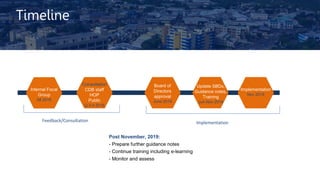
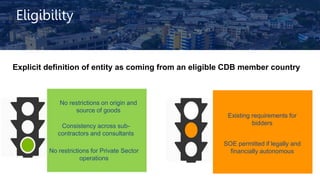
The document outlines the Caribbean Development Bank's updated procurement policy and procedures for projects financed by CDB, focusing on international best practices to ensure value for money and integrity. It highlights the implementation timeline and key components such as eligibility, procurement methods, sustainability considerations, and a structured complaints system. The policy aims to improve efficiency and compliance while accommodating diverse procurement arrangements and supporting capacity-building in borrowing member countries.