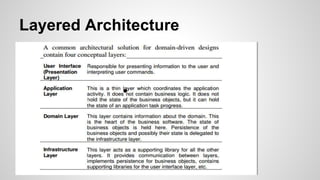
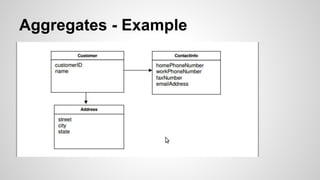
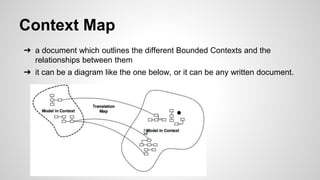
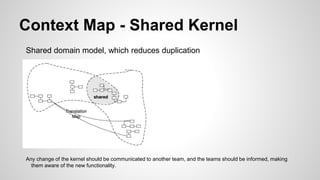
Domain-Driven Design (DDD) is a methodology that helps developers create software by emphasizing object systems and domain models that encapsulate complex business logic. Key concepts include ubiquitous language, layered architecture, entities, value objects, and bounded contexts, which facilitate clear communication between domain experts and developers. By organizing related concepts into modules and maintaining clear boundaries, DDD aims to align software design with business realities.