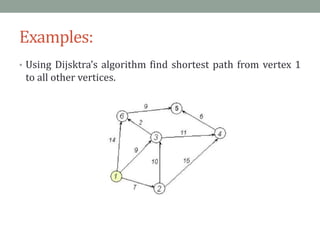
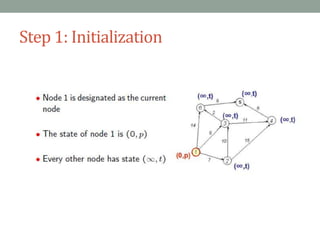
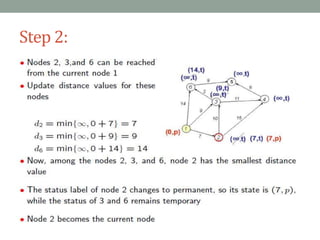
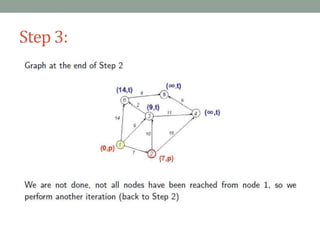
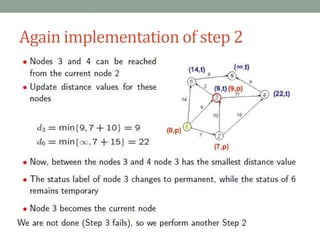
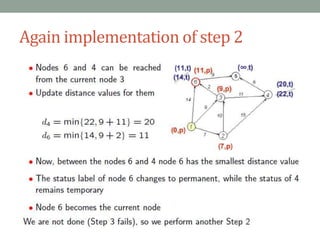
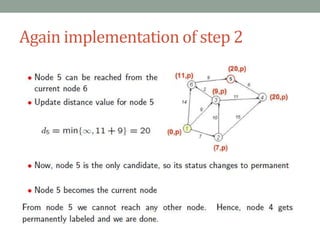
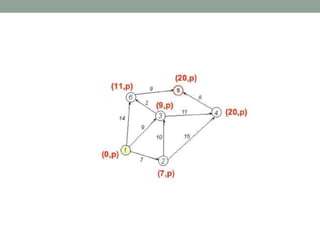
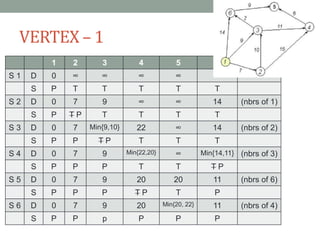
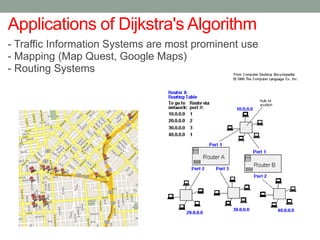
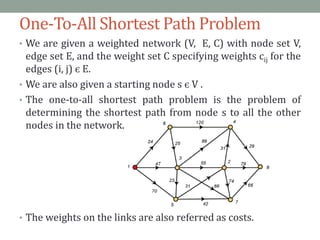
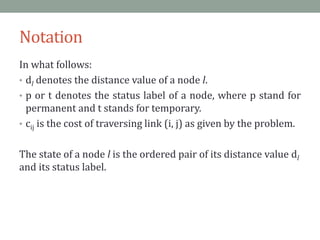
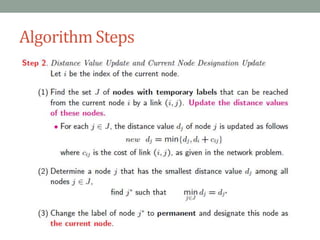
Dijkstra's algorithm is used to find the shortest path from a starting node to all other nodes in a network. It works by assigning initial distance values to all nodes from the starting node and then iteratively updating the distances by considering connections to neighboring nodes. At each step, it selects the node with the smallest distance value and designates it as permanent until all nodes have been reached.





![Step 1: First of all, define two sets-
1) One set will contain all those vertices which have been visited in the shortest path
tree. In the beginning, this set will be empty.
2) Other set will contain all those vertices which are not visited in the shortest path
tree. In the beginning, this set will contain all the vertices of the graph.
Step 2: For each vertex of the graph, define a three tuple as-
1) P[v] which denotes the parent (predecessor) of vertex ‘v’
2) d[v] which denotes the shortest path estimate of vertex ‘v’ from the source vertex.
3) St[v] which denotes the status of the vertex, whether visited ‘V’ or not ‘NV’.
Step 3: Initially, set the value of the tuple for each vertex as-
1) Set the value of variable ‘P’ for each vertex to NIL i.e. P[v] = NIL.
2) Set the value of variable ‘d’ for source vertex to 0 i.e. d[S] = 0.
3) Set the value of variable ‘d’ for rest of the vertices to ∞ i.e. d[v] = ∞.
4) Set the value of variable ‘St’ for source vertex to 0 i.e. St[S] = V.
5) Set the value of variable ‘St’ for rest of the vertices to NV i.e. St[v] = NV.
Step 4: Consider all outgoing edges from the visited vertex/vertices, and update the tuple of
the vertices on the outgoing edges.
Step 5: Now among not visited vertices, we choose a vertex with the minimum value of
variable ‘d’, accordingly change the status of the vertex to ‘V’.
Step 6: Repeat Step 4 and Step 5 until all the vertices of the graph are visited.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dijkstra123-220925150337-f264f281/85/DIJKSTRA_123-pptx-10-320.jpg)