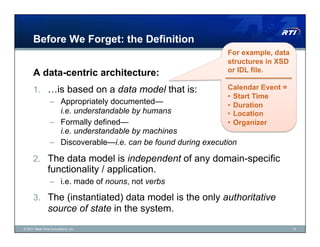
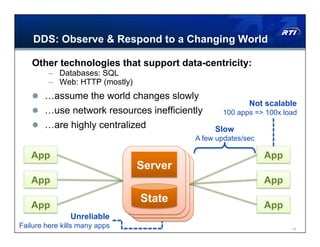
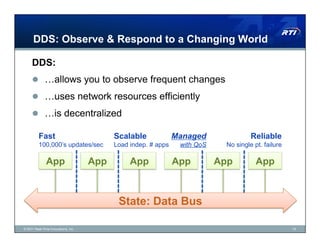
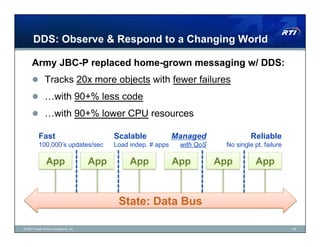
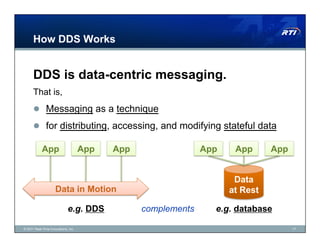
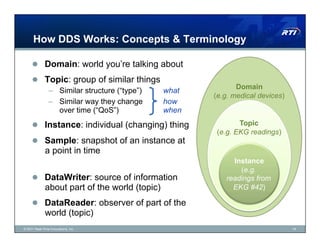
The document discusses Data Distribution Service (DDS) as a data-centric messaging architecture that enhances system integration and efficiency by maintaining a unified state across applications. It emphasizes the benefits of data-centricity, including faster implementation, easier updates, and more reliable systems, while contrasting with message-centric approaches that rely on message reconstruction. By leveraging DDS, organizations can manage dynamic systems effectively, improving resource utilization and reducing development costs.