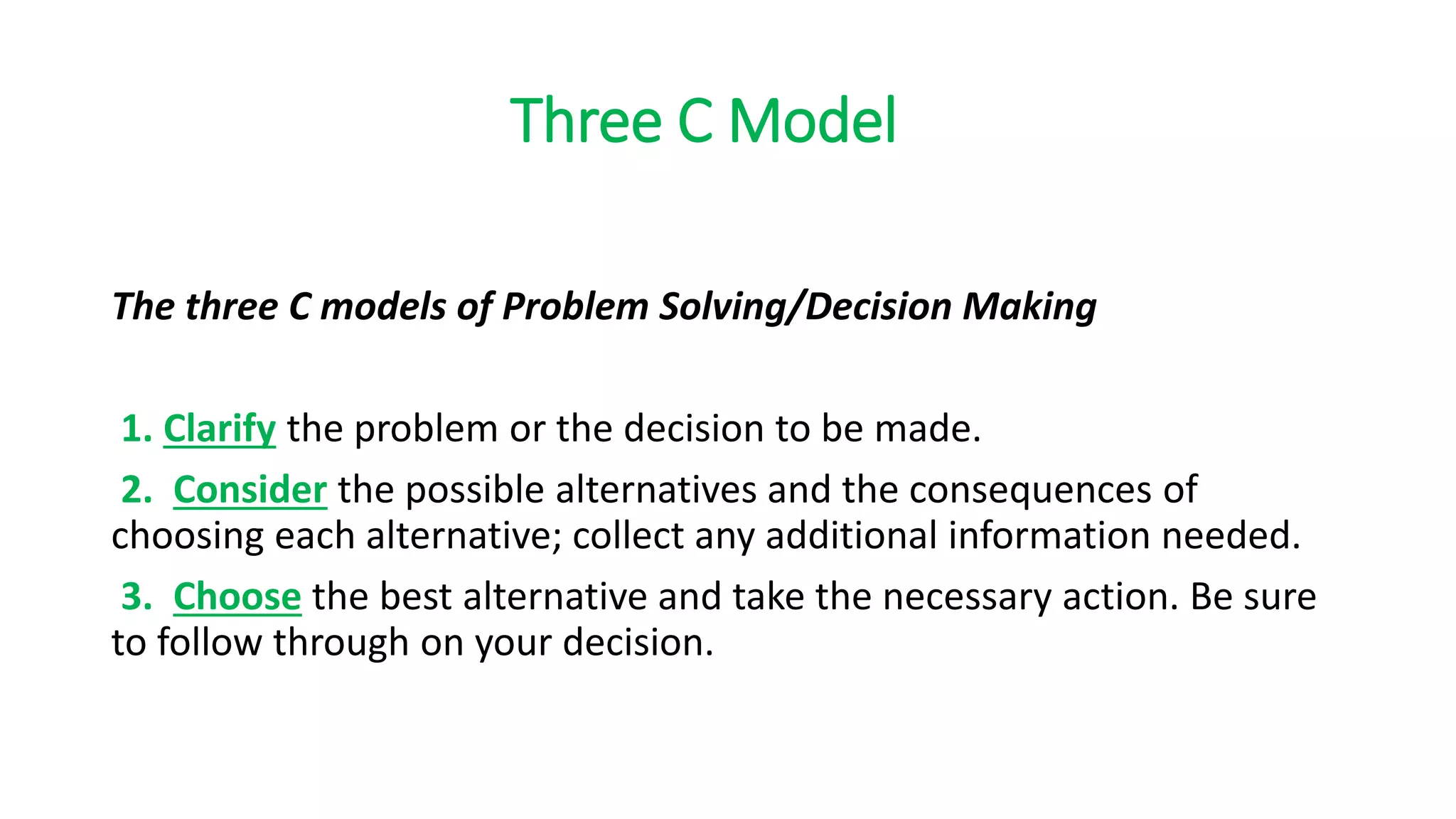
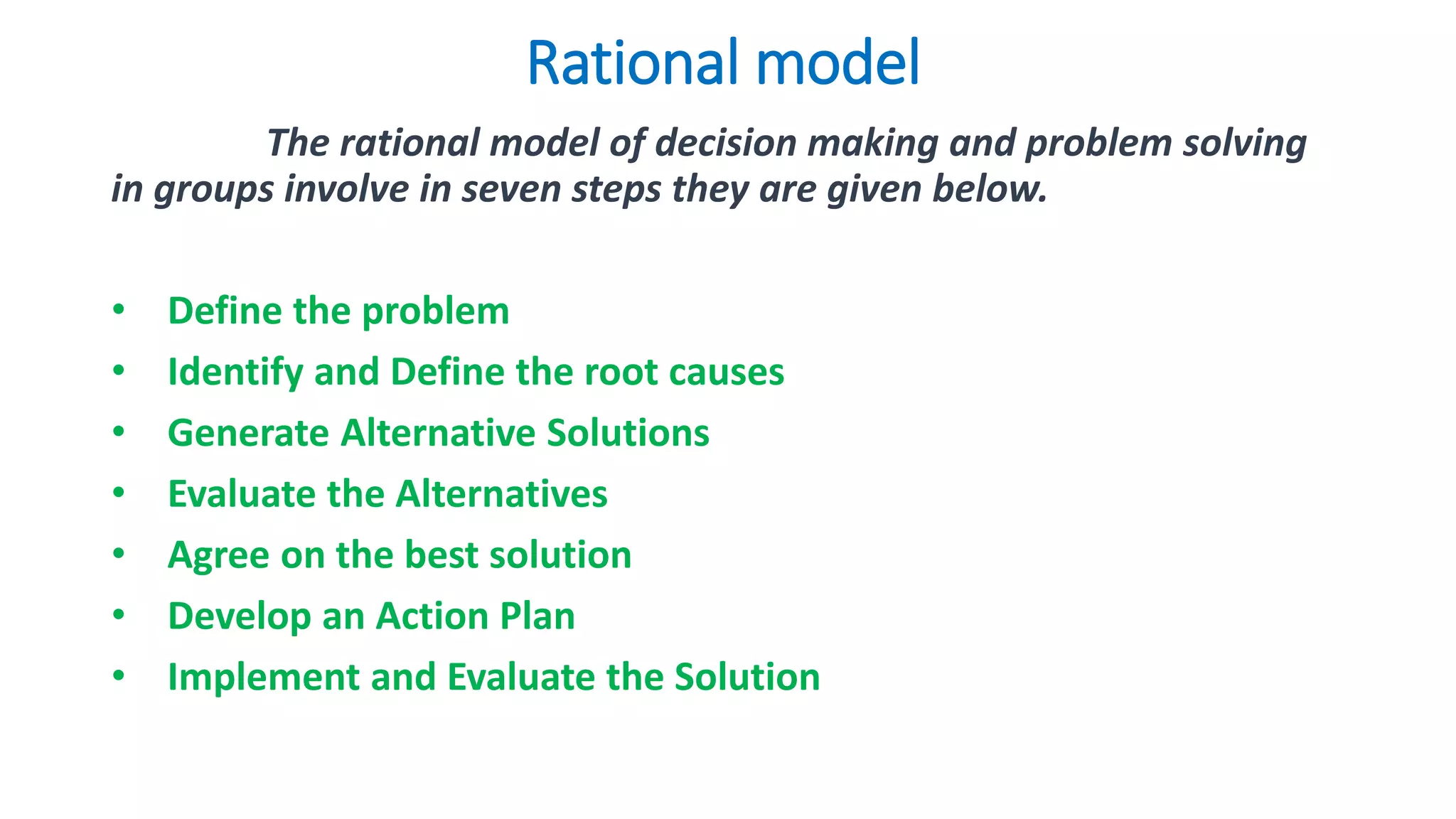
The document discusses two models for group decision making and problem solving: the Three C Model and the Rational Model.
The Three C Model is a three step process: 1) Clarify the problem, 2) Consider alternatives and consequences, 3) Choose the best alternative.
The Rational Model is a seven step process: 1) Define the problem, 2) Identify root causes, 3) Generate alternatives, 4) Evaluate alternatives, 5) Agree on a solution, 6) Develop an action plan, 7) Implement and evaluate the solution.