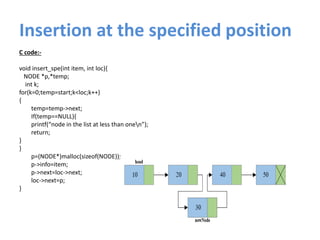
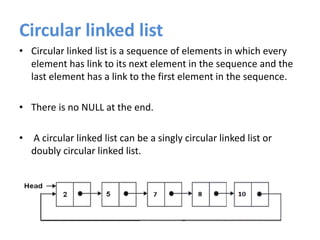
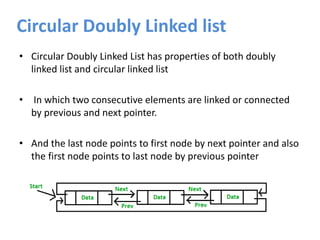
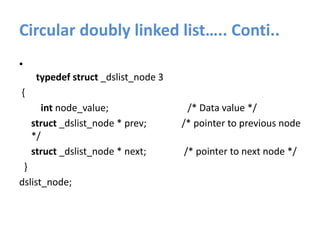
A linked list is a linear data structure where each node contains a link to the next node. There are several types of linked lists including singly-linked, doubly-linked, circular, and circular doubly-linked lists. Linked lists allow for efficient insertion and removal of nodes and can grow and shrink dynamically. Common operations on linked lists include creation, insertion, deletion, traversal, searching, and concatenation.






![Inserting a node at beginning
• Algorithm:-
1) Insert_first(Start, item)
[Check the overflow]
if ptr=NULL, then
Print “overflow
Exit
else
Ptr=(node*)malloc(size of node));
End if
2) Set ptr->Info=item
3) Set ptr->next=start
4) Set start=ptr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-180205102652/85/Linked-list-using-Dynamic-Memory-Allocation-7-320.jpg)
![Inserting a node at the end
Insert _last(Start , item)
1) [check over flow?]
if ptr=NULL, then
print ”over flow”
exit
else
ptr=(node*)malloc(sizeOf(node));
end if
2) Set ptr->info=item
3) Set ptr->next=NULL
4) If start=NULL and if then set start=p;
5) loc=start
6) Repeate step 7 until loc->next!=NULL
7) Loc=loc->next
8) Loc->next=p](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-180205102652/85/Linked-list-using-Dynamic-Memory-Allocation-8-320.jpg)