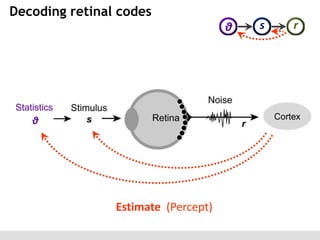
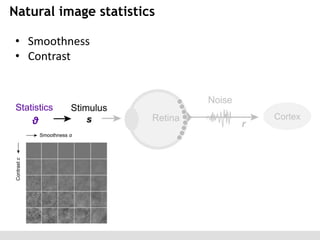
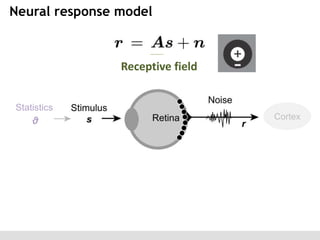
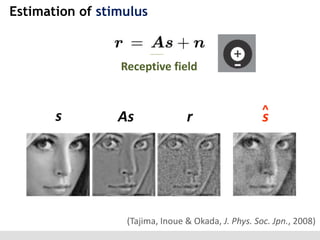
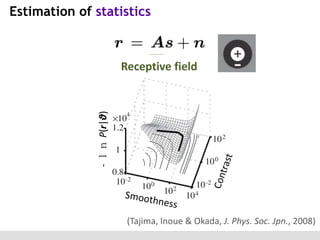
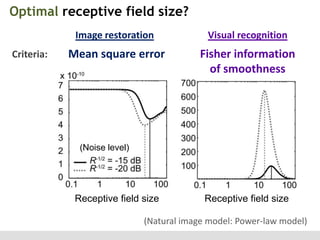
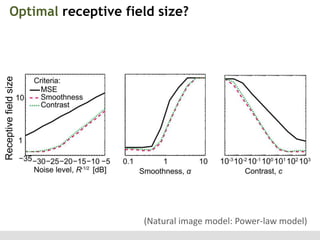
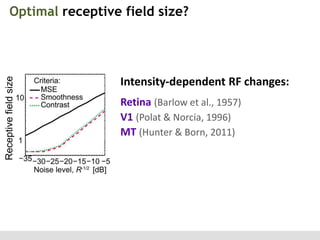
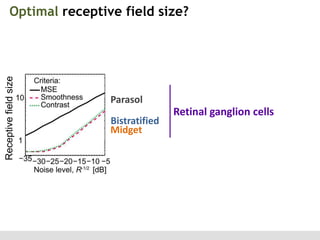
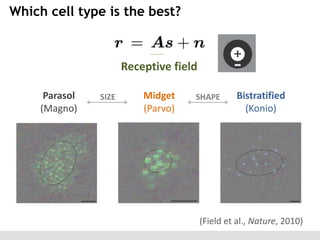
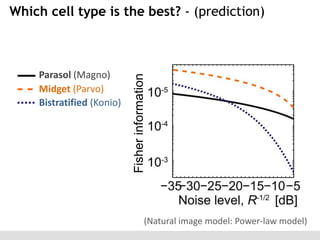
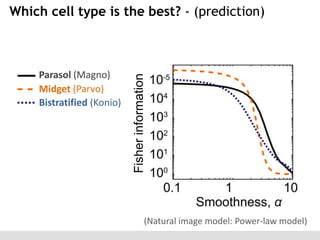
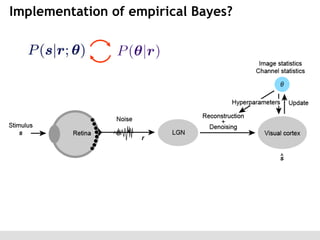
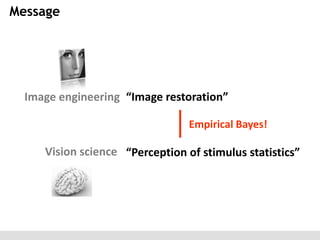
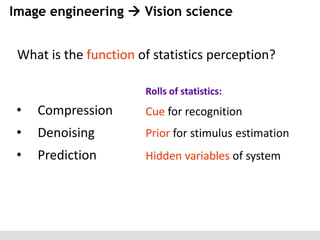
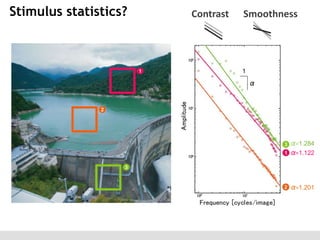
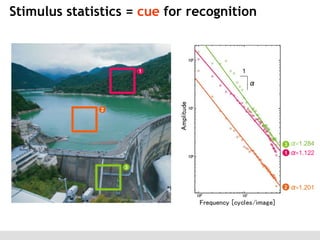
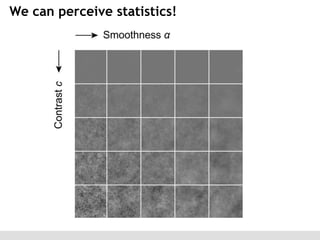
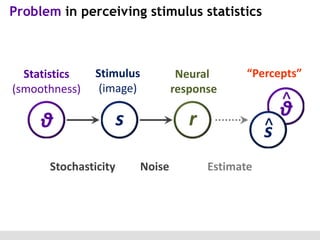
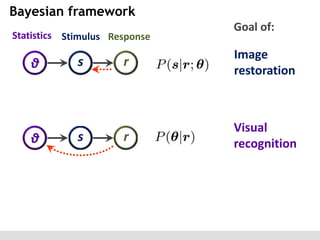
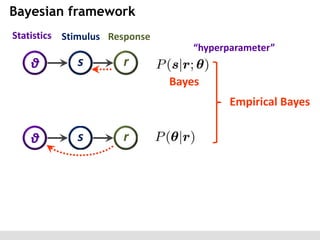
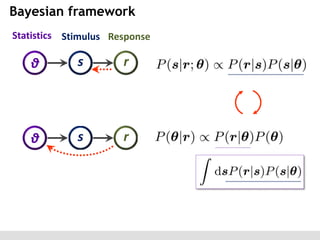
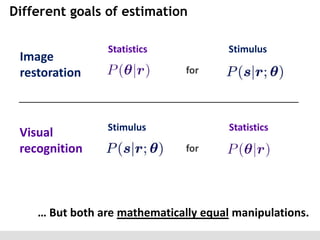
The document discusses the perception of image statistics using an empirical Bayes estimation approach. It explores various aspects of statistical perception, including the criteria for image restoration and visual recognition, as well as the implications of different receptive field sizes in the context of natural image statistics. The author highlights the roles of statistics in recognition, denoising, and compression, emphasizing the application of empirical Bayes methods in vision science and image engineering.



![Different criteria
Image
restoration
Visual
recognition
Mean square error
E [ s
ˆ
s
2
/N]
Variance of
estimate
Fisher information
E [-
ln P ( r | θ )]
ˆ ] -1
Var [
(Ideal observer)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hi-tajima-eb2-131226022707-phpapp02/85/Defining-statistical-perceptions-with-an-empirical-Bayesian-approach-13-320.jpg)
![Different criteria
Image
restoration
Visual
recognition
Mean square error
E [ s
ˆ
s
2
/N]
Signal detection
theory
Fisher information
E [-
ln P ( r | θ )]
(d ' )
(Ideal observer)
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hi-tajima-eb2-131226022707-phpapp02/85/Defining-statistical-perceptions-with-an-empirical-Bayesian-approach-14-320.jpg)