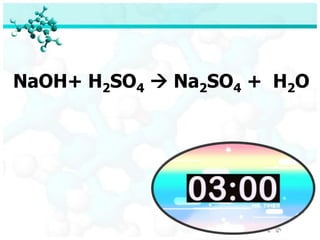
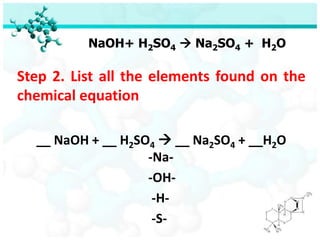
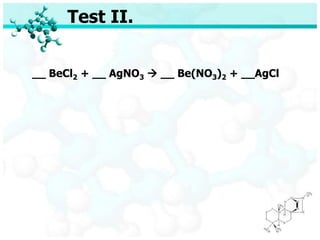
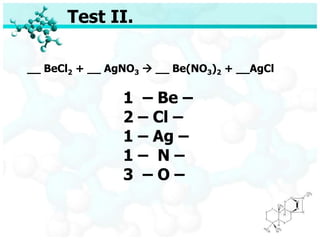
The document discusses balancing chemical equations. It begins by defining key terms like elements, compounds, and chemical reactions. It then explains the steps to balance chemical equations: 1) Identify reactants and products, 2) List elements, 3) Determine atom counts on each side, 4) Adjust with coefficients so atom counts are equal. Two examples show balancing the equations Na + FeCl2 → NaCl + Fe and NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O. A quiz provides balanced and unbalanced equations to identify.