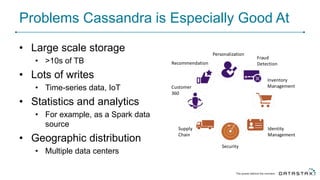
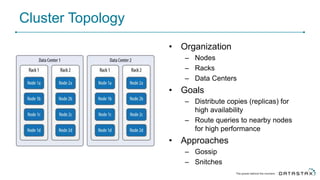
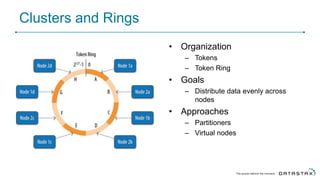
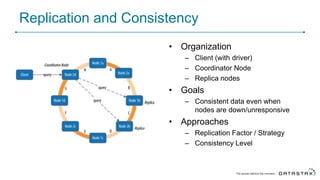
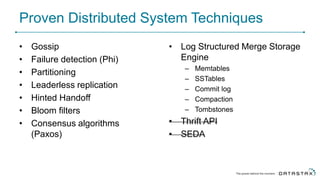
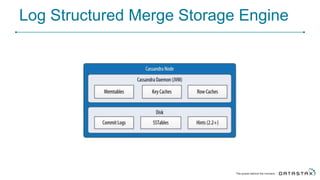
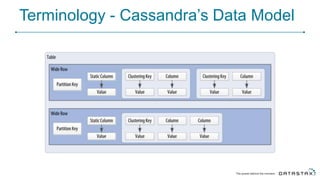
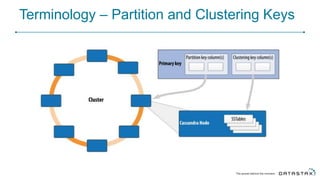
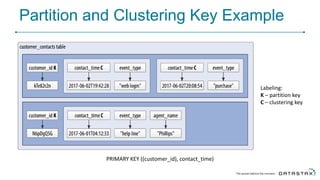
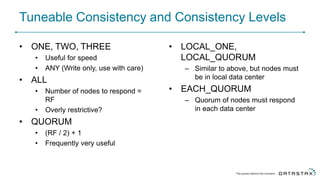
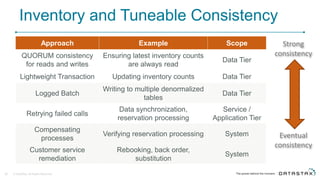
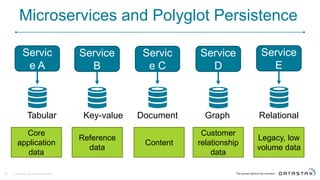
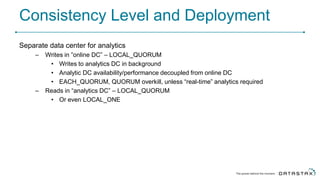
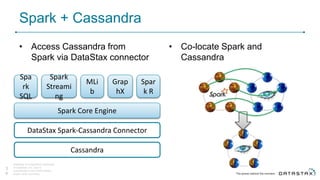
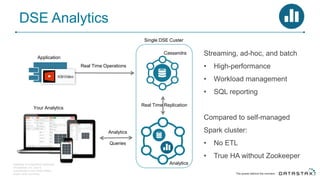
Cassandra is a distributed database that is especially well-suited for handling large volumes of writes and data across many servers. It provides high availability through replication and tunable consistency levels. The document discusses Cassandra's architecture including its use of a ring topology, log-structured storage, and data model using a partition key and clustering columns. It also explains how Cassandra can be used as part of a polyglot persistence strategy along with complementary technologies like Spark and DSE Analytics.