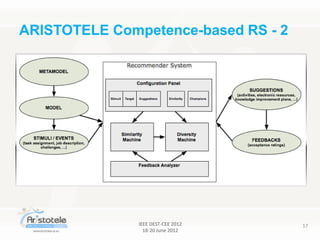
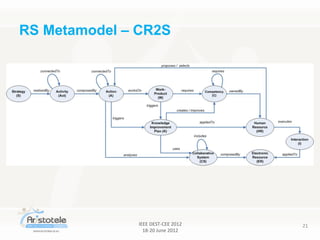
The document discusses the Aristotele project, which focuses on designing competence-based recommender systems (RS) for knowledge-intensive organizations. The project emphasizes integrating organizational, learning, and social collaboration processes to foster innovation and improve decision-making through tailored recommendations. It identifies key principles and preconditions necessary for developing effective RS that leverage user competencies and contextual information.