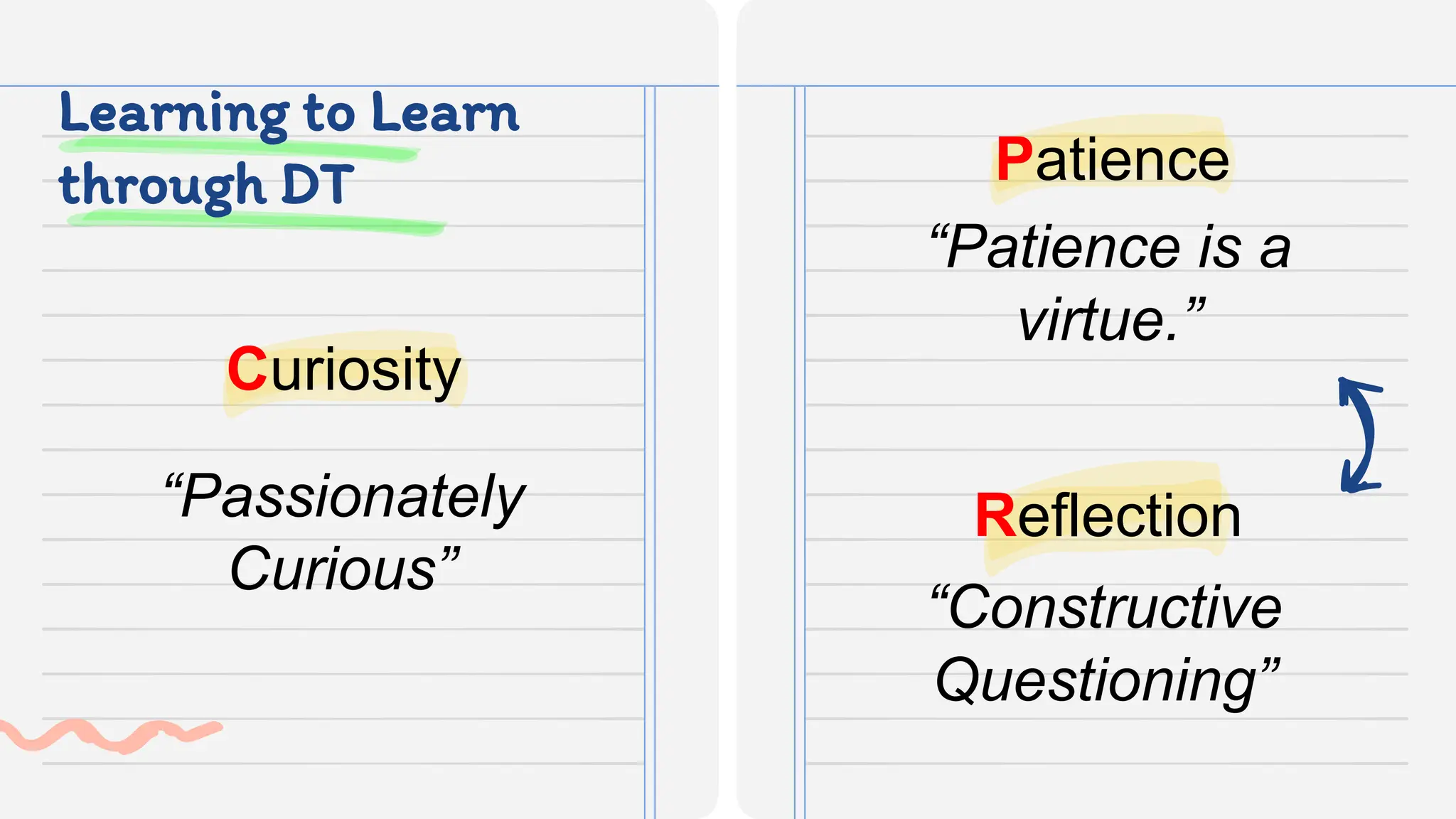
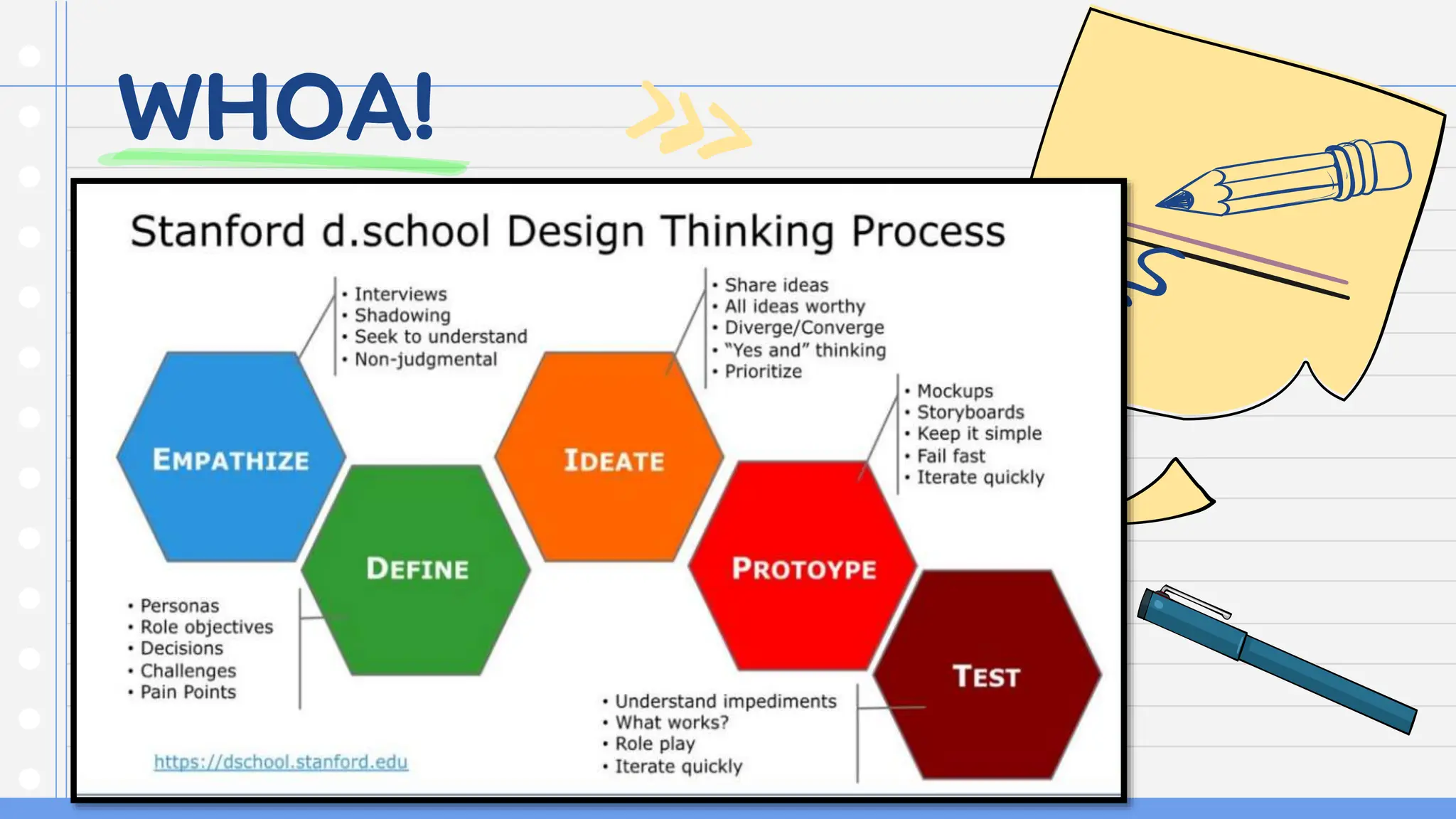
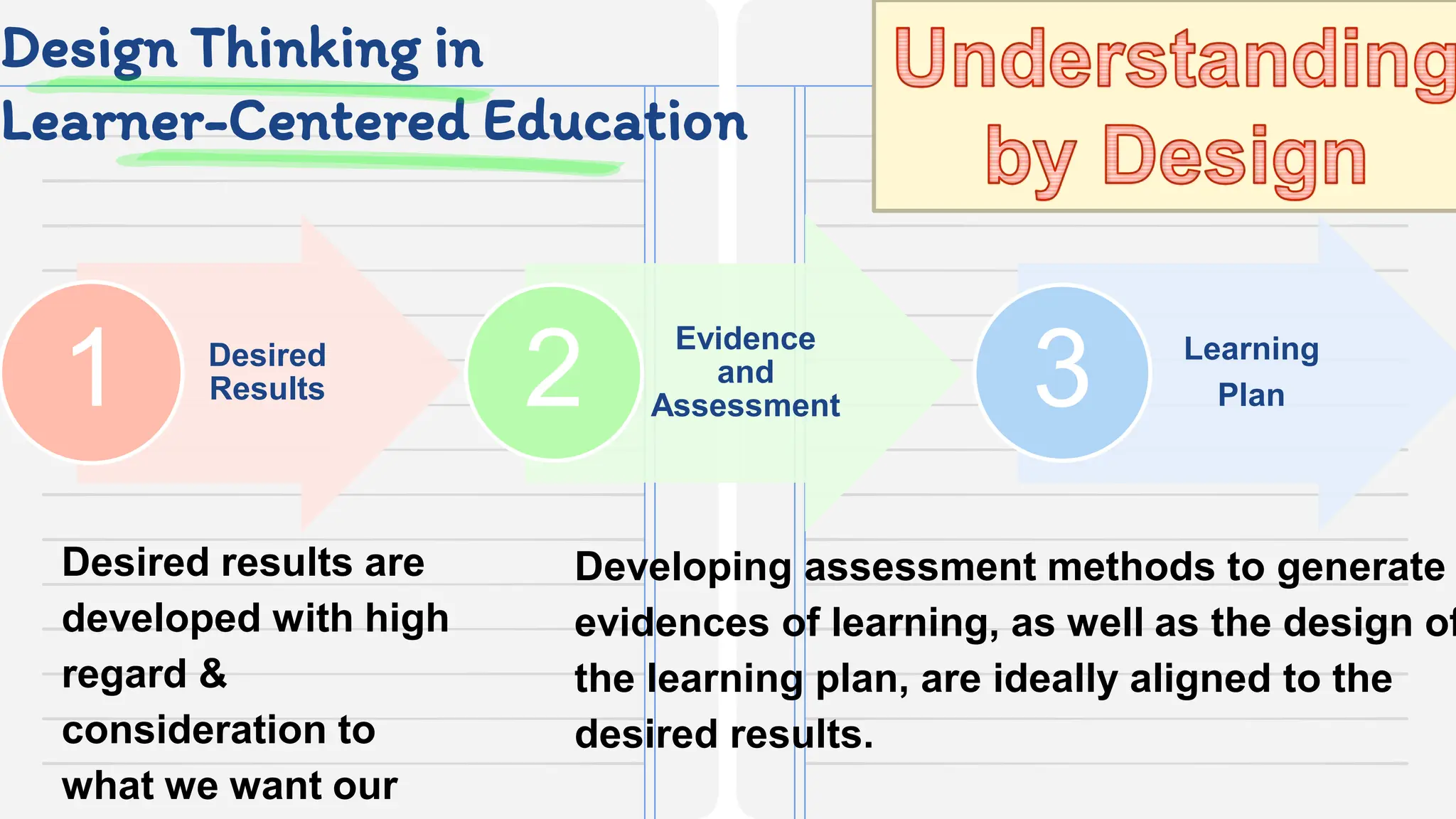
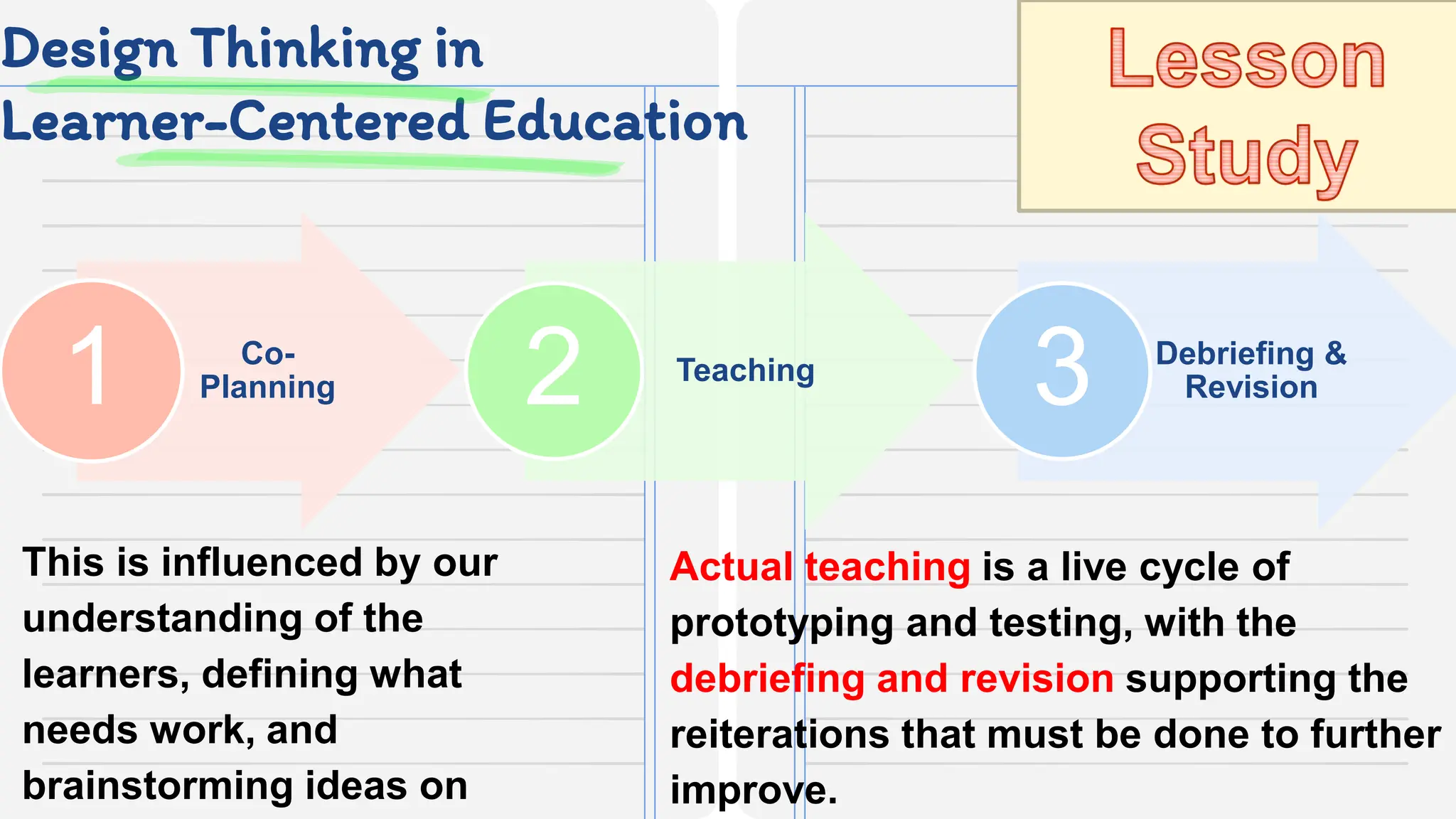
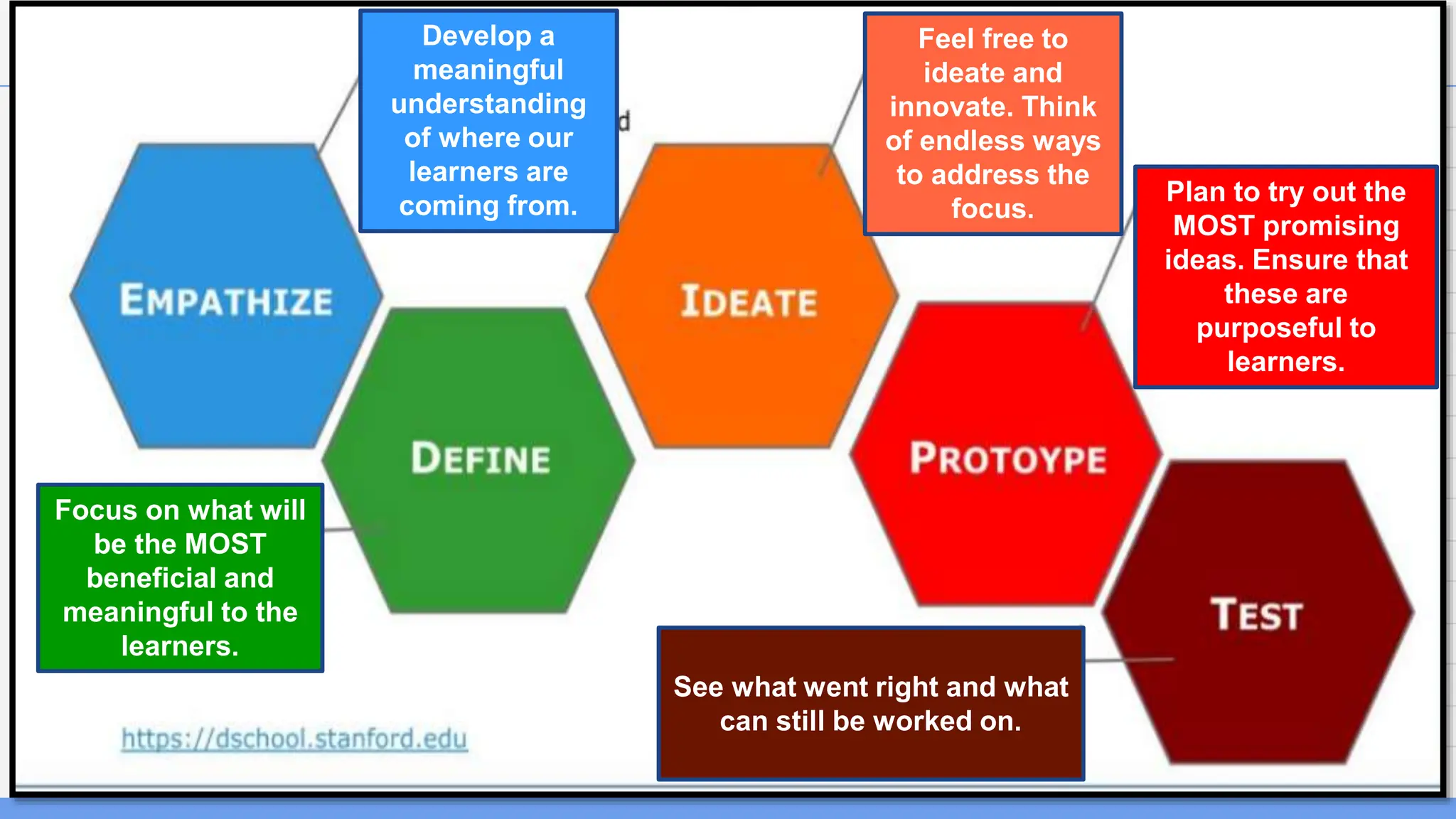
This document discusses applying design thinking in education. It begins by outlining the session objective of using design thinking to develop teaching innovations. It then discusses key ideas of design thinking, including demonstrating empathy, defining problems clearly, and solving problems iteratively. Design thinking is presented as a model for reframing methods and outcomes to help students develop skills like critical thinking, creativity, collaboration, curiosity, patience, and reflection. The document provides examples of how these design thinking concepts can be applied in an educational context, such as understanding learners, defining learners' concerns, and brainstorming and prototyping ideas with involved parties.