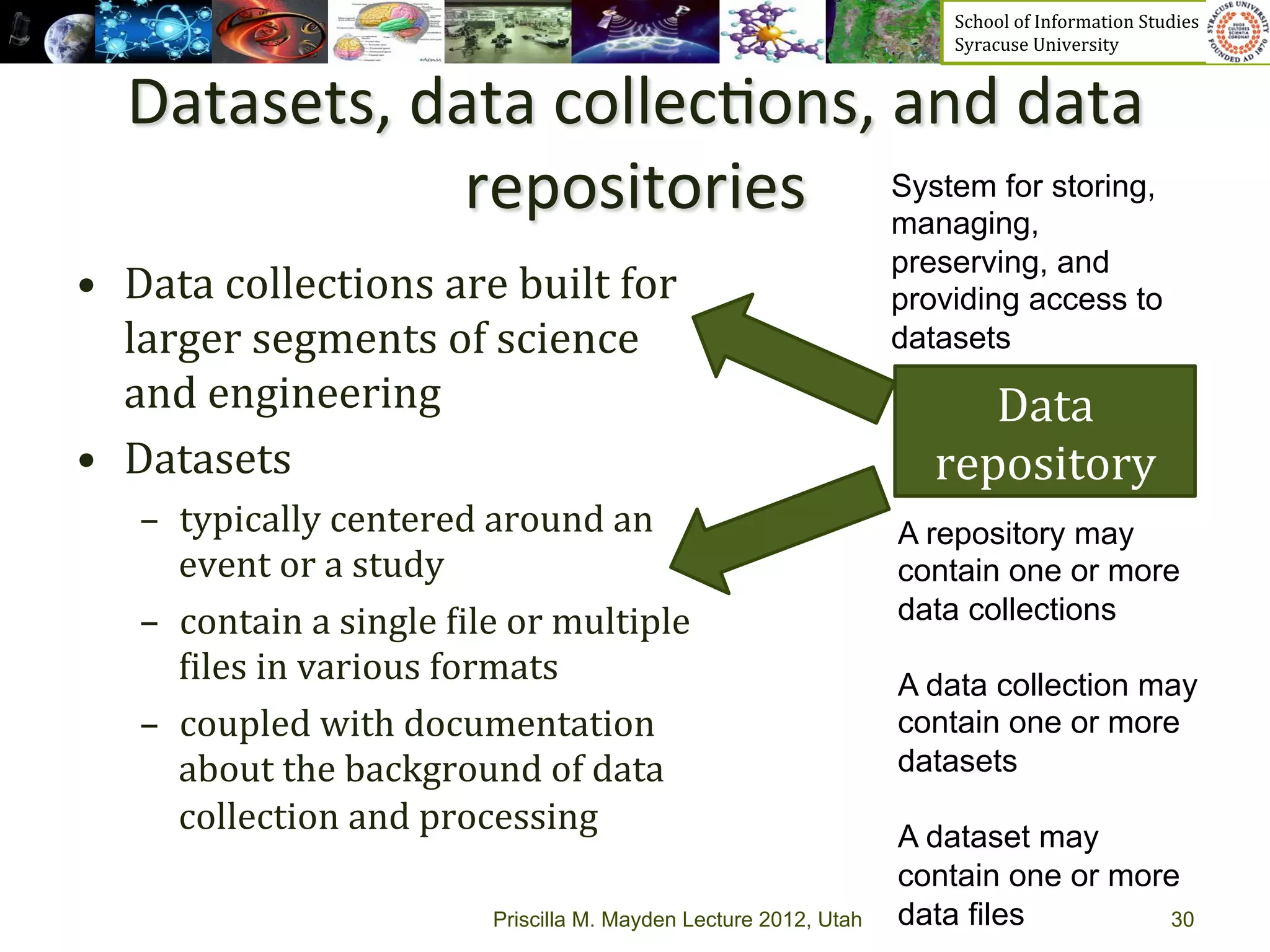
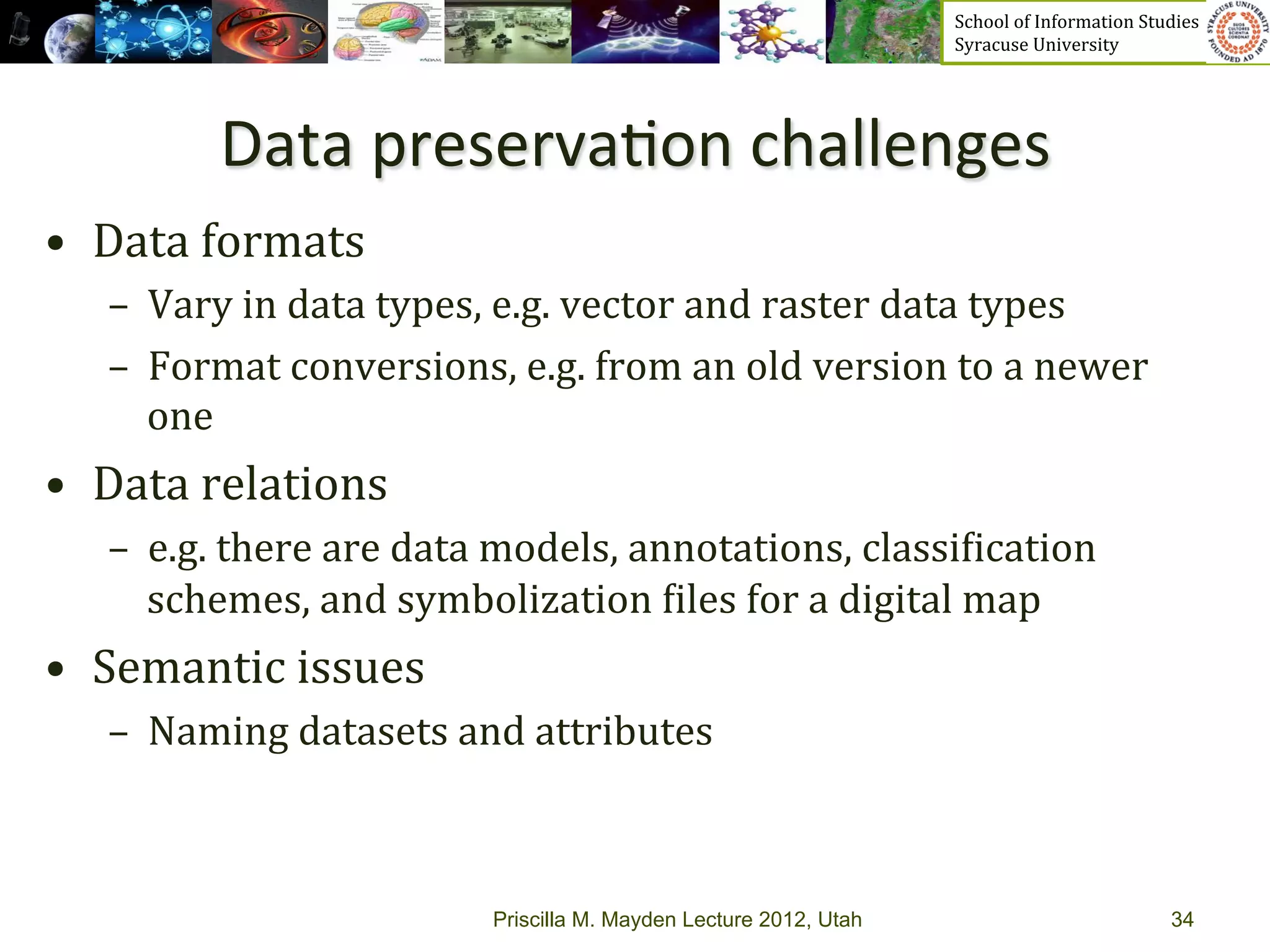
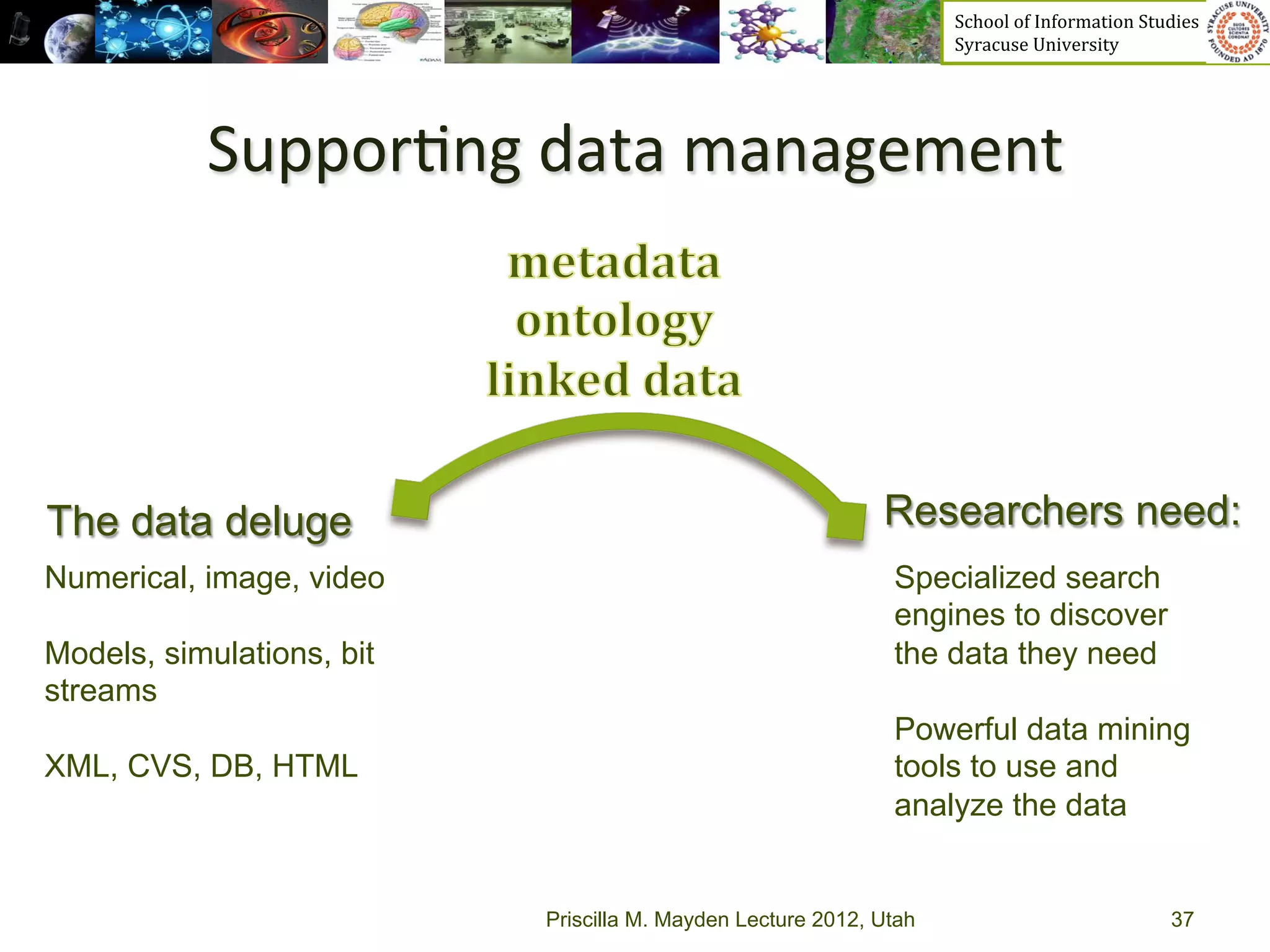
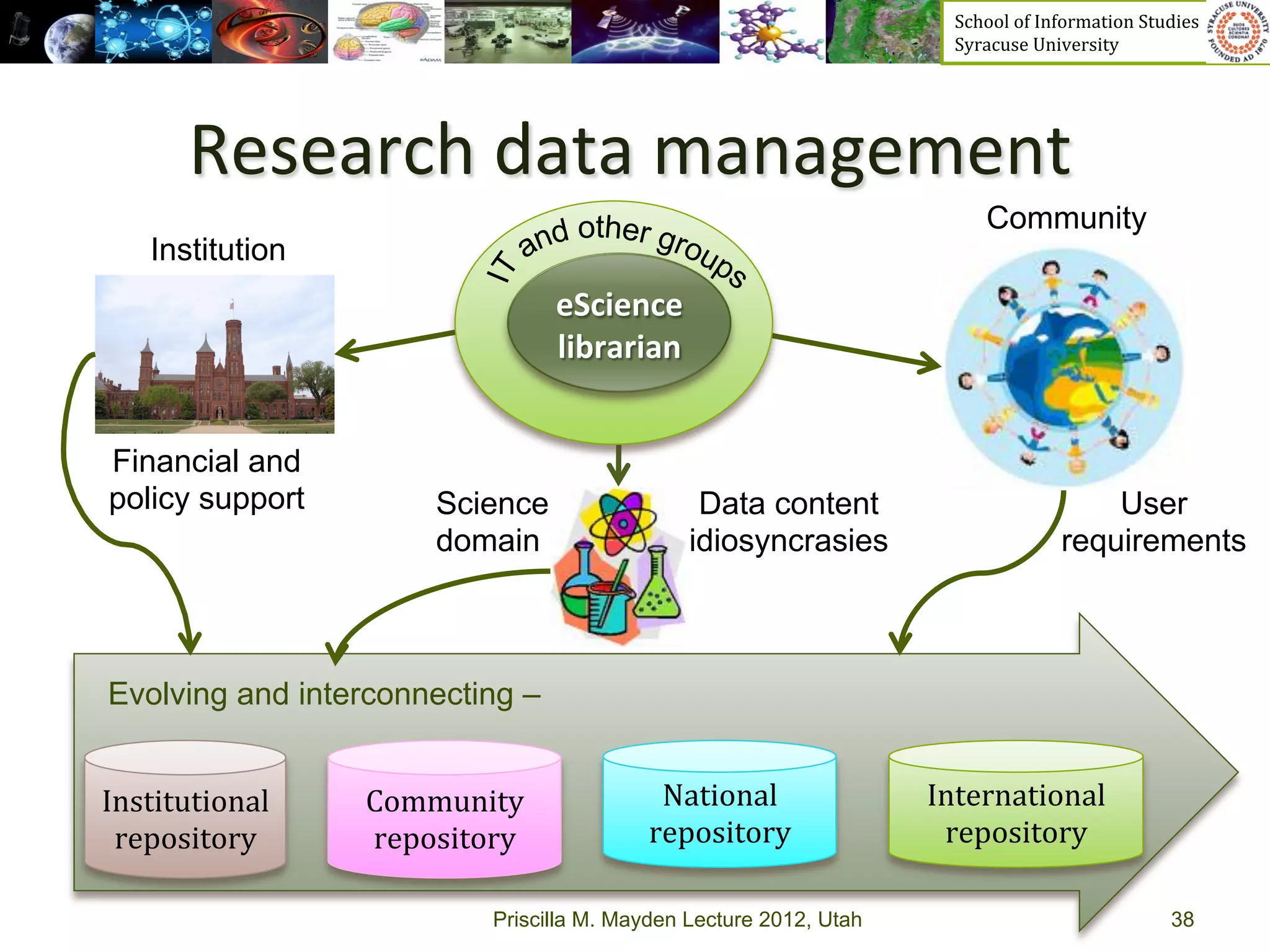
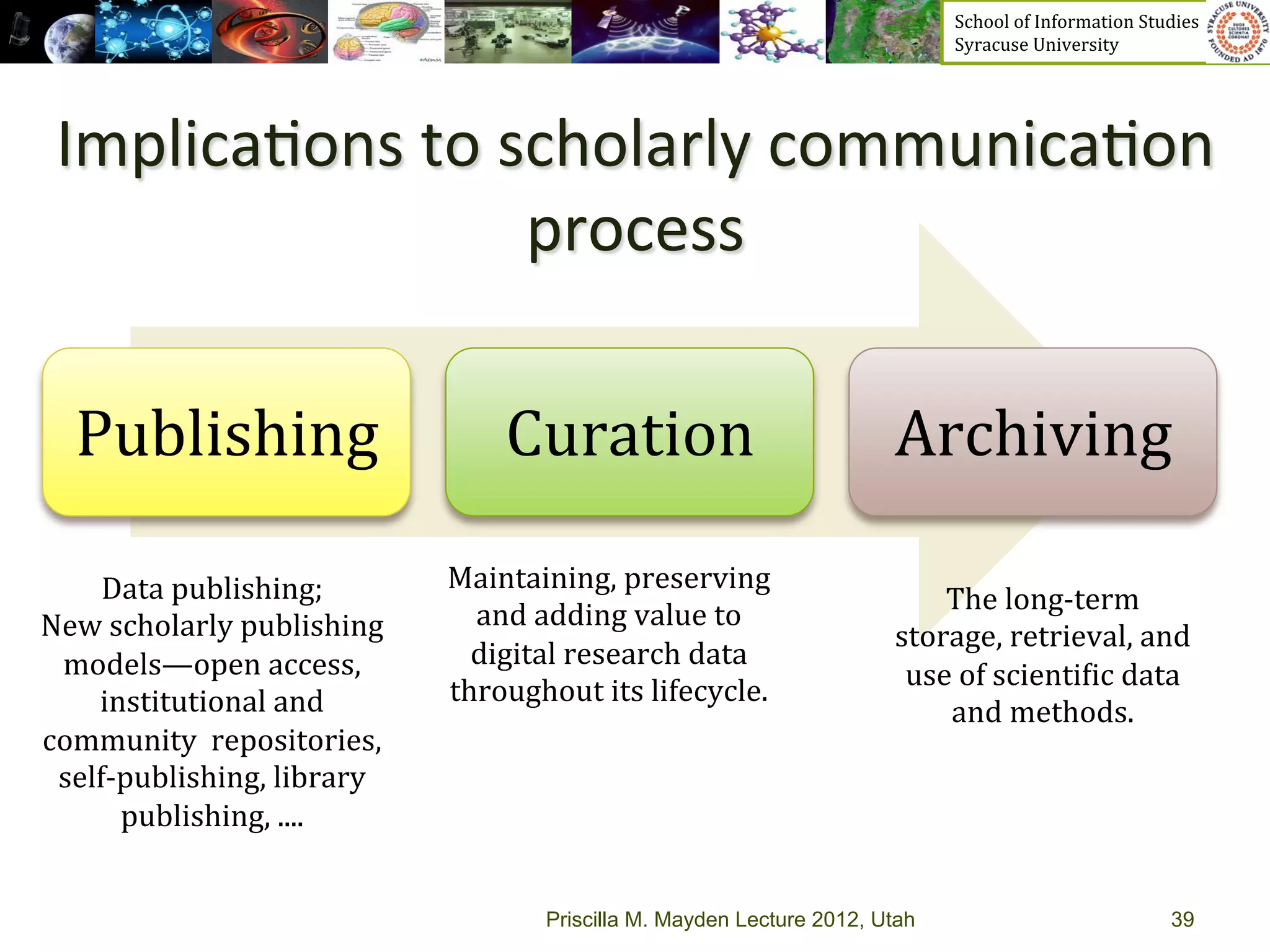
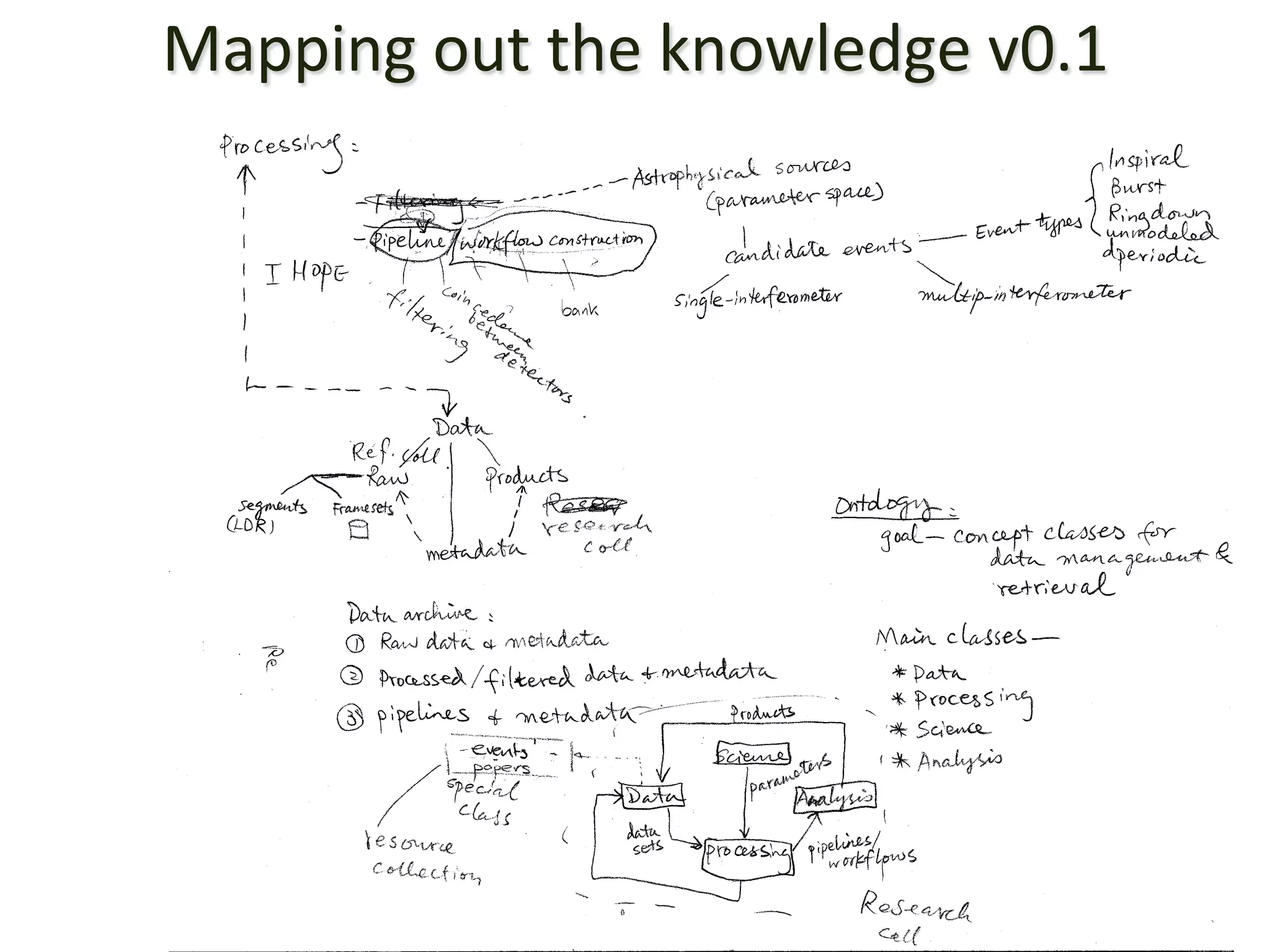
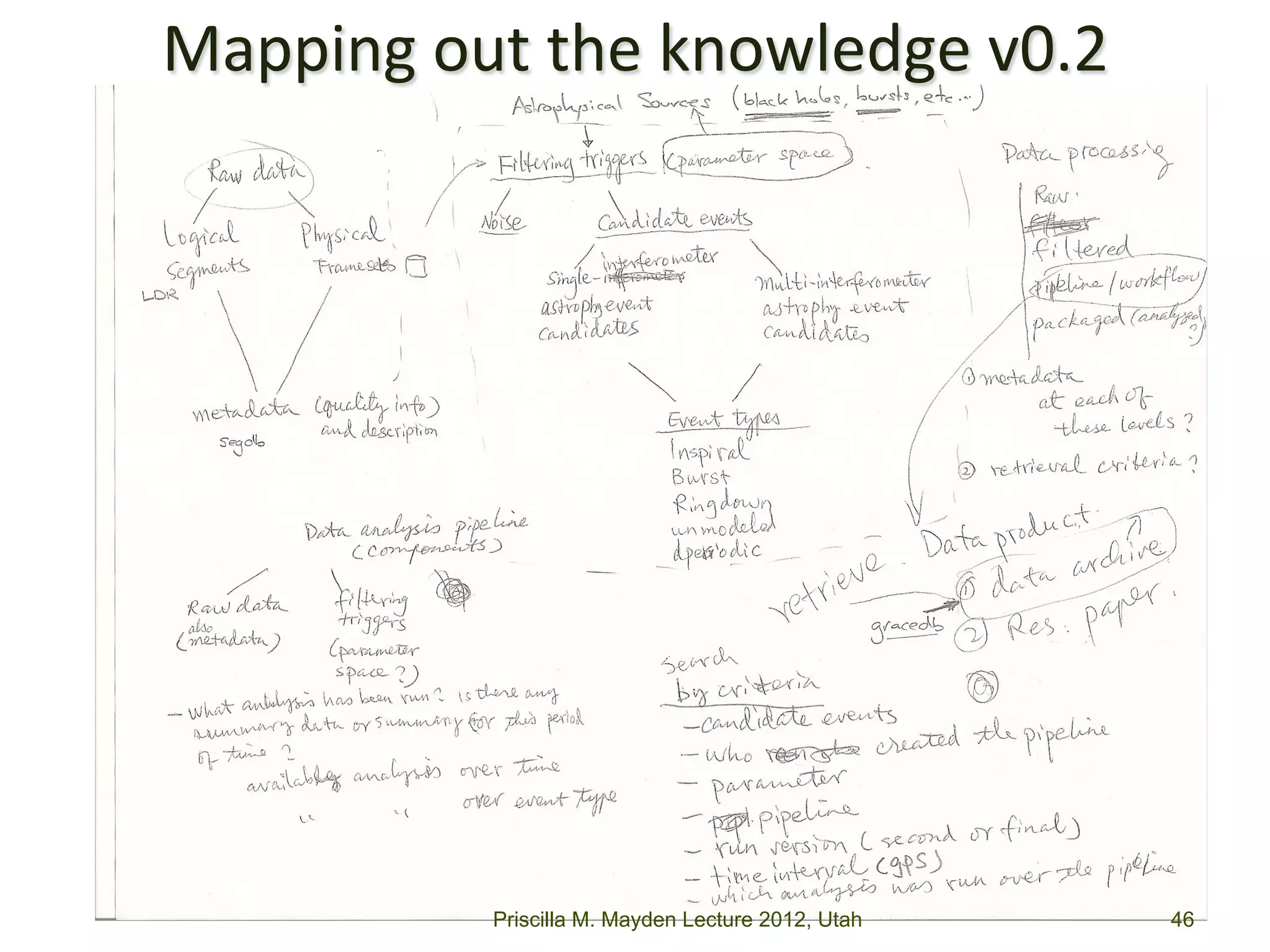
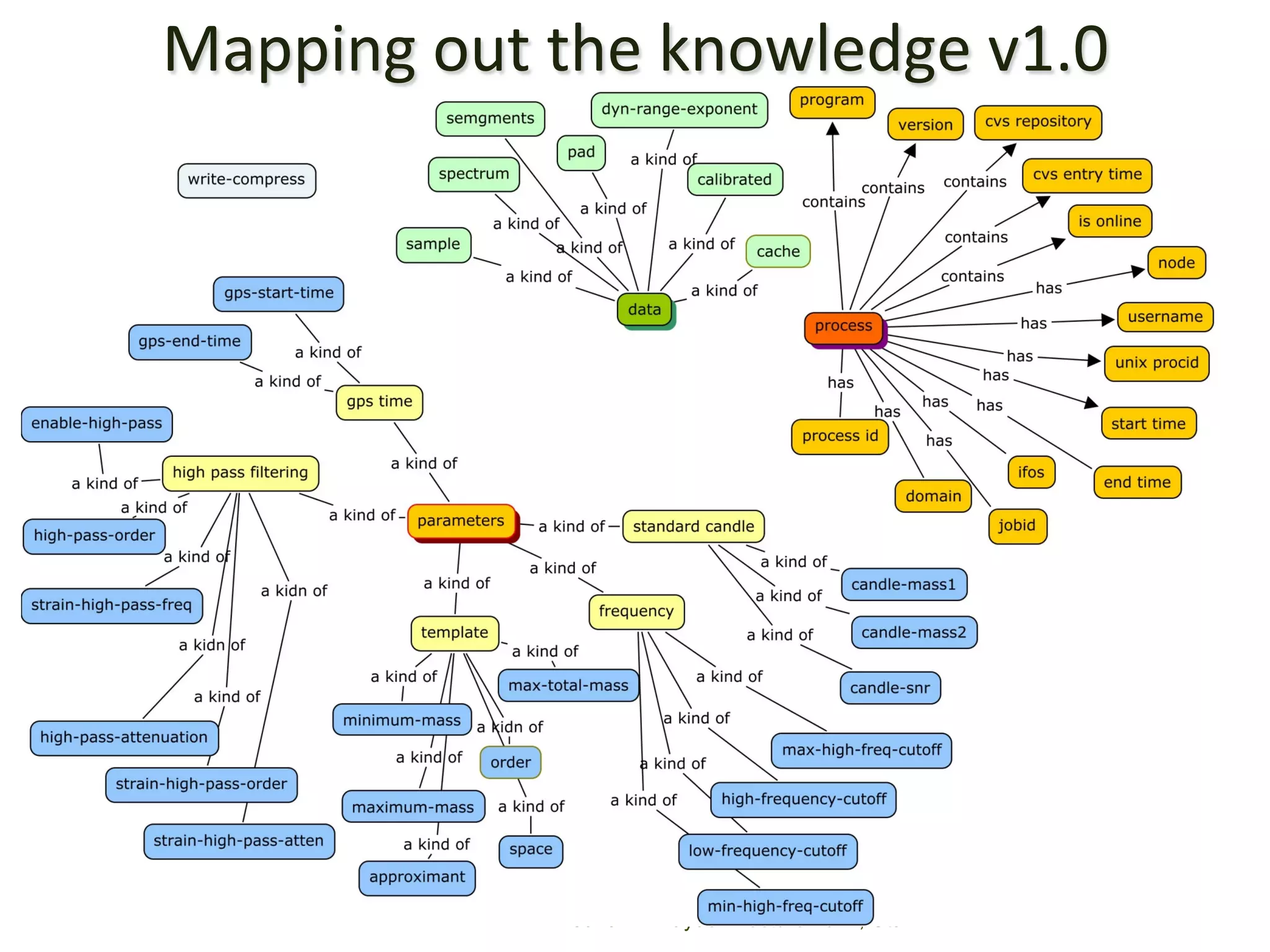
The document discusses the development of data services to support eScience/eResearch. It provides an overview of eScience, including that it involves large-scale collaborative science enabled by the internet using digital data. Characteristics of eScience include being data-driven, distributed, collaborative, and trans-disciplinary. Libraries are important to eScience because it involves large data sets, collections, and repositories. The document also discusses how science paradigms have shifted to become more computational and data-focused.