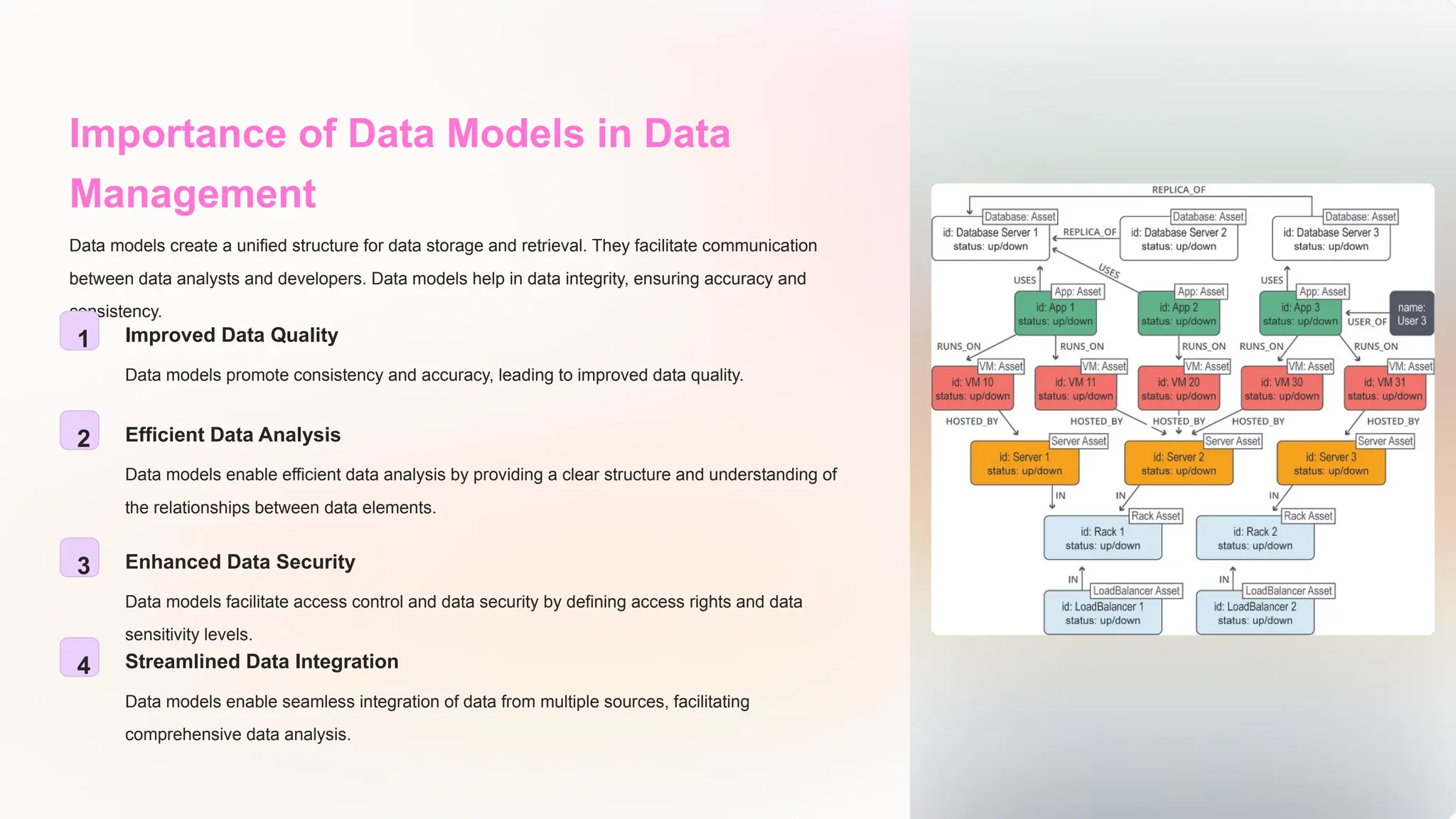
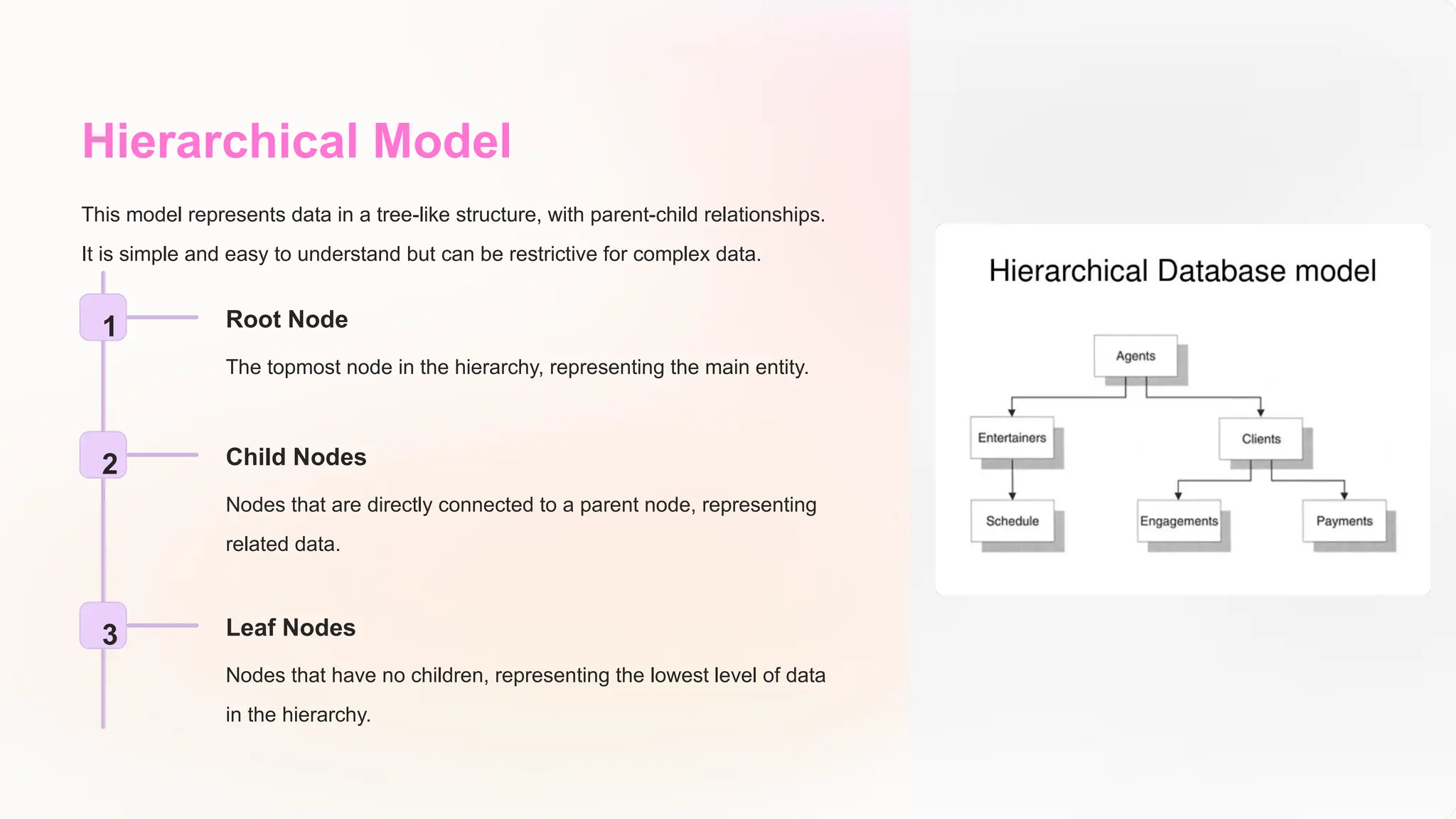
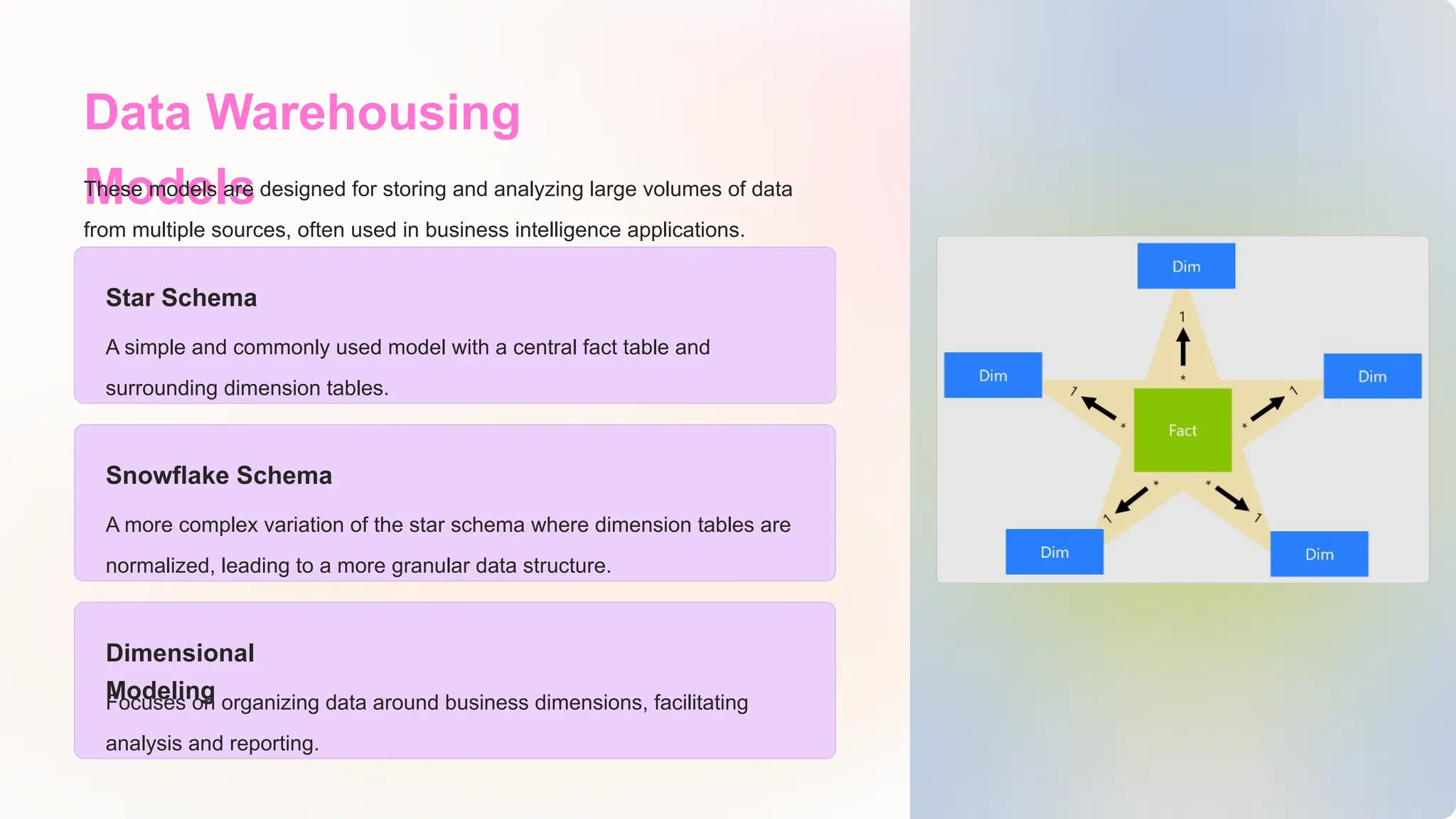
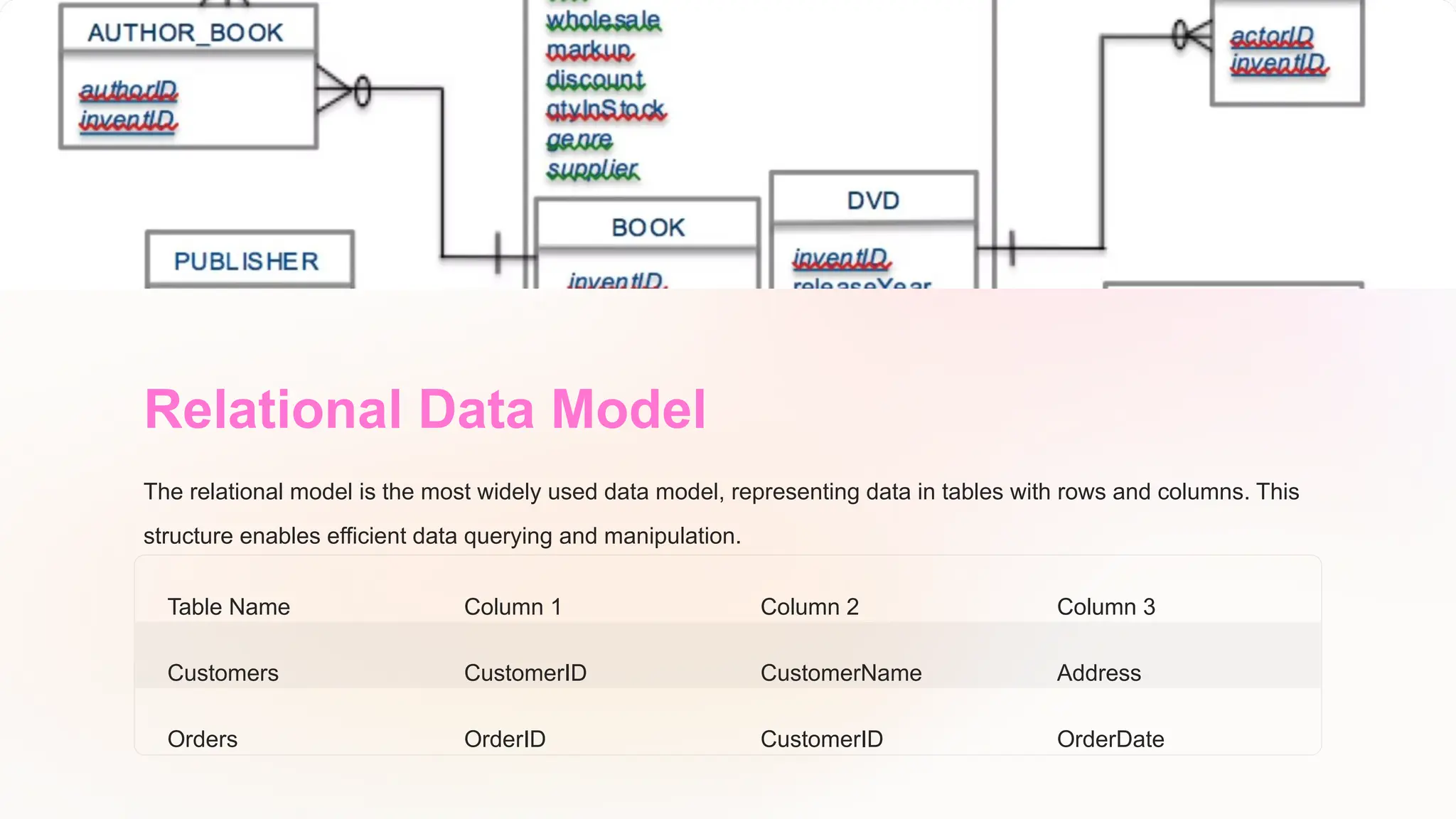
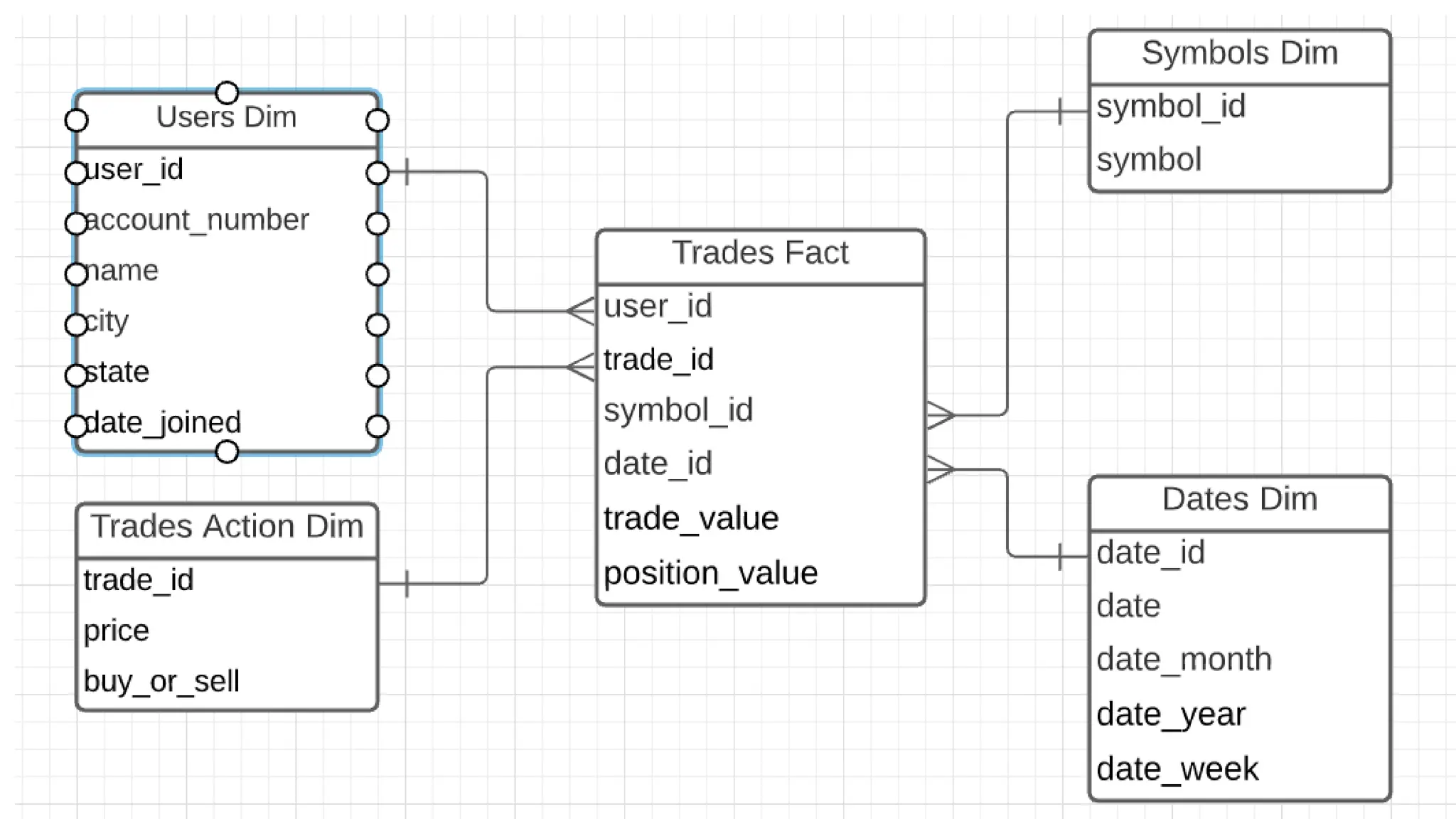
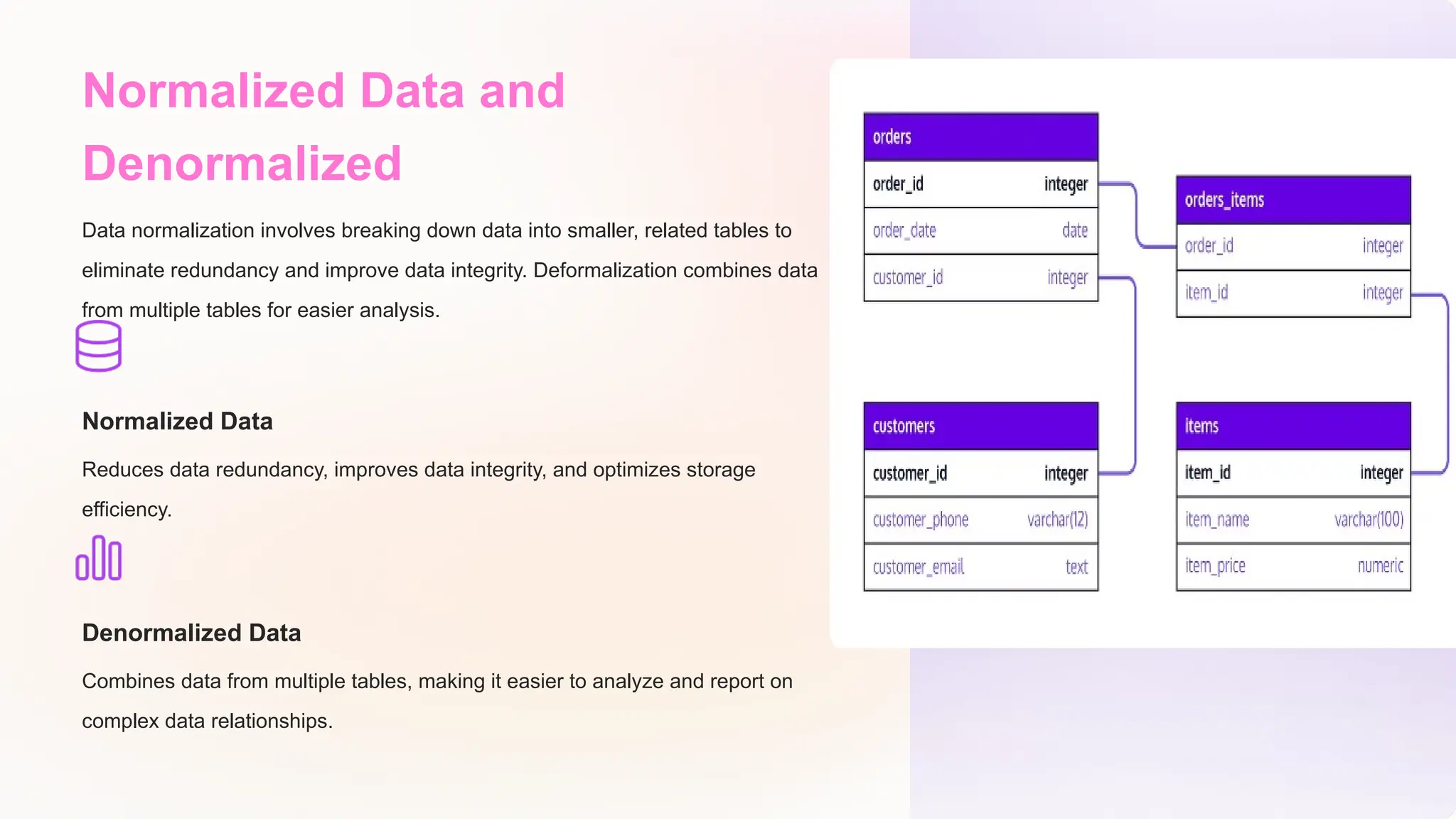
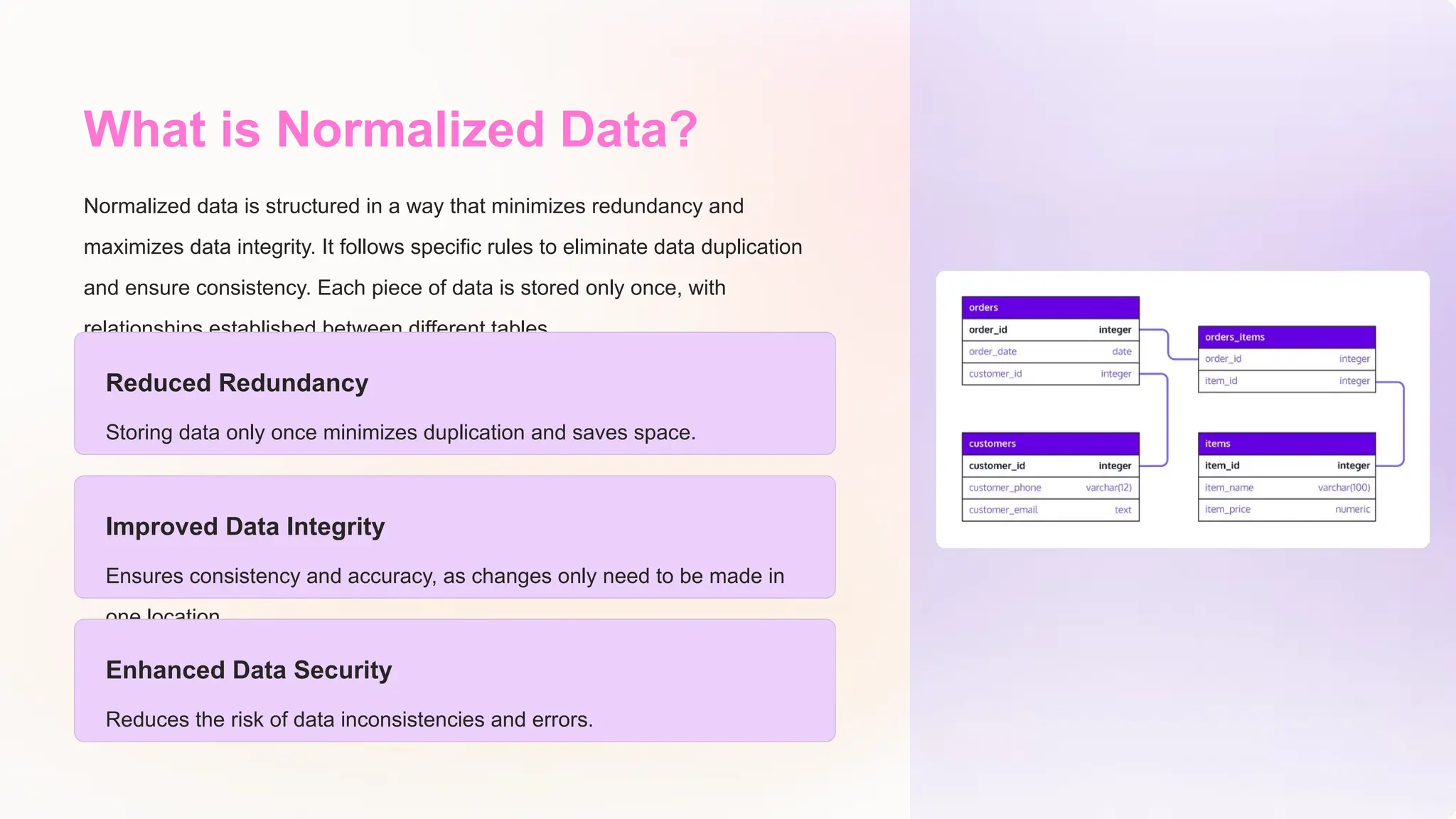
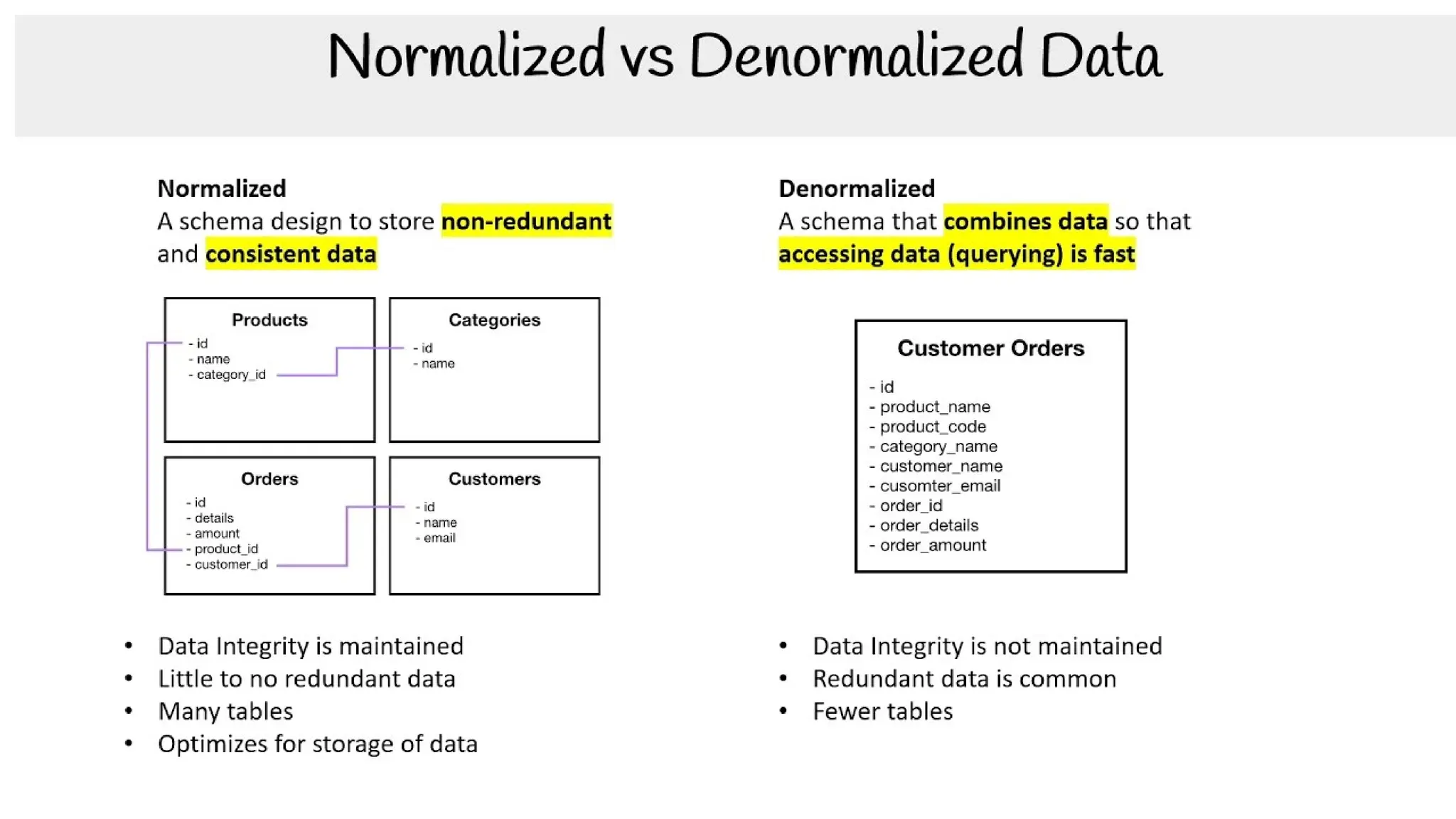
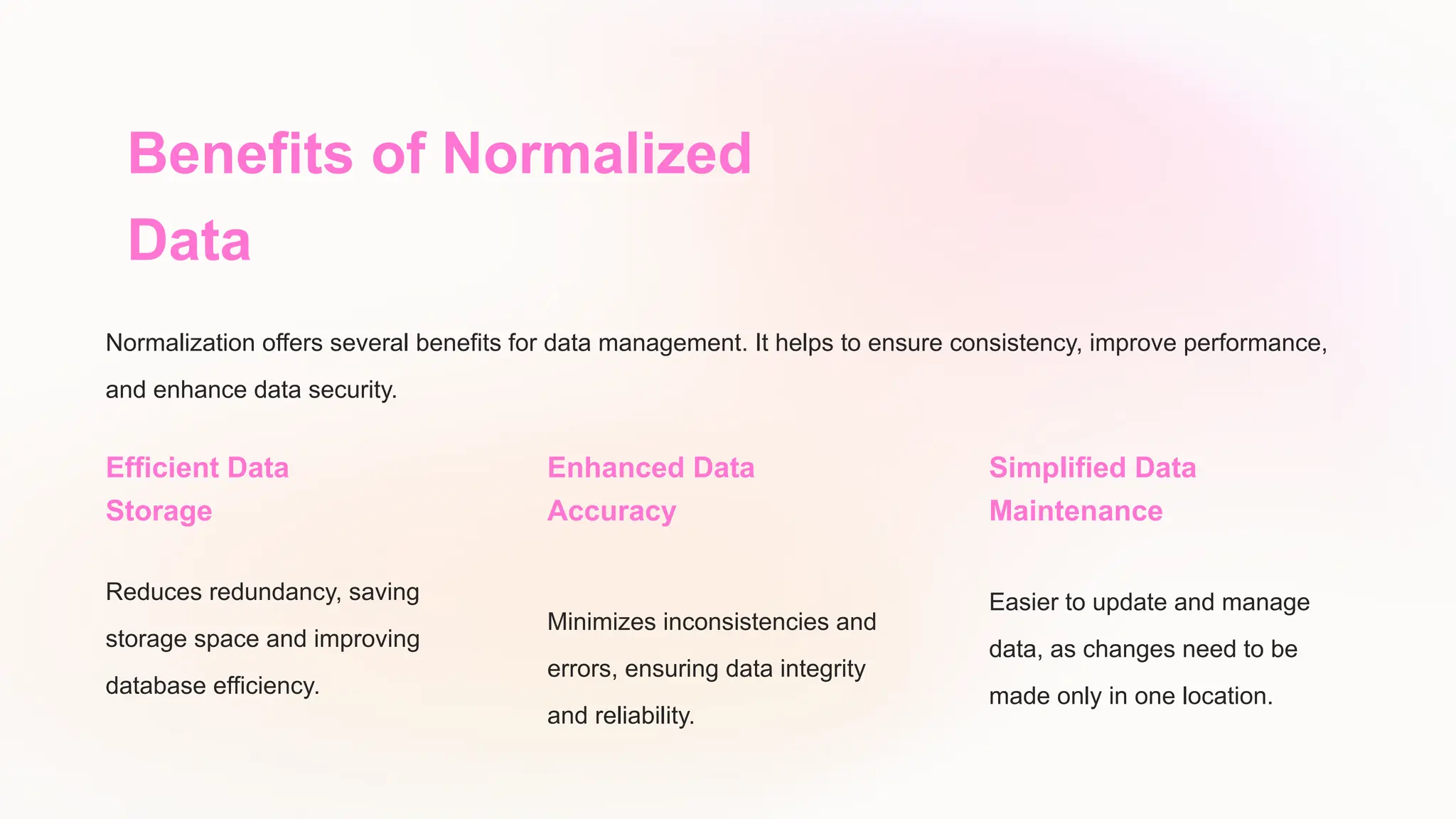
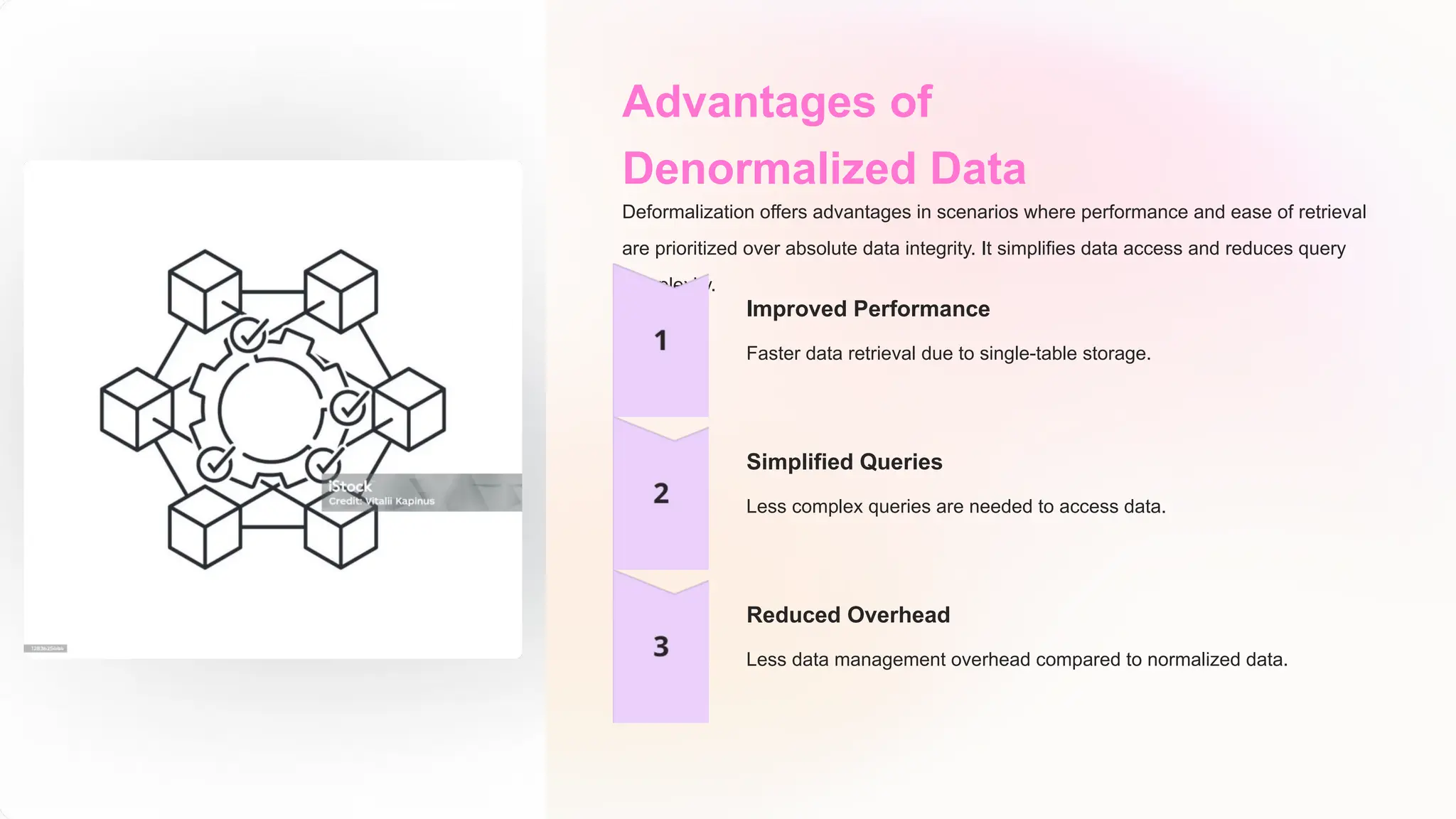
The document discusses the importance of data models and standards in managing data effectively, emphasizing their roles in improving data quality, facilitating efficient analysis, enhancing security, and enabling integration. It outlines various data models, including hierarchical, relational, network, and object-oriented models, as well as different data warehousing models such as star and snowflake schemas. It also compares normalized and denormalized data, highlighting their advantages and challenges based on specific application needs.