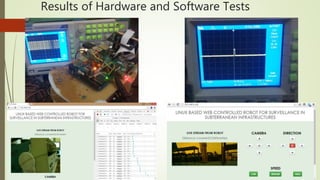
This document describes the design and construction of a Linux-based, web-controlled surveillance unmanned ground vehicle (UGV). The UGV was developed to remotely survey sewer infrastructure using a camera to determine if the infrastructure is suitable for deploying optical fiber cables. Key aspects included a Raspberry Pi single board computer running Debian Linux, a web interface for remote control and live video streaming, and wheel odometry sensors to track distance traveled. Testing showed the UGV could successfully be controlled remotely via a web interface to navigate and stream live video from inside sewers.