Embed presentation
Download to read offline



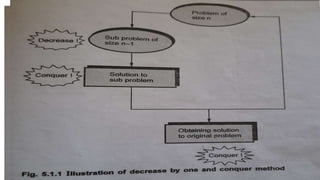
This technique involves breaking down a large problem into smaller subproblems, solving those subproblems, and combining the solutions to solve the original problem. It can be applied recursively or iteratively by decreasing the problem size by a constant amount each iteration. Examples where it is used include insertion sort, depth-first search, breadth-first search, and topological sorting.




