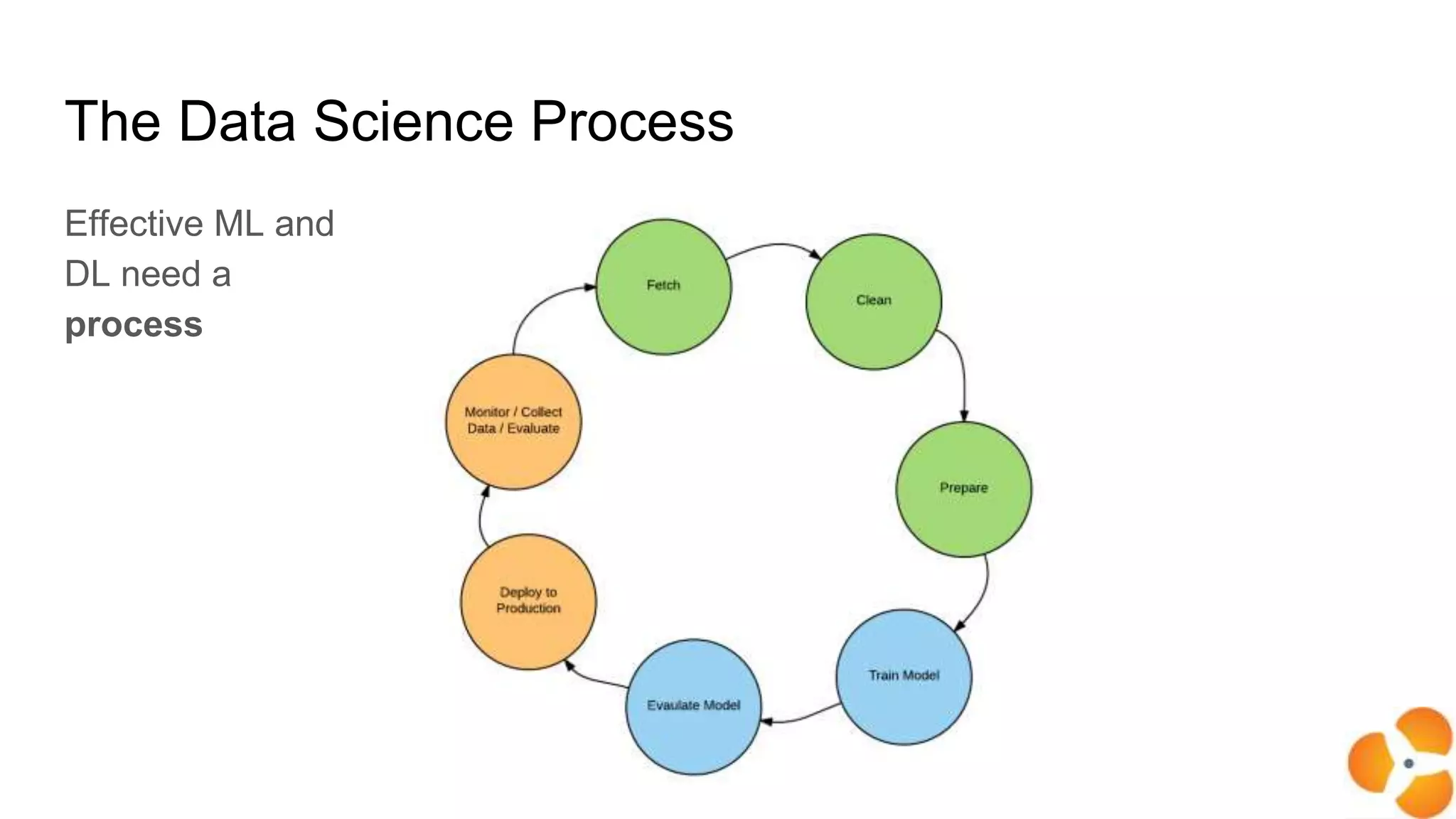
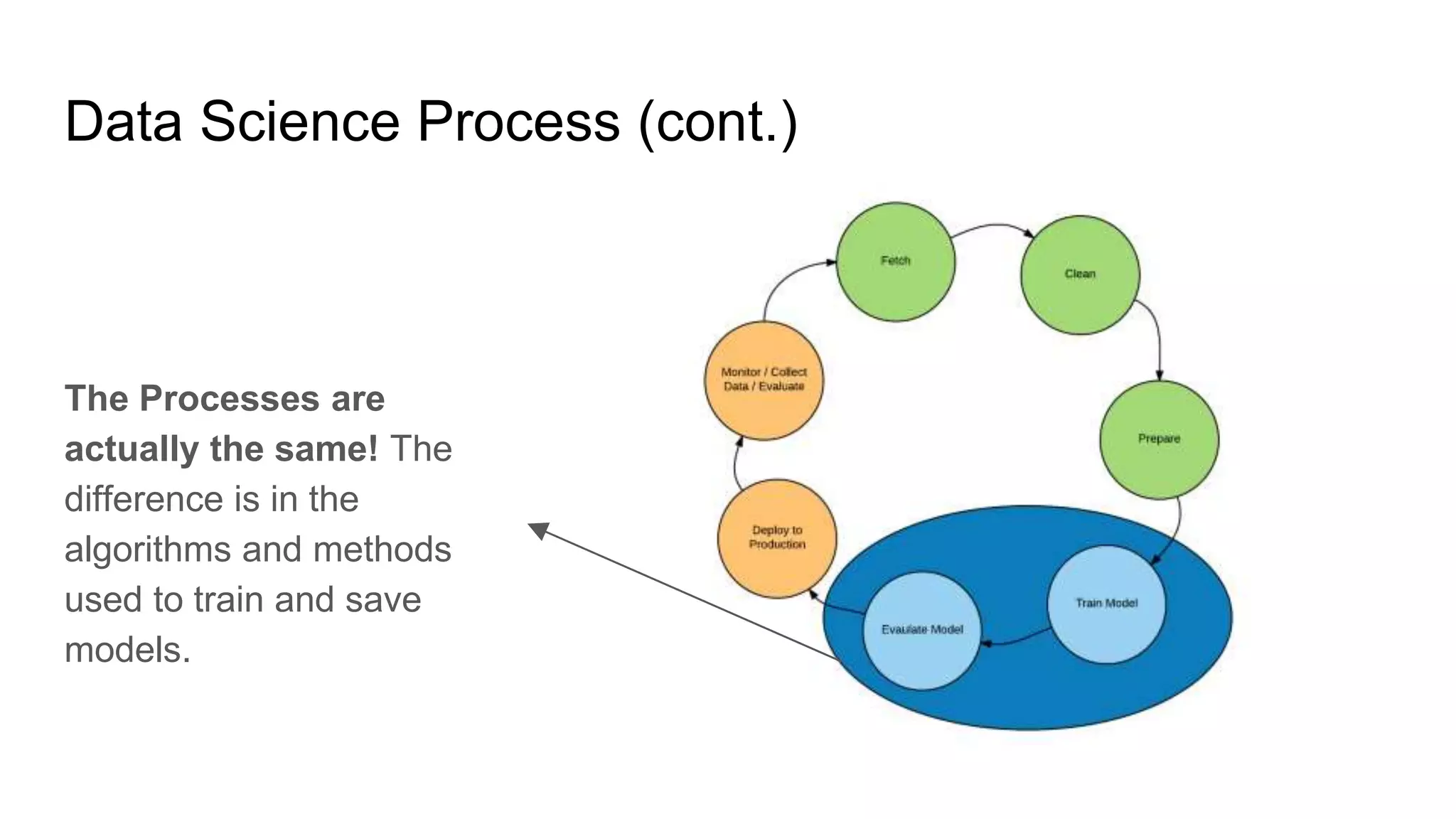
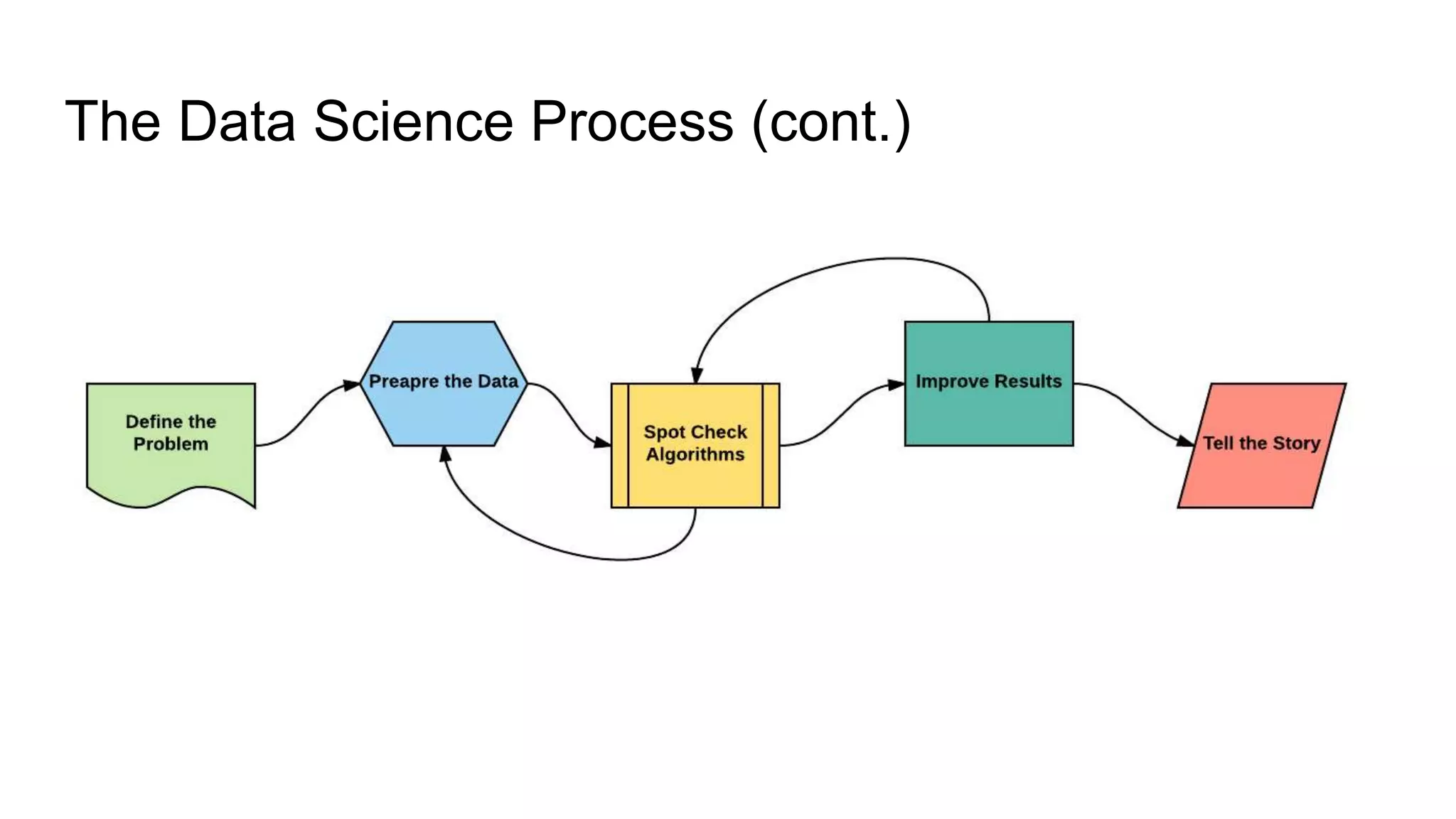
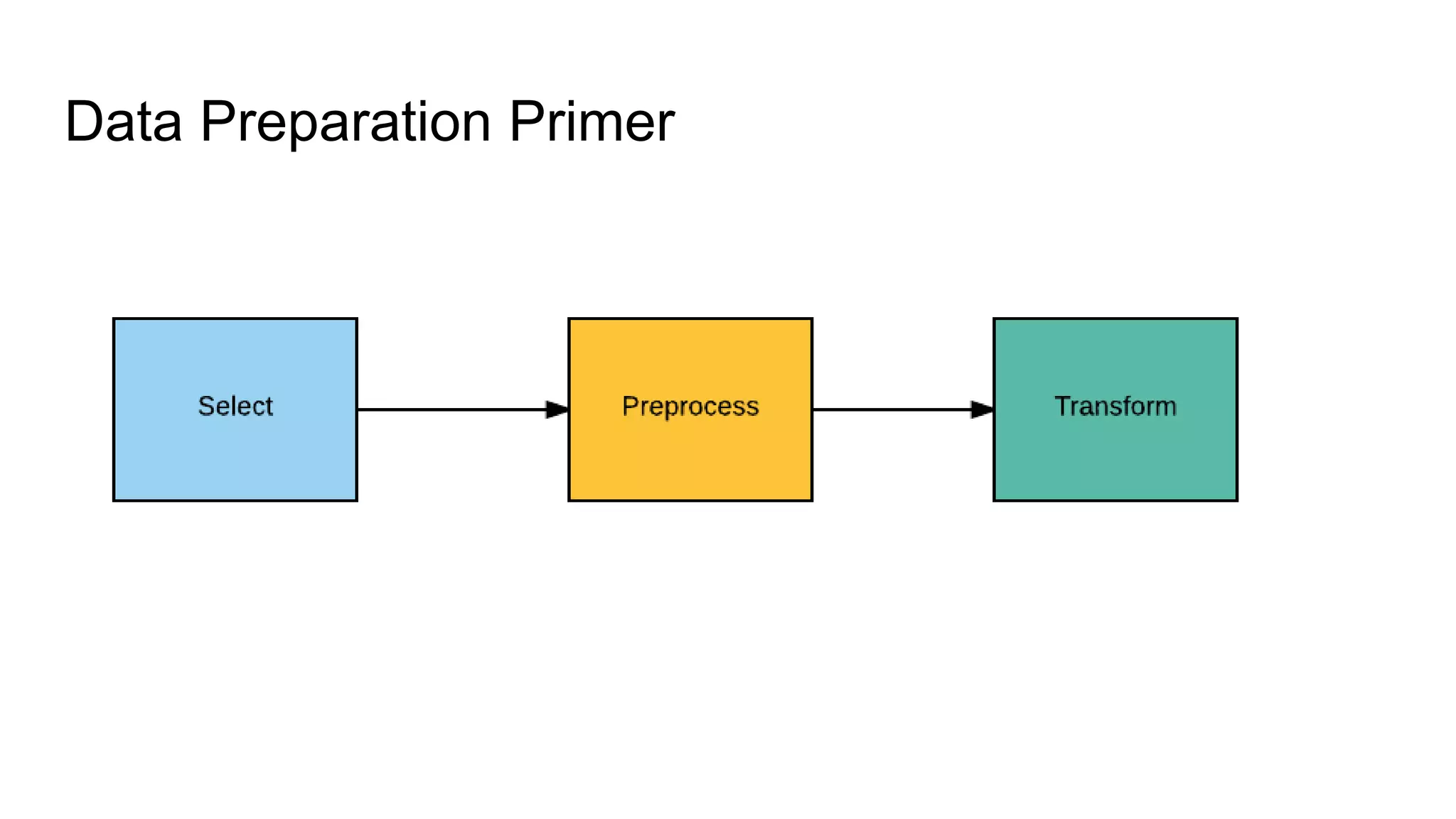
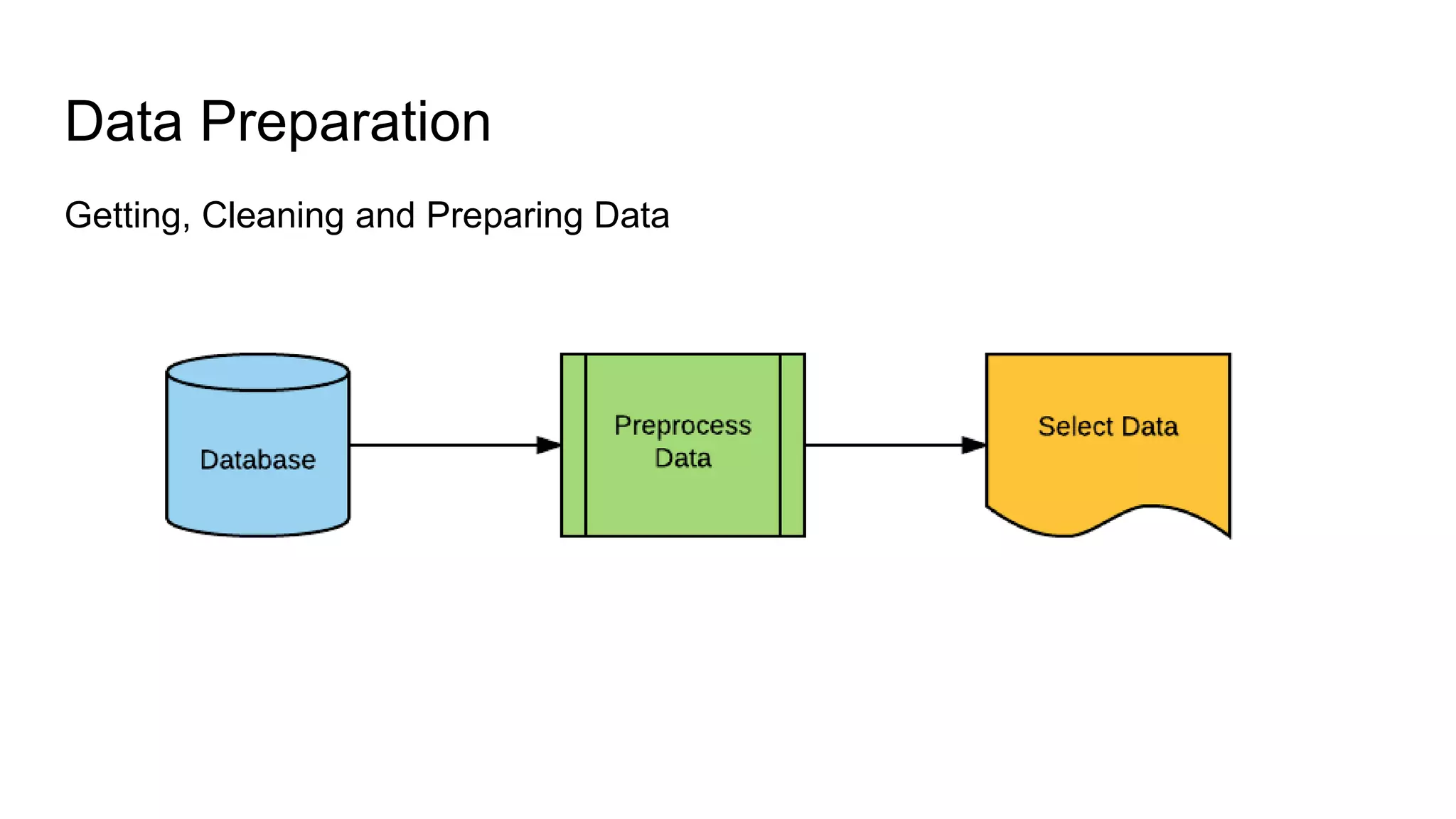
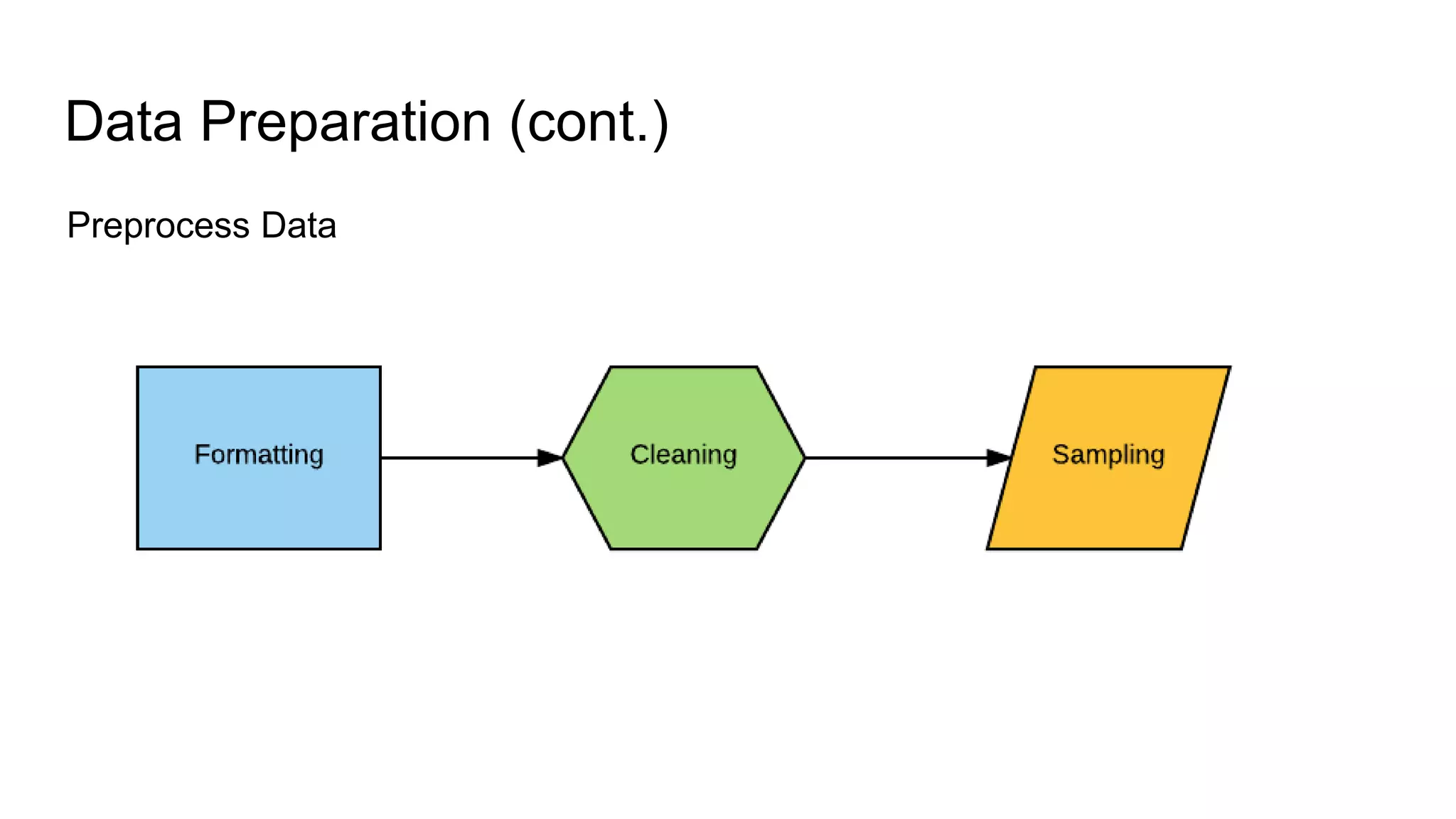
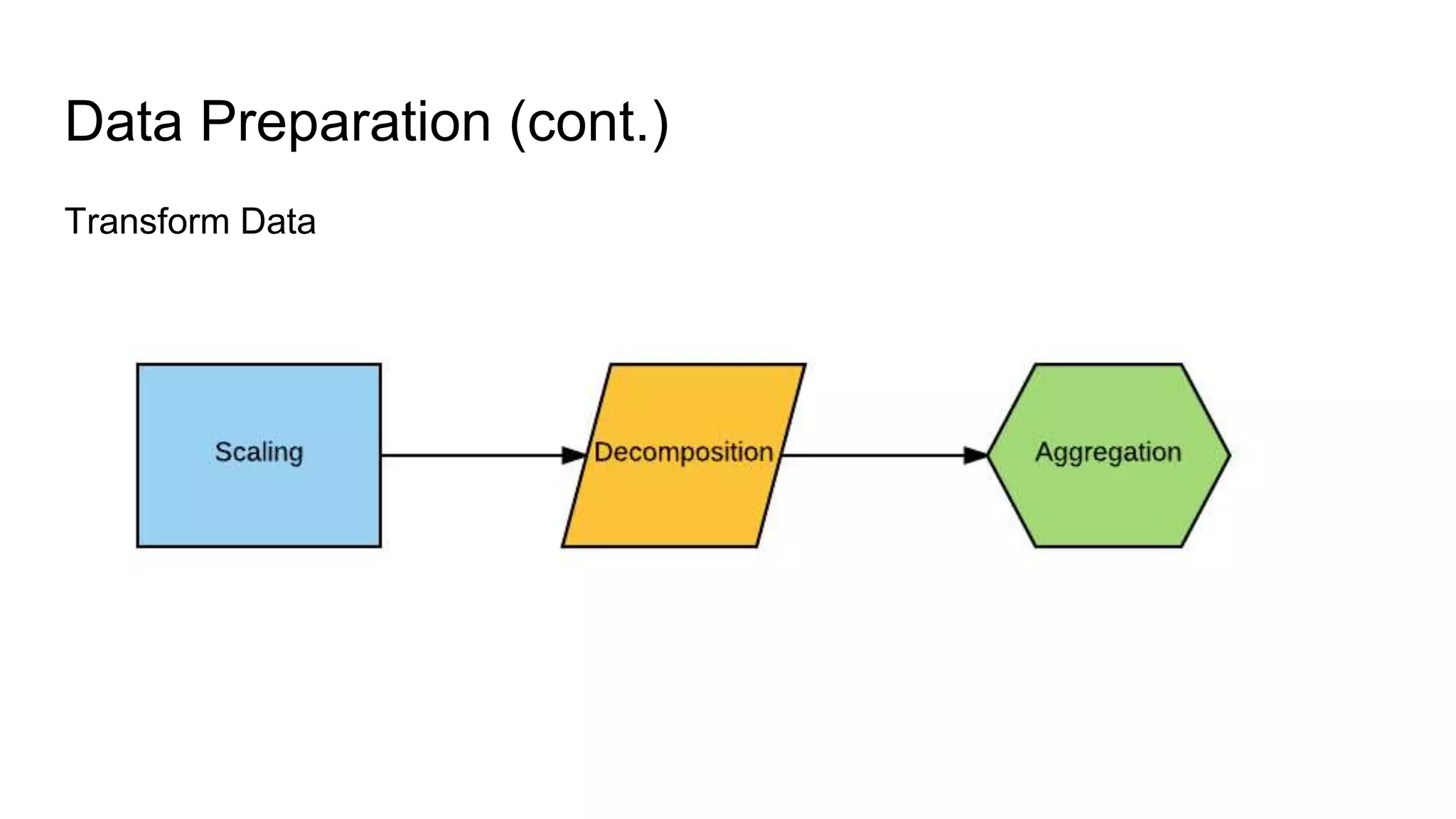
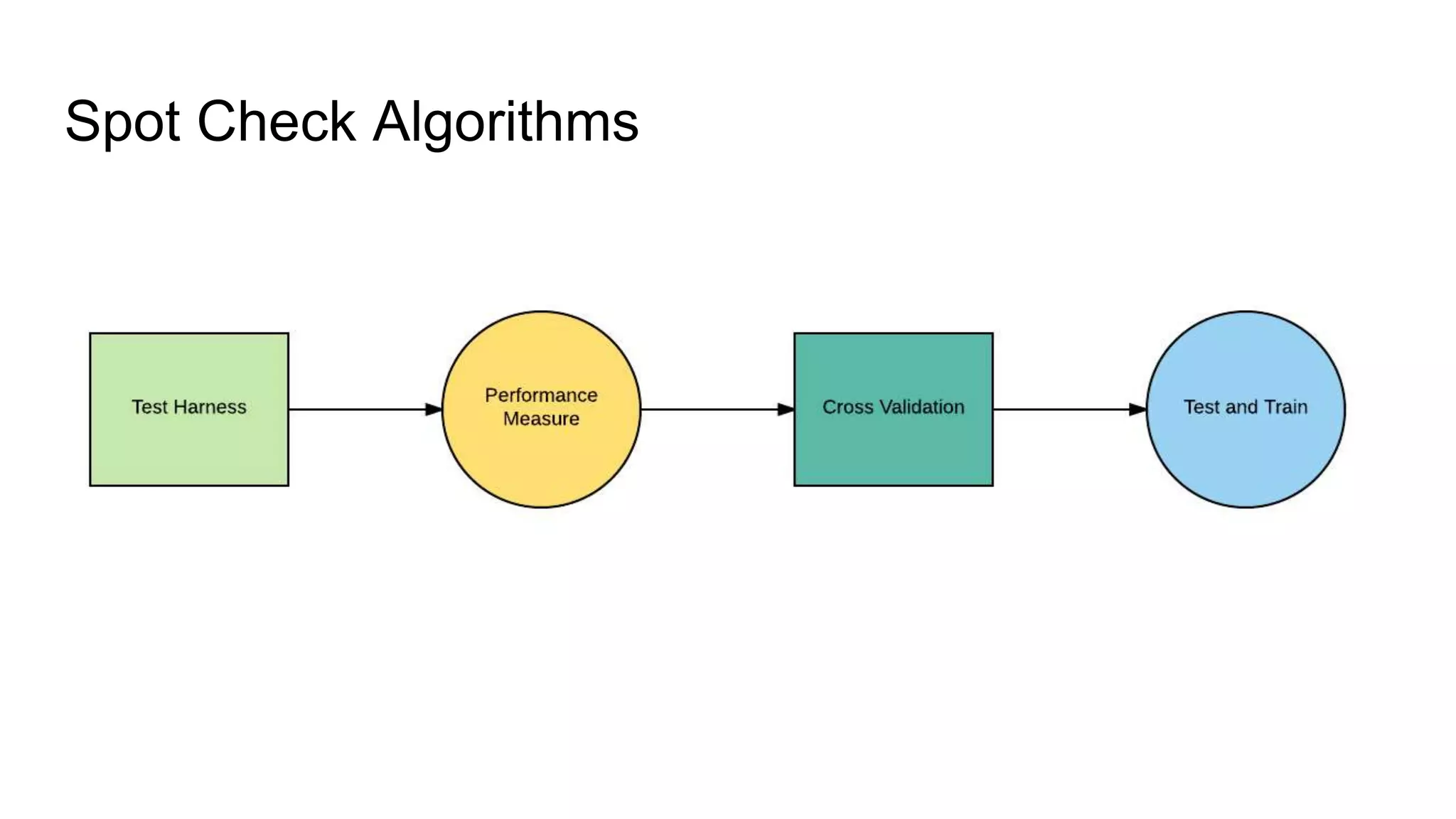
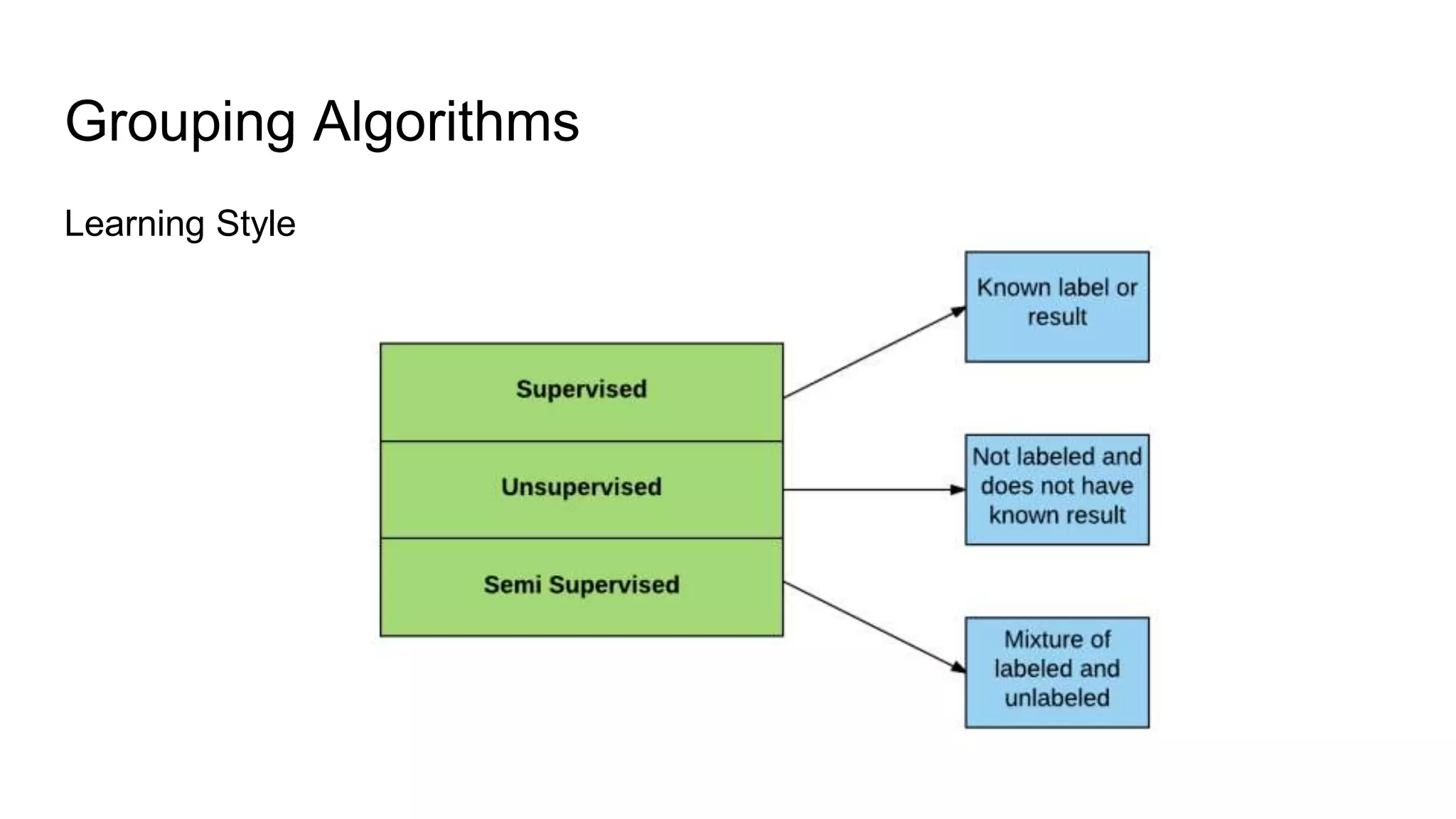
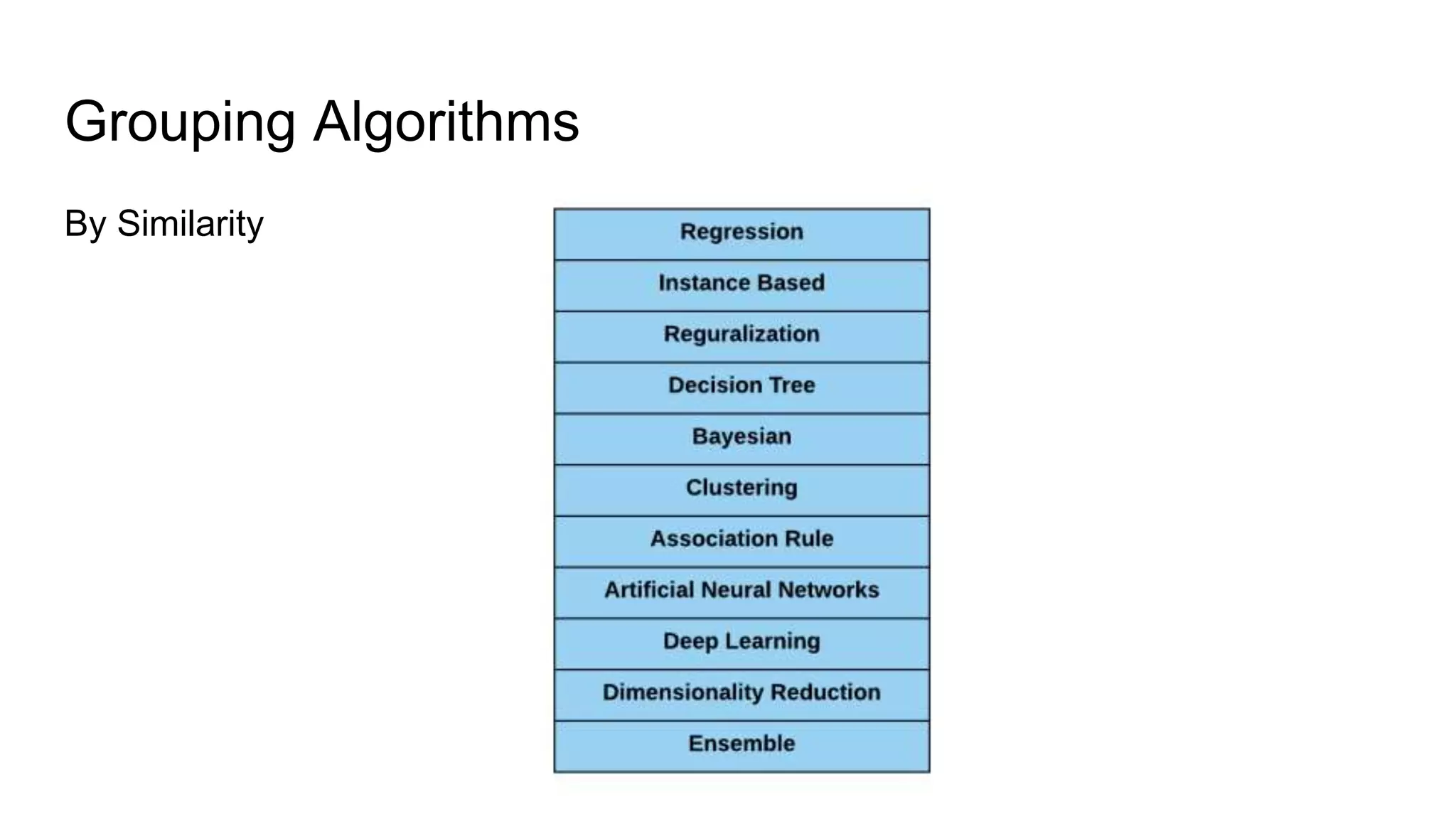
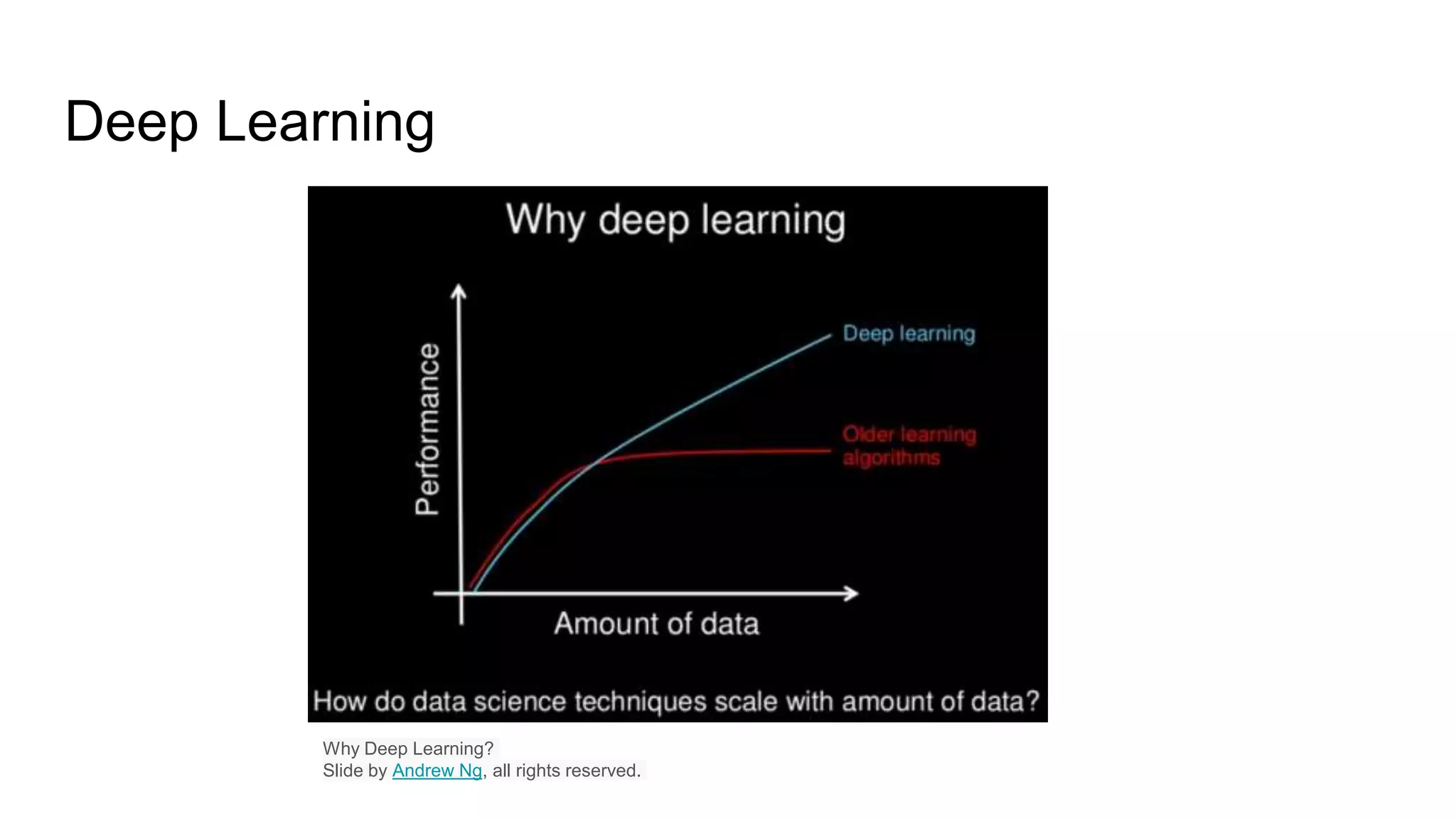
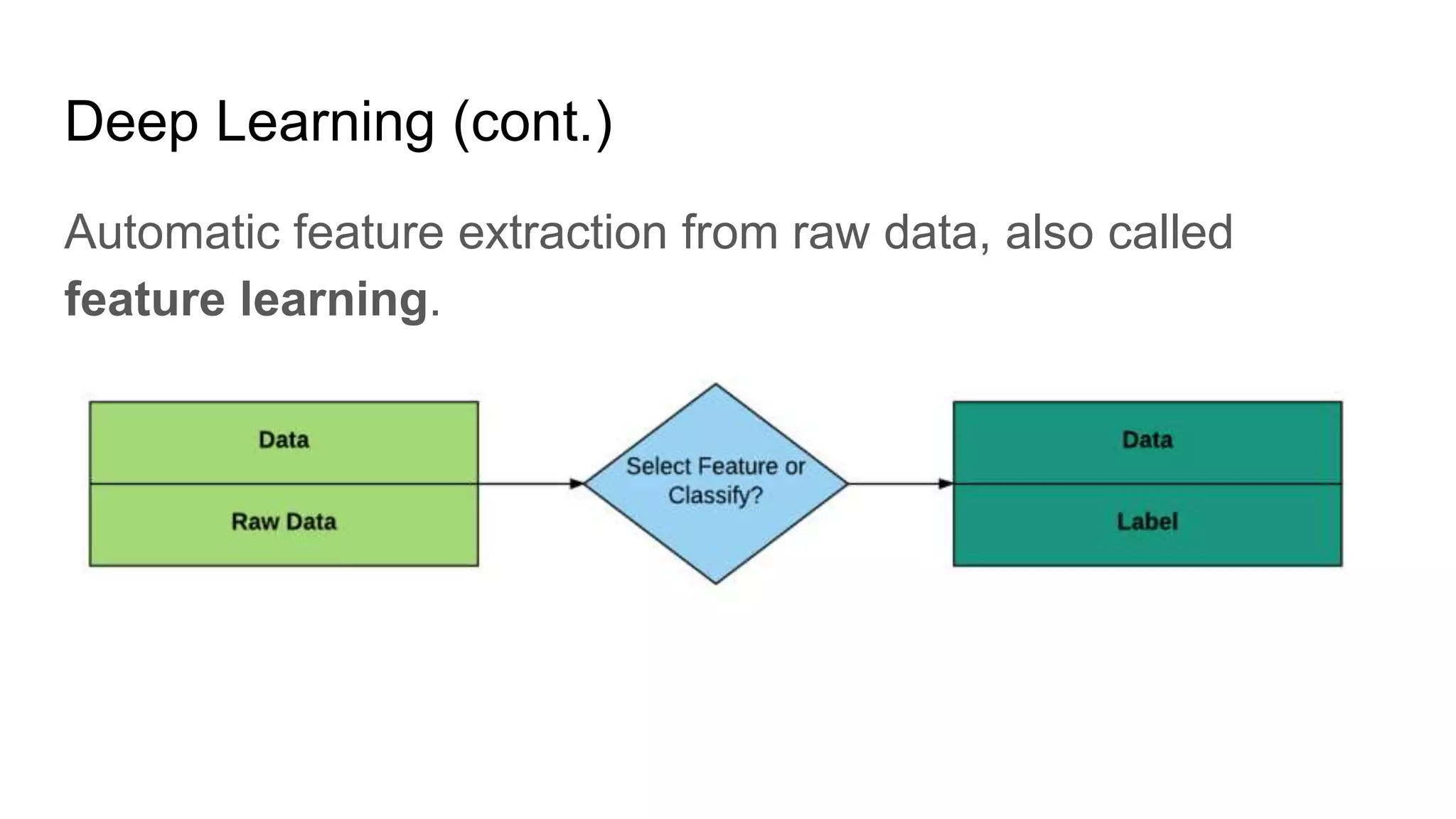
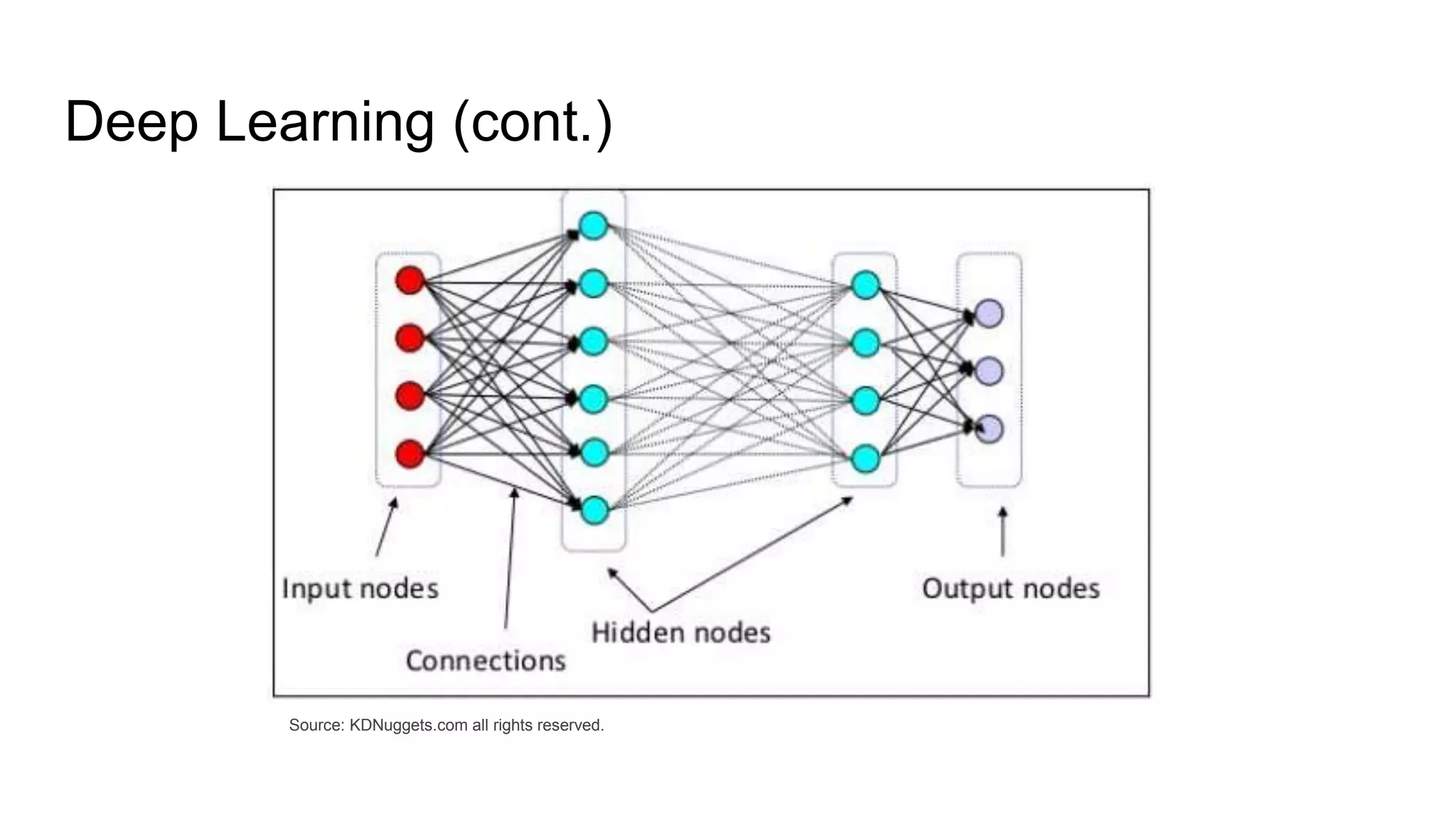
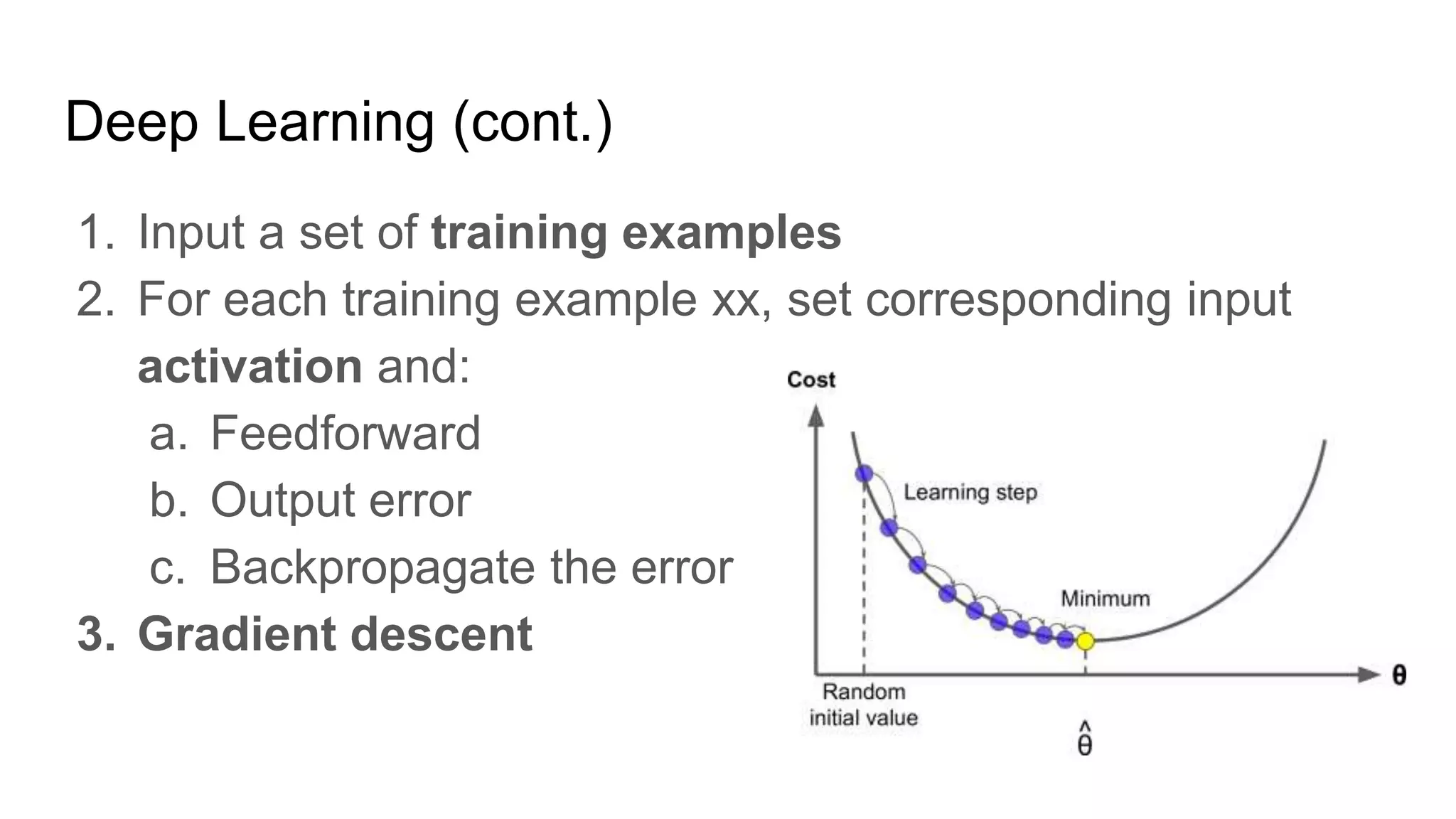
The document presents a guide distinguishing between machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), and artificial intelligence (AI) while covering goals, use cases, and the data science process. It emphasizes that ML and DL are related with DL primarily used for supervised learning and focuses on the importance of data preparation and optimization techniques. Additionally, it highlights the necessity of automating the ML/DL pipeline and provides resources for further engagement.