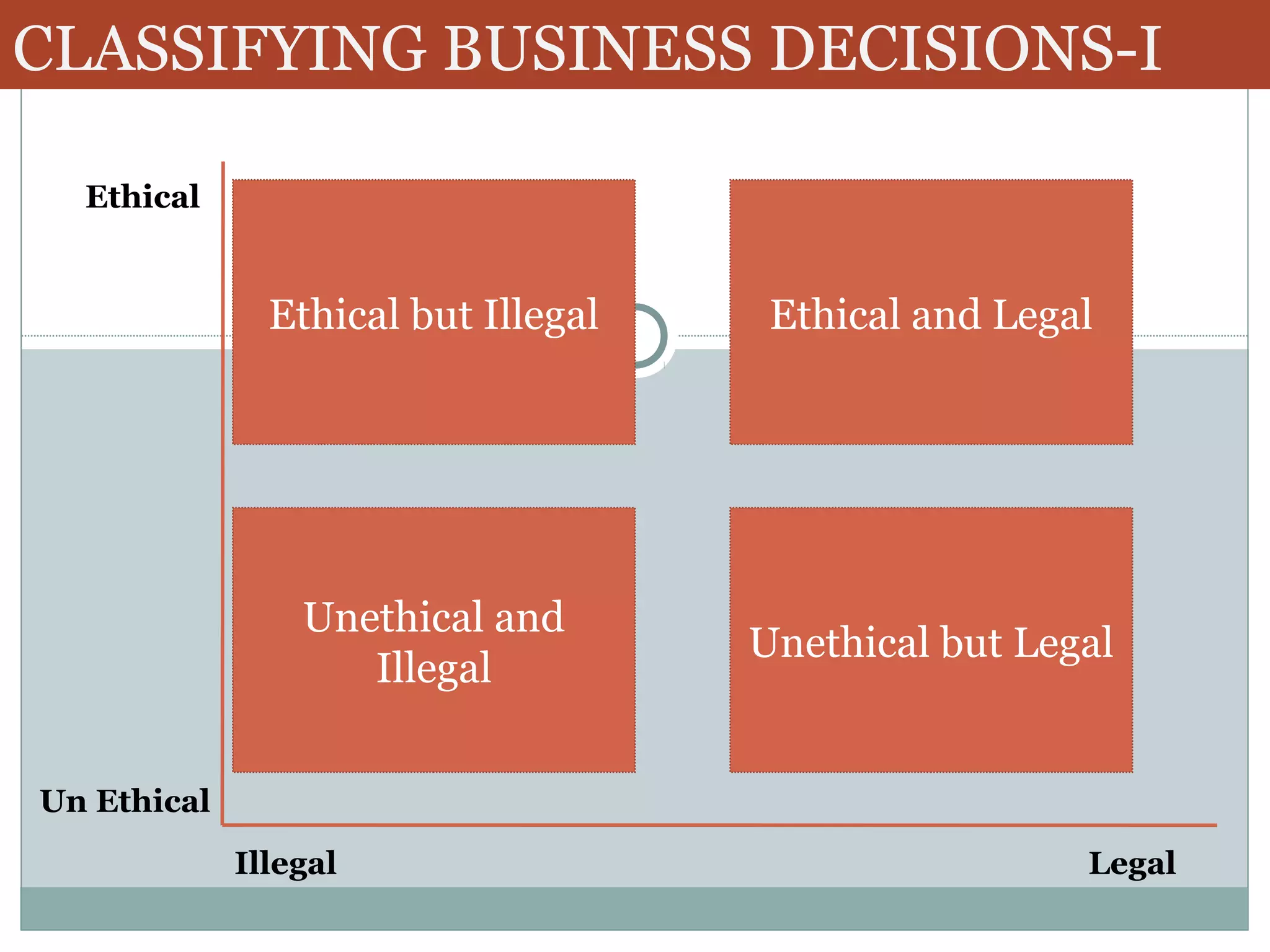
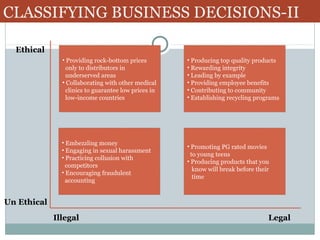
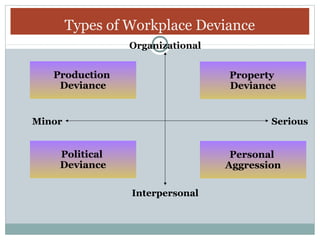
The document discusses various classifications of business decisions, emphasizing ethical, legal, and unethical practices, including examples like embezzlement and labor discrimination. It highlights workplace deviance, noting behaviors such as production deviance and personal aggression, and explores the correlation between early cheating in college and later dishonest behaviors in the workplace. Additionally, it outlines different ethical decision-making styles, including individualists, altruists, pragmatists, and idealists.