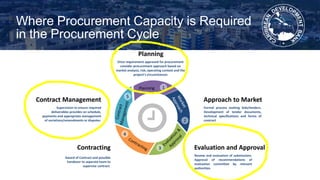
The document discusses the importance of developing capacity in public procurement management, highlighting its significant impact on public service delivery and economic savings. It outlines necessary reforms, including establishing procurement policies, training stakeholders, and improving contract management to ensure effective procurement processes. The Caribbean Development Bank's new procurement framework emphasizes best practices centered on value for money, integrity, and transparency while addressing the complexities of modern procurement.