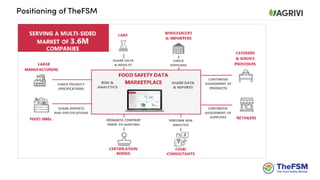
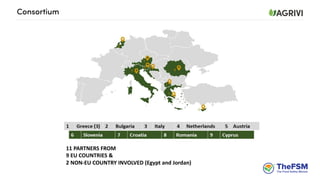
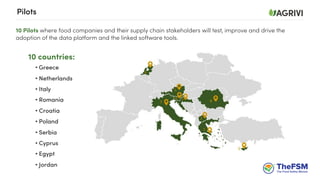
This document discusses strategies for crop sourcing that minimize risks, including ensuring traceability in the supply chain. It notes that traceability is key to securing good agriculture supply chain management and minimizing possible financial losses. Challenges to traceability are described, such as not knowing which crops come from which farms, which could lead to partial or complete delivery waste if pesticide residues are too high. The document also discusses responsible sourcing strategies, controlling chemical use, grower support practices like seasonal contracts and financing, and questions whether spreadsheets are sufficient as a traceability tool.