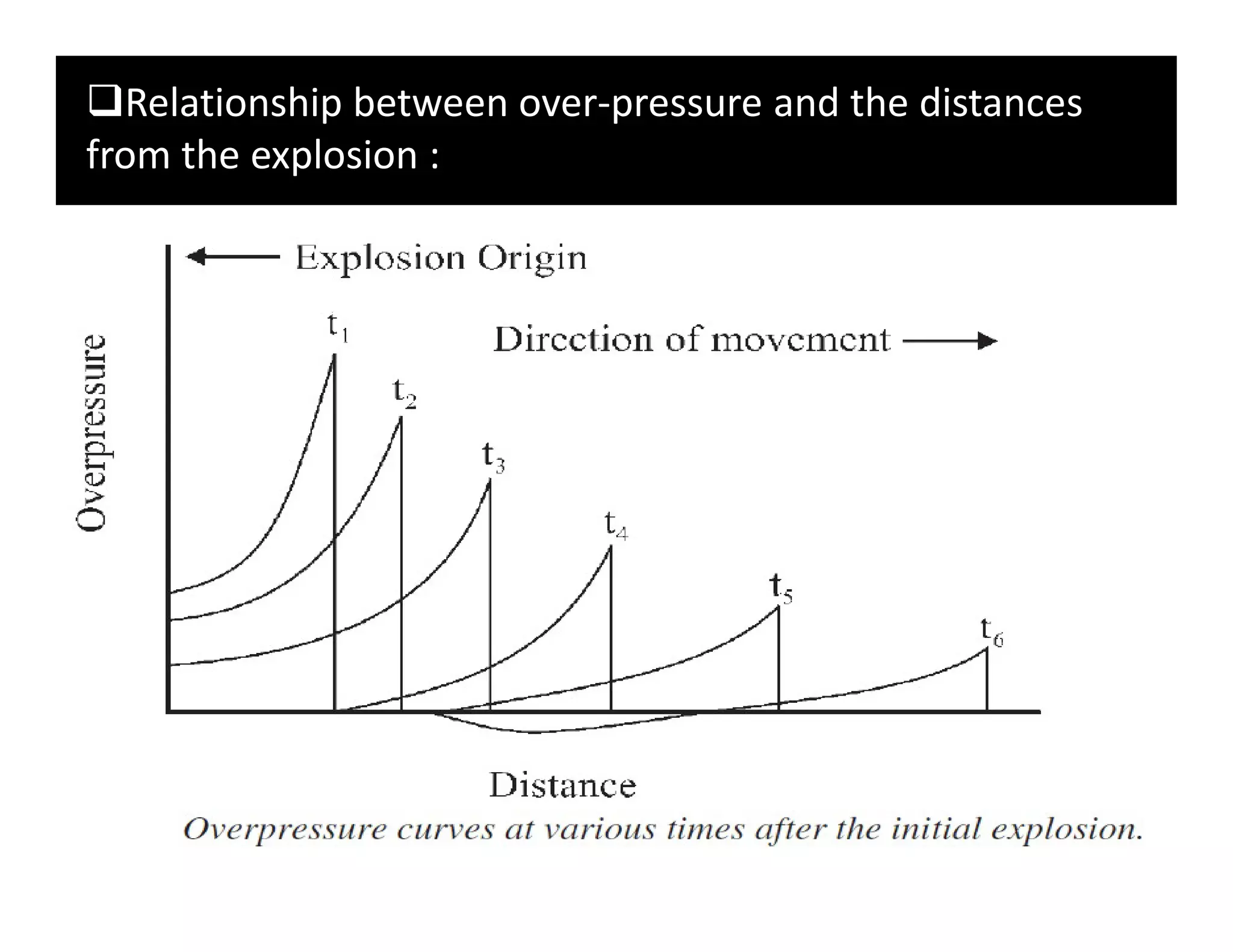
The document discusses explosions, defining them as sudden energy releases that create blasts and shock waves capable of causing damage and injury. It categorizes explosions into physical (such as vessel ruptures and thermal runaways) and chemical types, detailing the mechanisms behind each and the factors influencing their occurrence. Additionally, it highlights various explosion incidents, their consequences, and emphasizes the importance of understanding explosions for disaster management.

![Reference:
[Daniel_A.__Crowl]_Understanding_Explosions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-190610131843/75/Details-on-Chemical-Explosion-2-2048.jpg)