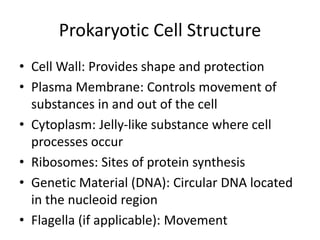
The document provides an overview of cell structure and function, highlighting the types of cells (prokaryotic and eukaryotic) and their key components and organelles. It discusses the significance of studying cells for understanding biology and medicine as well as the roles of specific structures like the nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum. The summary emphasizes the importance of cell organization and communication in biological processes.