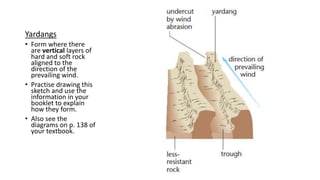
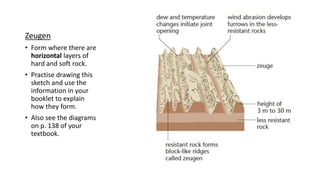
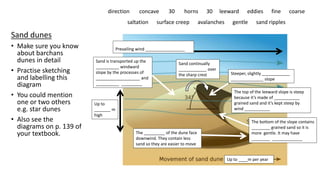
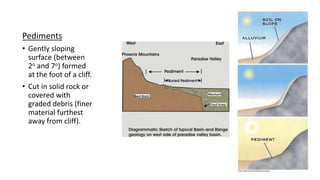
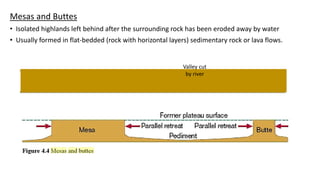
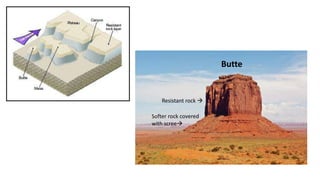
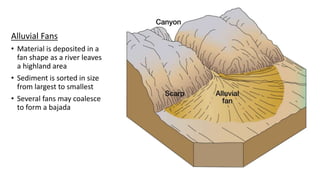
The document provides an overview of desert landforms, categorizing them into fluvial and aeolian types, and detailing specific formations such as yardangs, zeugen, sand dunes, pediments, and buttes. It emphasizes the need to understand the characteristics, sketches, and formation processes of these landforms, suggesting the use of diagrams for study. Additionally, there are practical activities to enhance learning through drawing and labeling each landform.