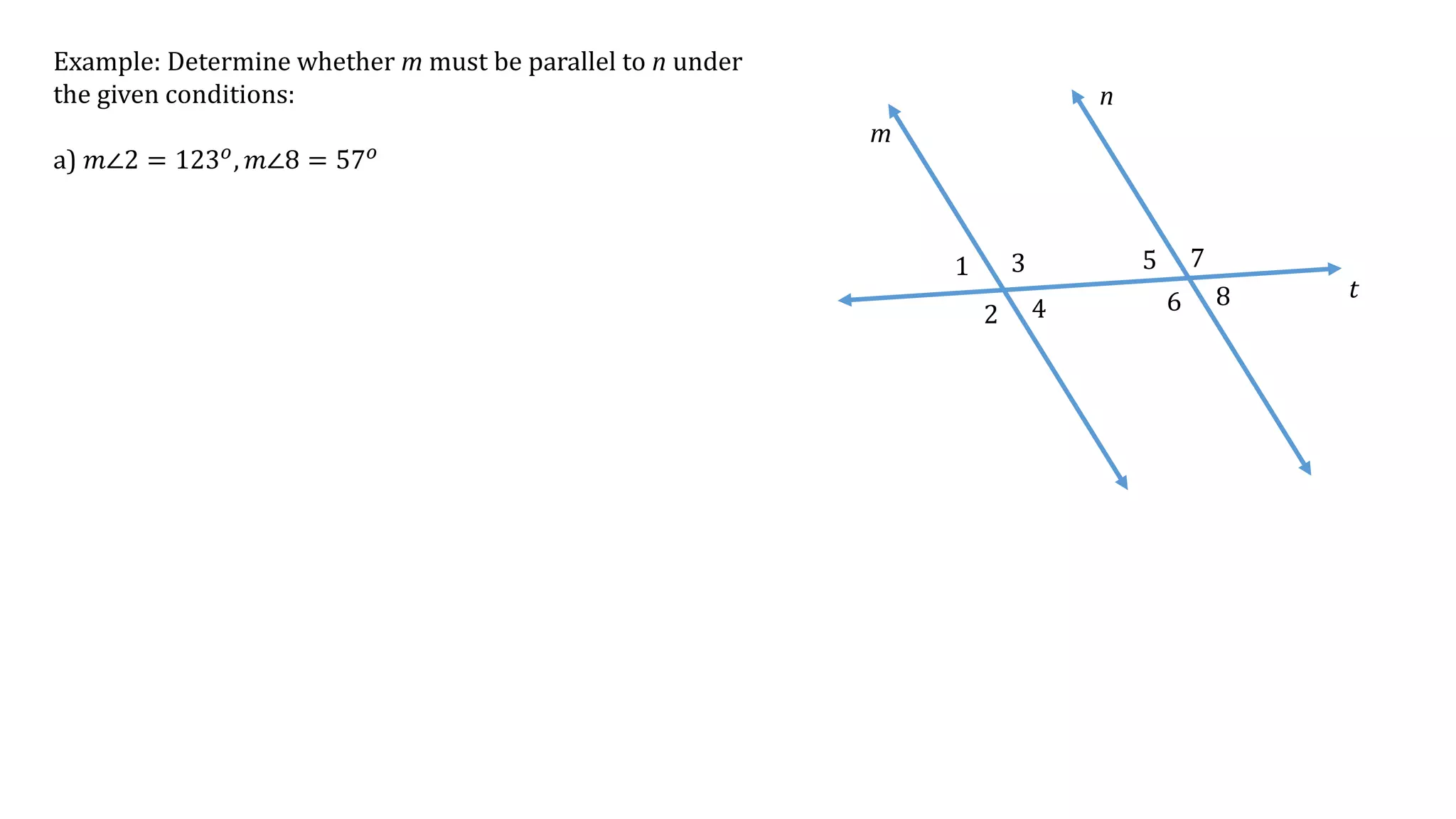
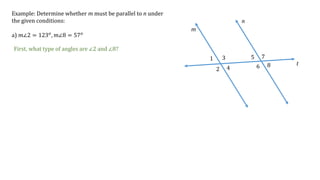
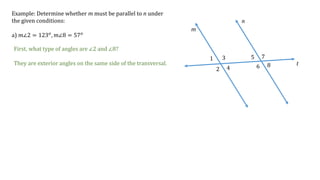
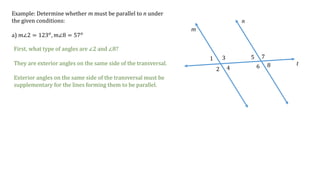
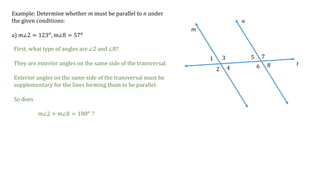
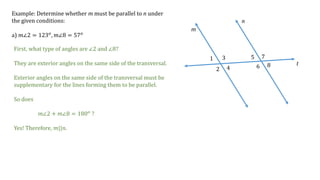
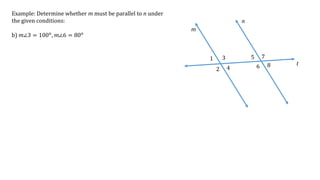
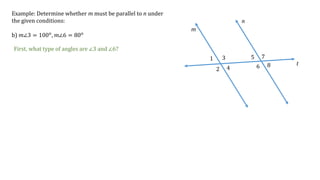
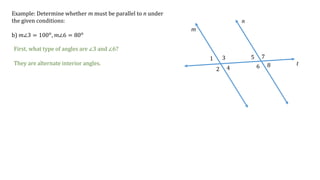
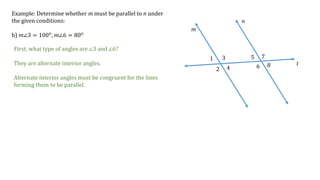
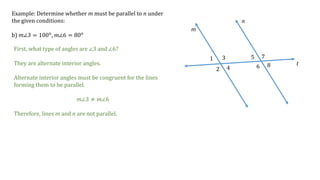
This document discusses determining whether two lines, m and n, are parallel based on given angle measurements. For the first example, where m∠2 = 123° and m∠8 = 57°, the angles are exterior angles on the same side of the transversal, which must be supplementary for the lines to be parallel. Since m∠2 + m∠8 = 180°, the lines m and n are parallel. For the second example, where m∠3 = 100° and m∠6 = 80°, the angles are alternate interior angles, which must be congruent for the lines to be parallel. But m∠3 ≠ m∠6, so lines m and n are not