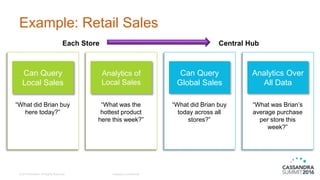
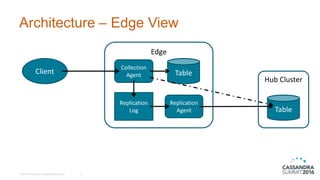
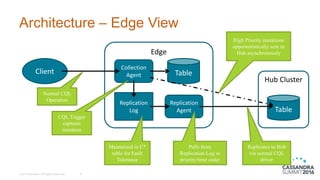
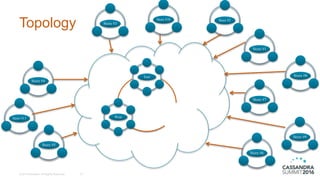
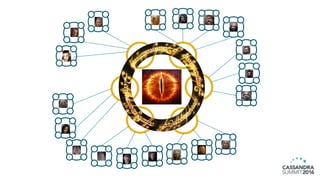
The document discusses DataStax Advanced Replication, which allows many edge clusters to replicate data to a central hub, addressing limitations of standard Cassandra replication in scenarios with disconnected nodes. It highlights functionalities such as prioritized streams, one-way replication, and support for active queries and analytics at both edge and hub clusters. Key terminology includes edge and hub clusters, replication logs, and collection/replication agents.