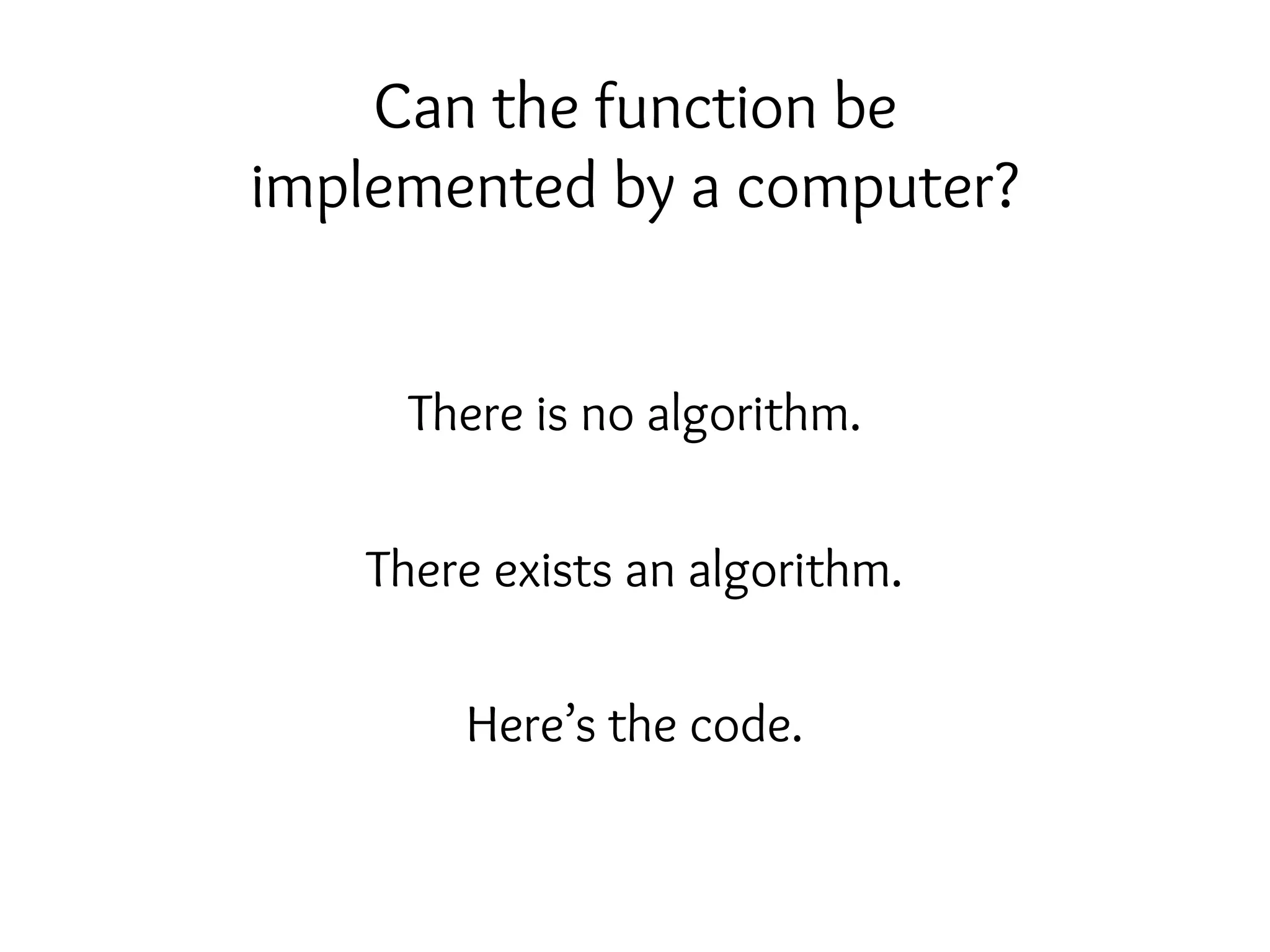
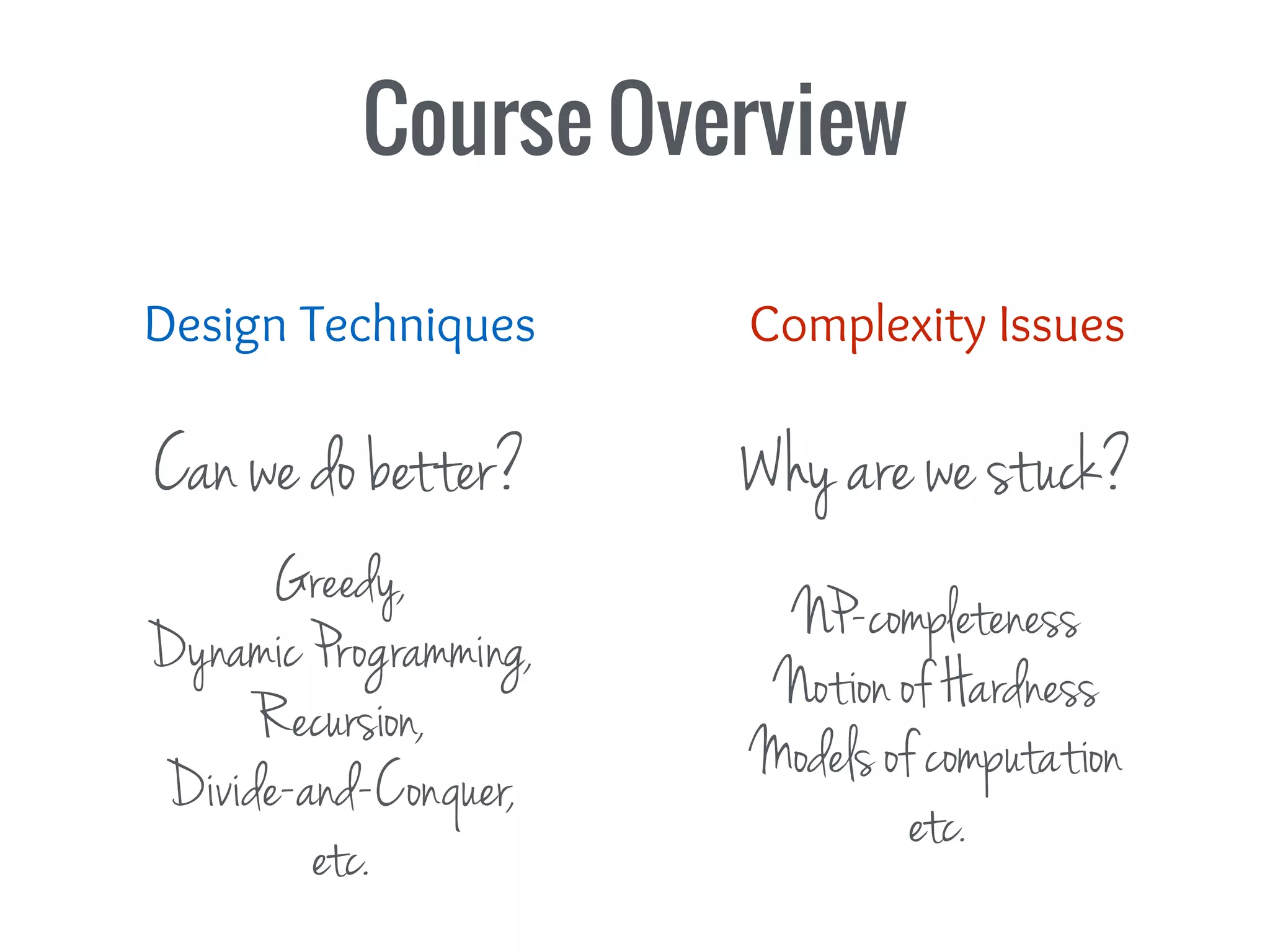
This document outlines the course details for CS 321 Algorithm Analysis and Design. It includes information on logistics like office hours and TAs, graded work like assignments and exams, starred problems, discussion policy, and an overview of design techniques, complexity issues, and key tools covered in the course. The document also provides pre-requisites and motivates the importance of algorithms through quotes about using both theory and practice to improve each other.

![Logistics
[Optional] Extra Sessions.
Office Hours: 2PM to 3PM on class days.
TAs: Shivdutt and Supratim.
Course Webpage: http://cs321.xyz
Reference material: http://algorithms.wtf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0030decintroduction-160212160434/75/00-30-Dec-Introduction-2-2048.jpg)



![Key Tool
Reductions
Too lazy to write findMin when sort is available.
A.sort; min(A) = A[0]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0030decintroduction-160212160434/75/00-30-Dec-Introduction-7-2048.jpg)