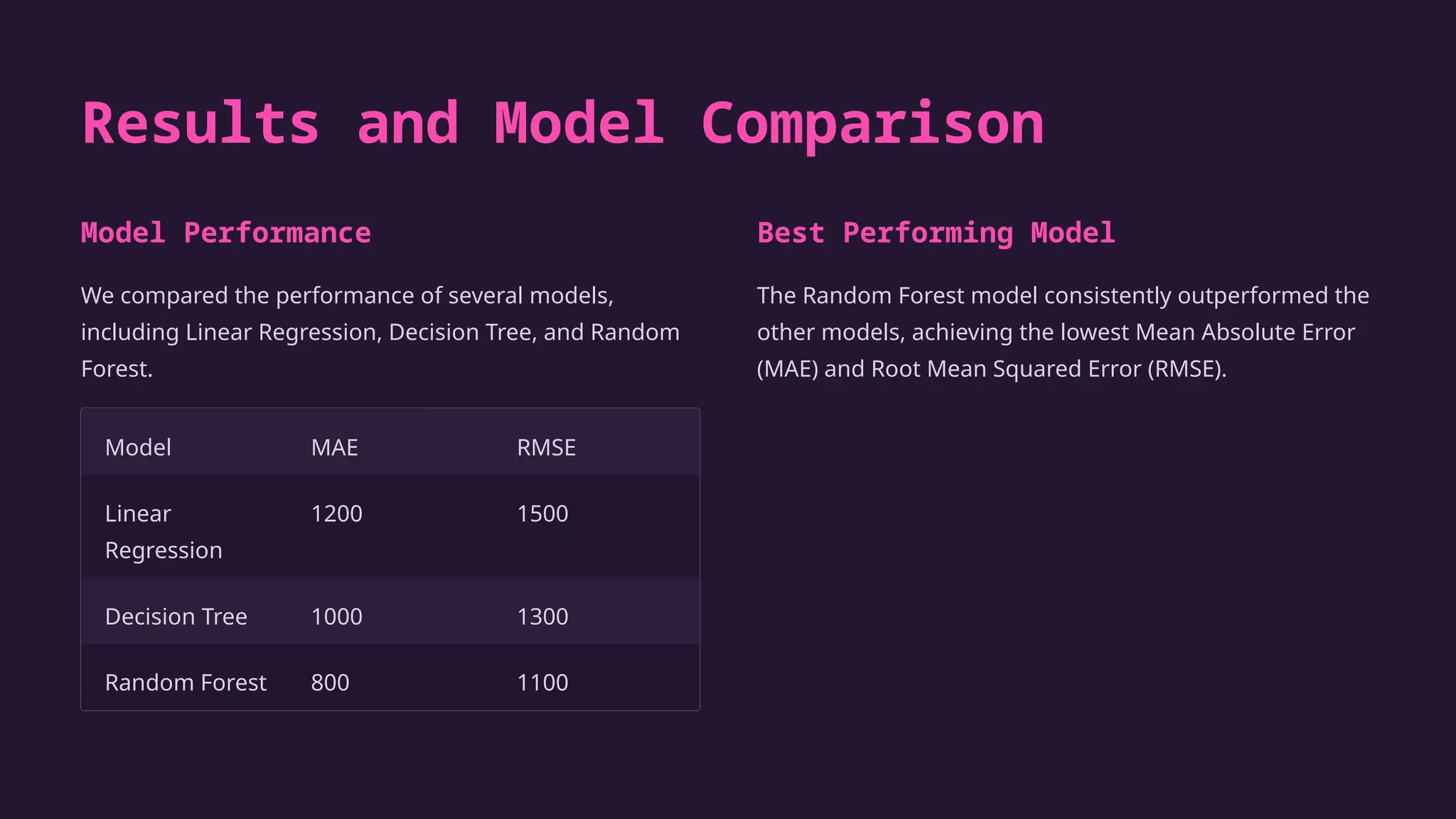
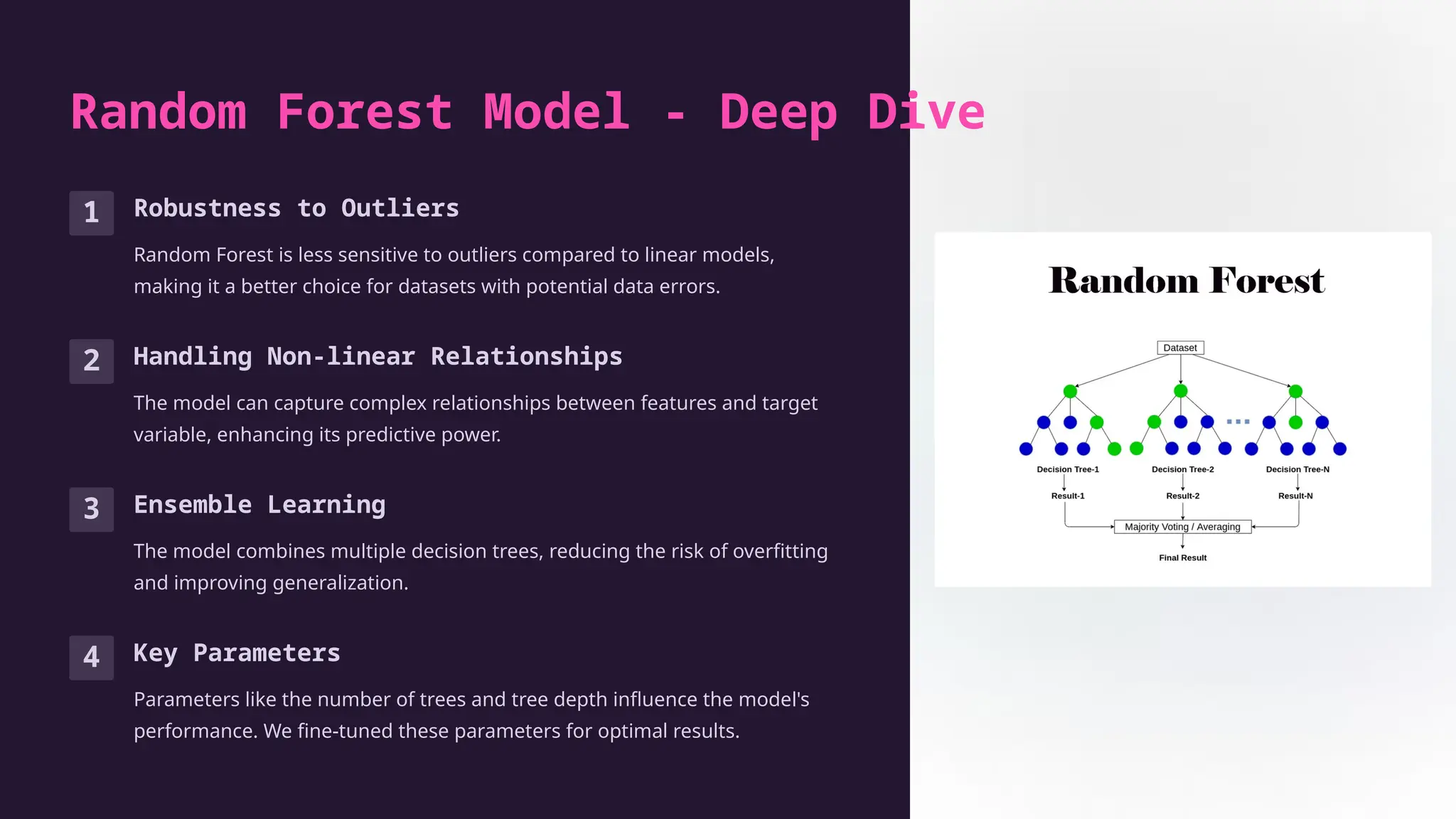
The document presents an overview of a data science internship at YBI Foundation, focusing on developing a used car price prediction model using machine learning techniques. The project involved comprehensive data analysis, model training, and evaluation, ultimately resulting in a highly accurate random forest model that significantly improved price estimations for the used car market. Future plans include incorporating additional features and real-time data integration to enhance model performance.