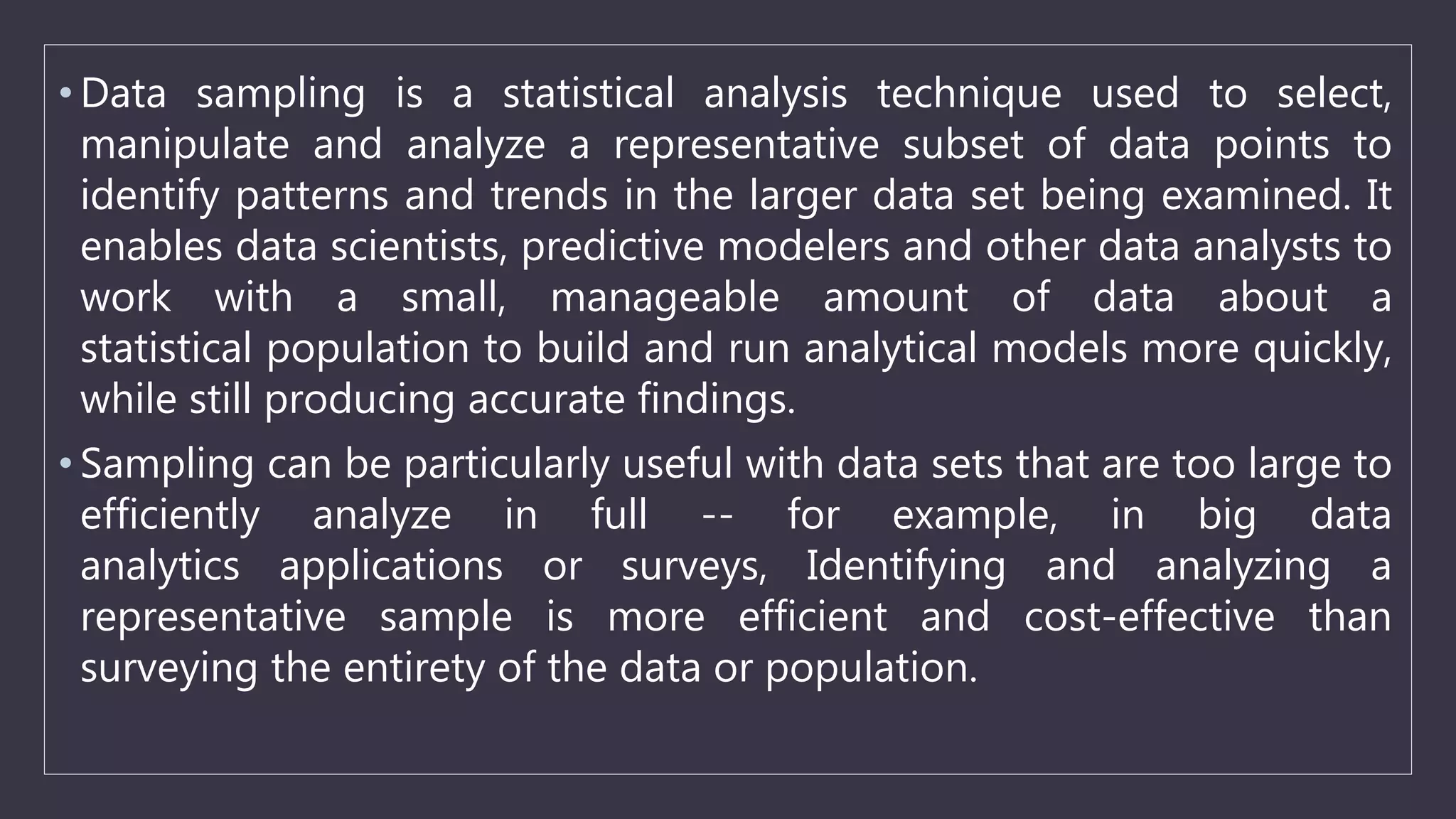
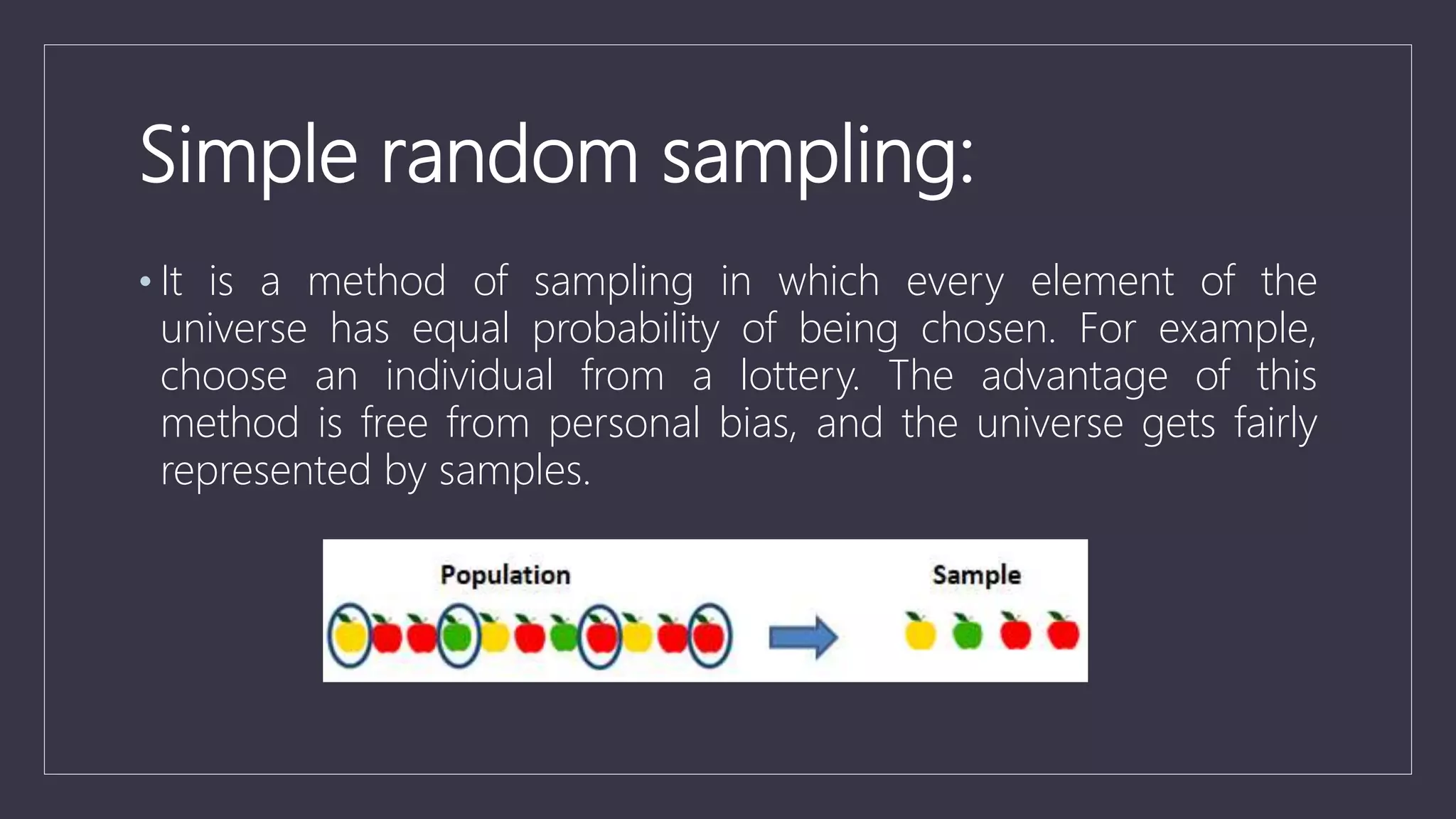
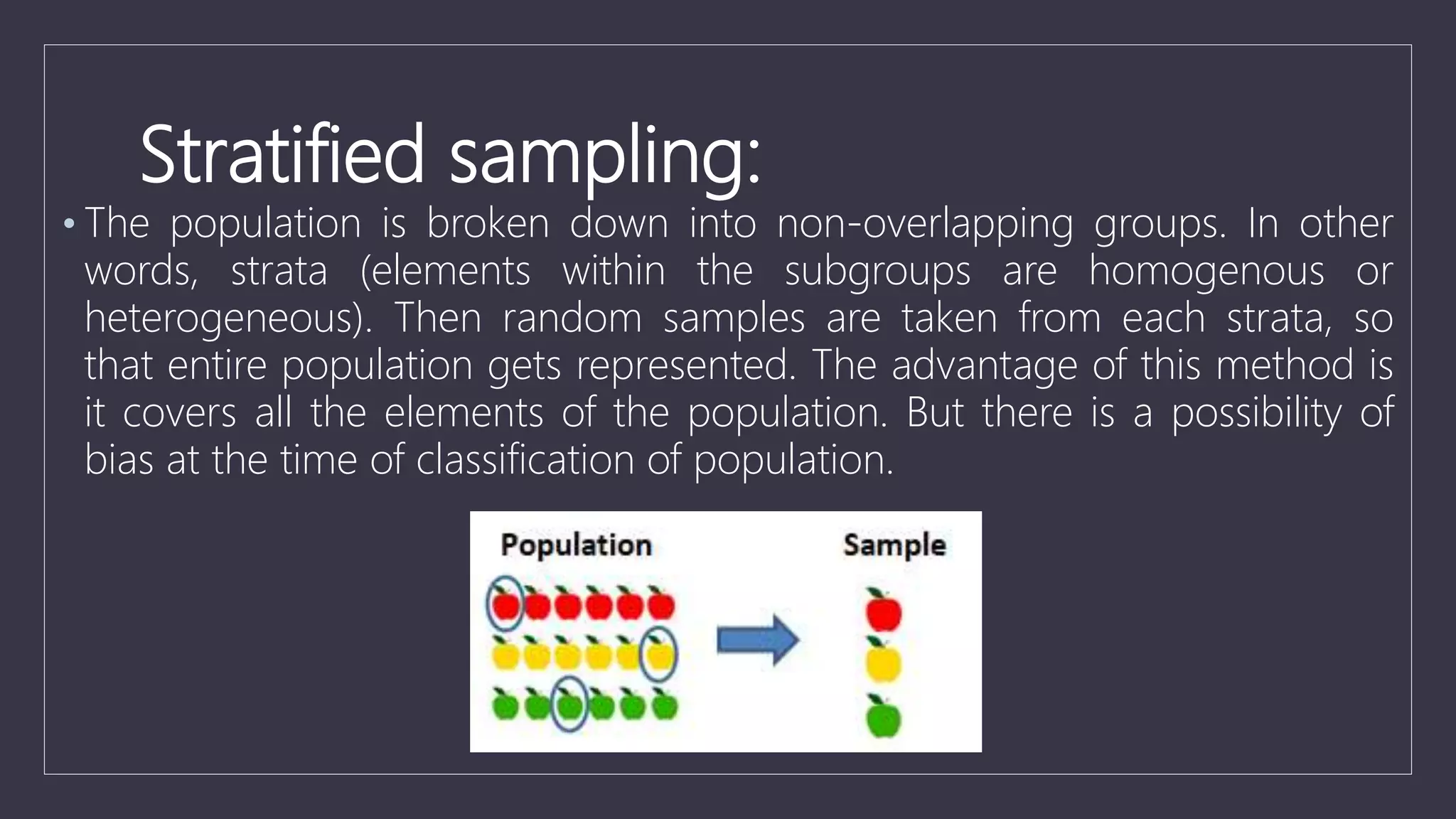
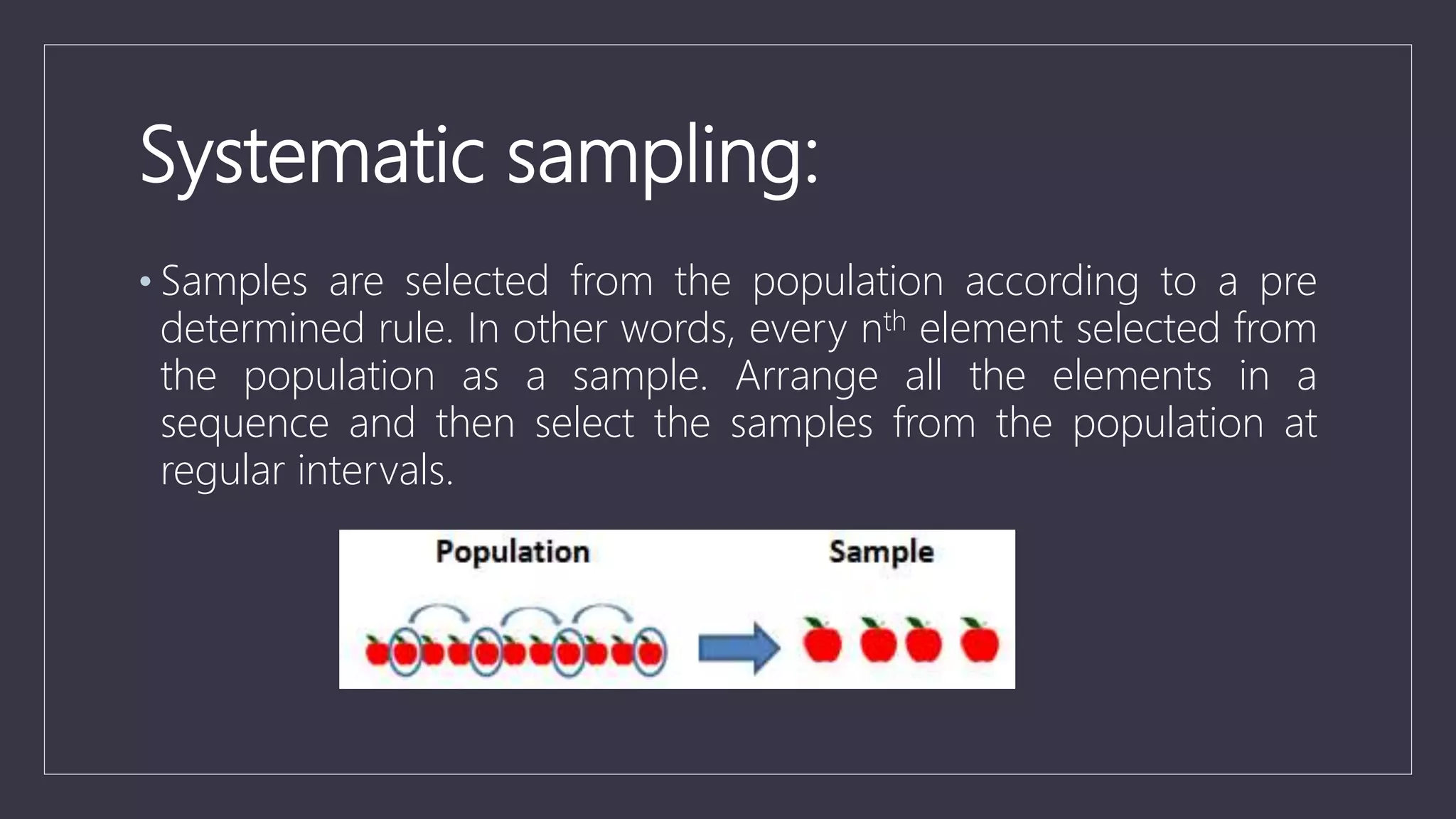
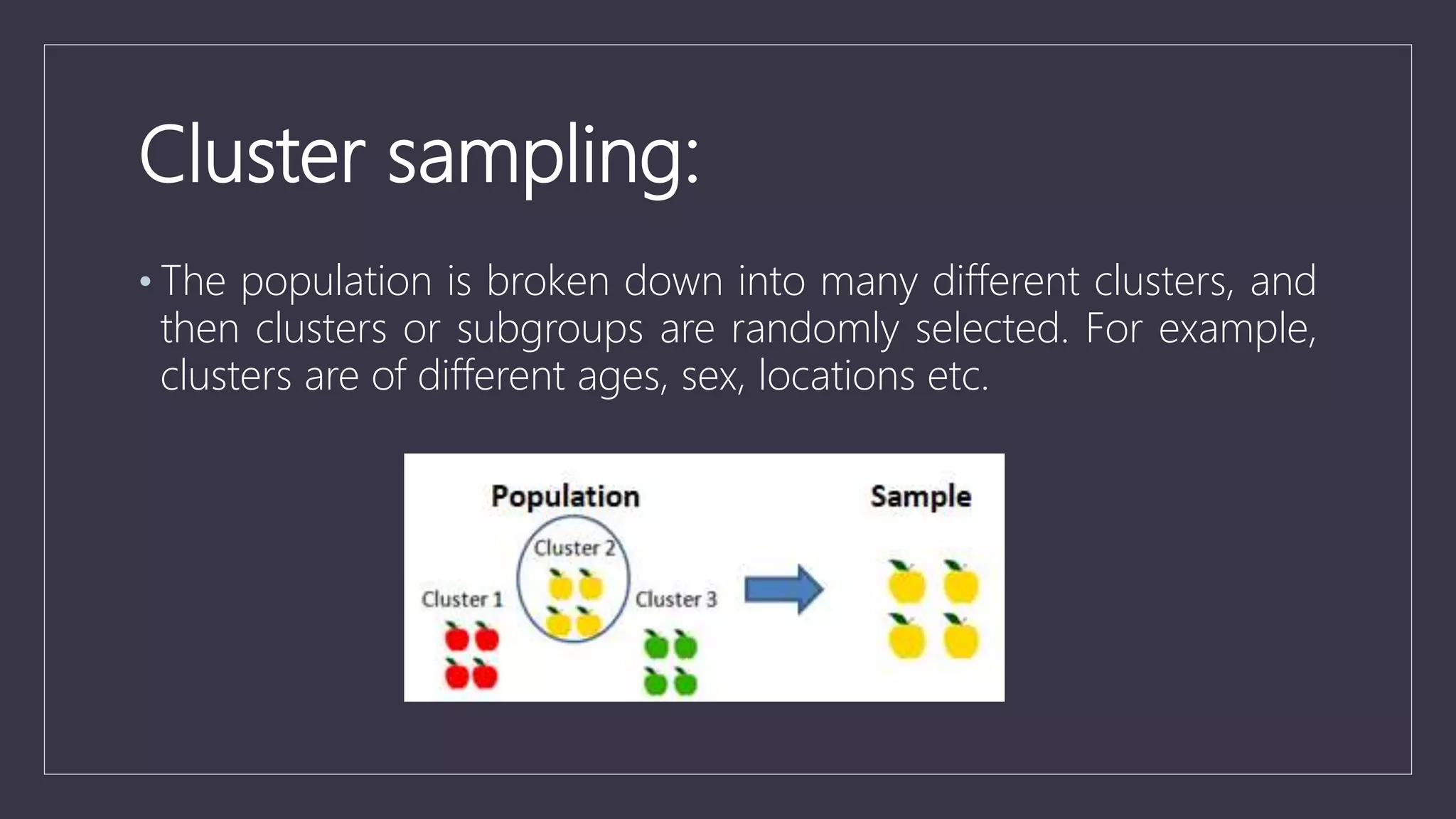
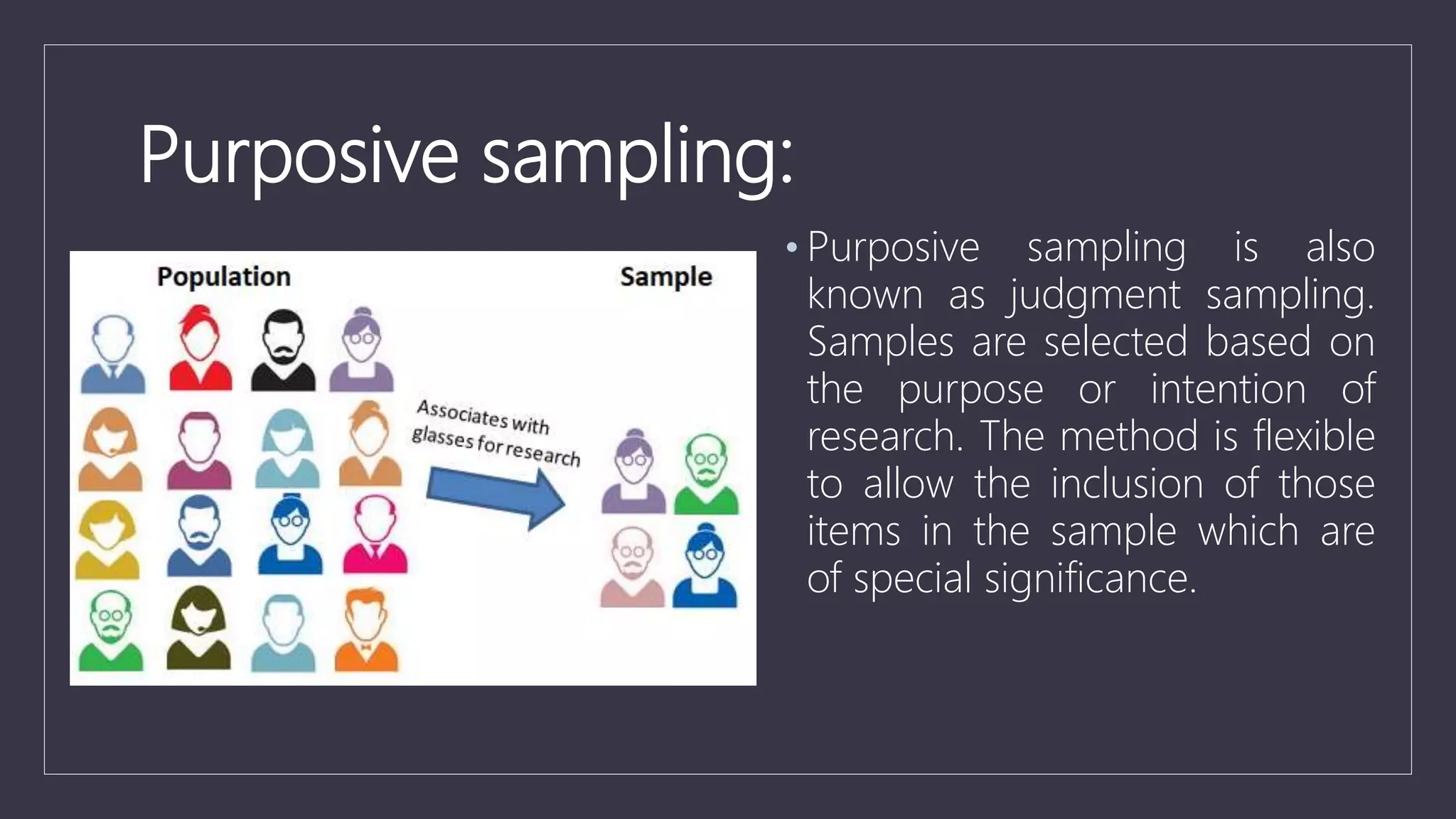
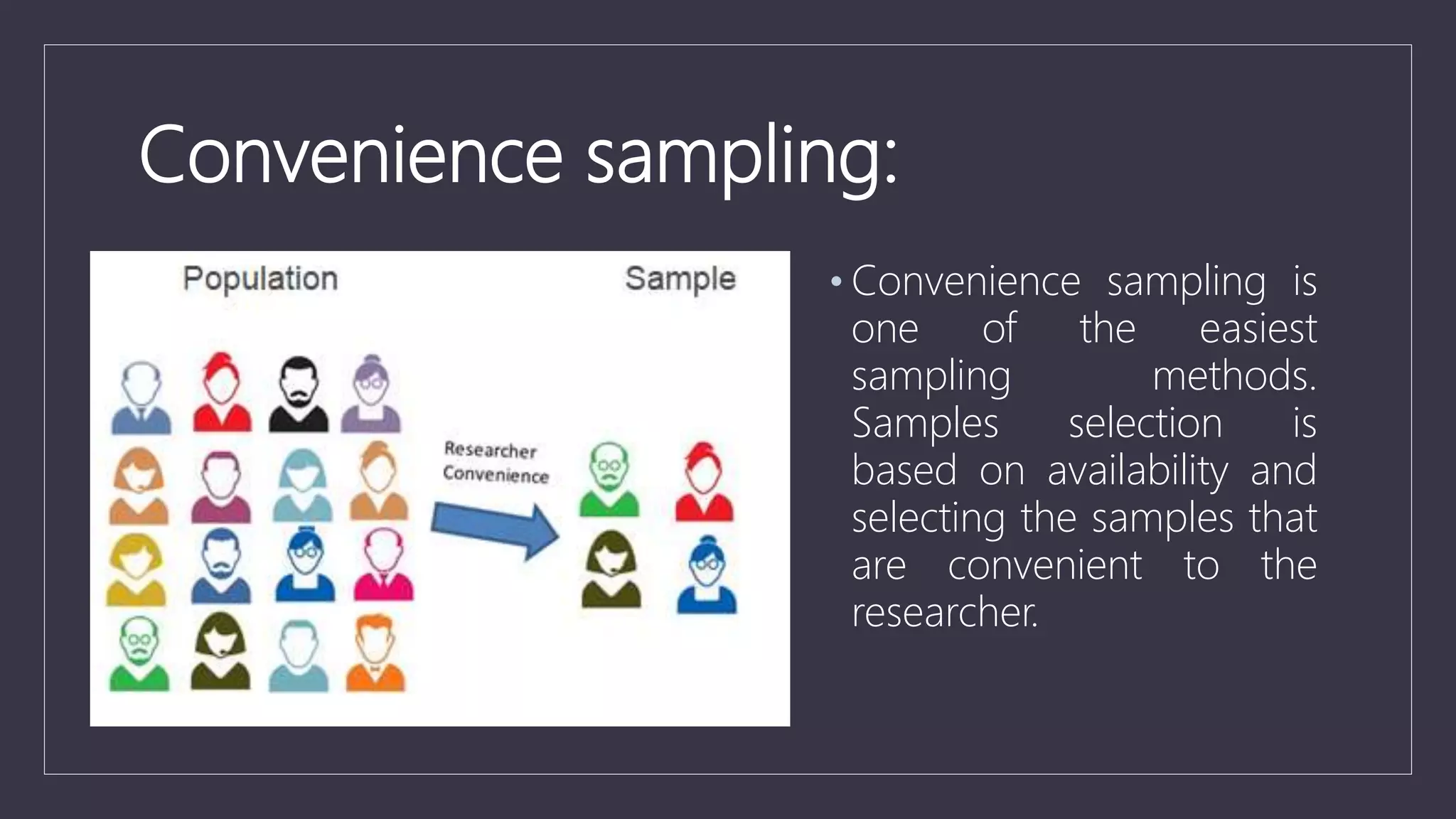
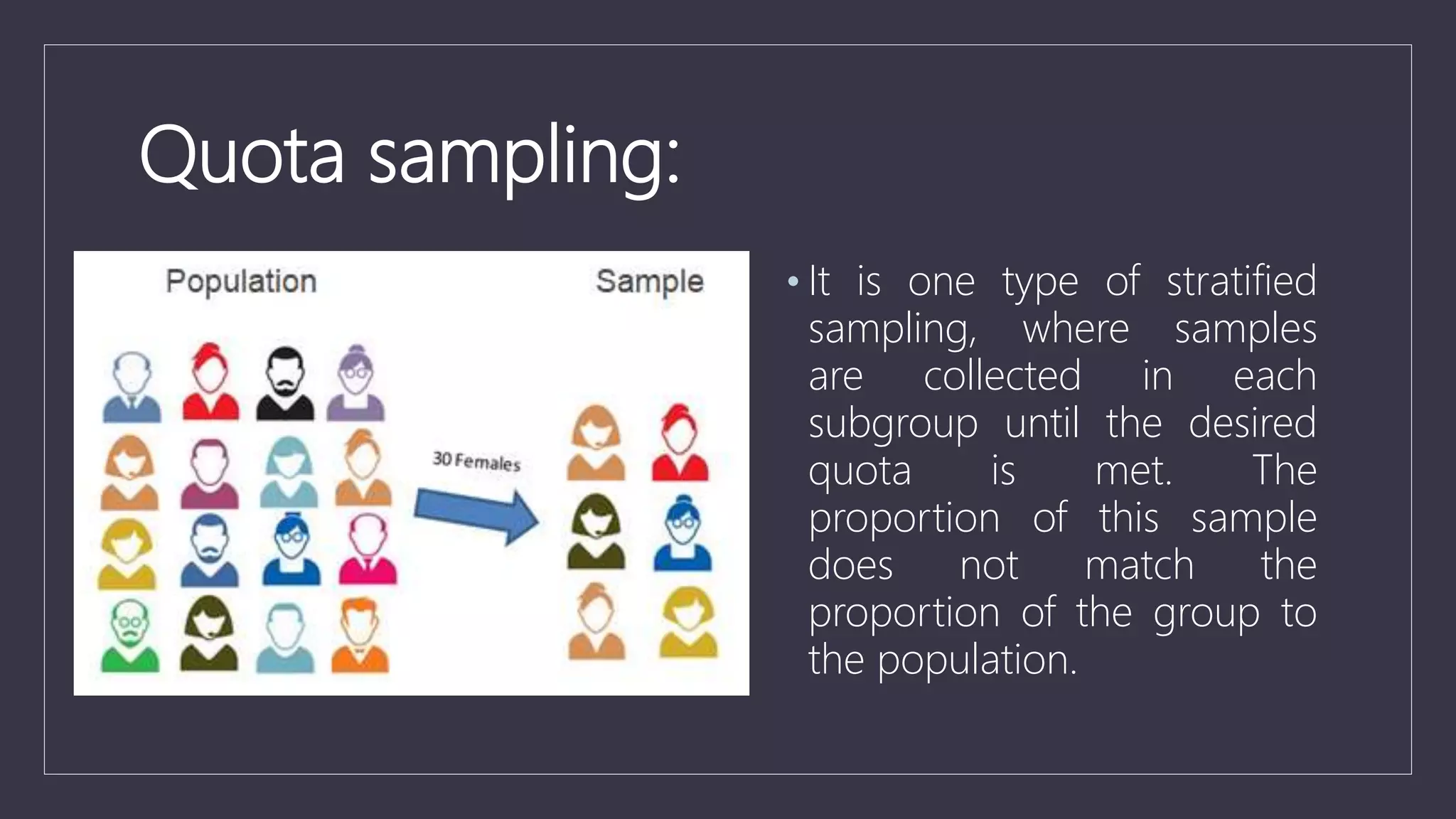
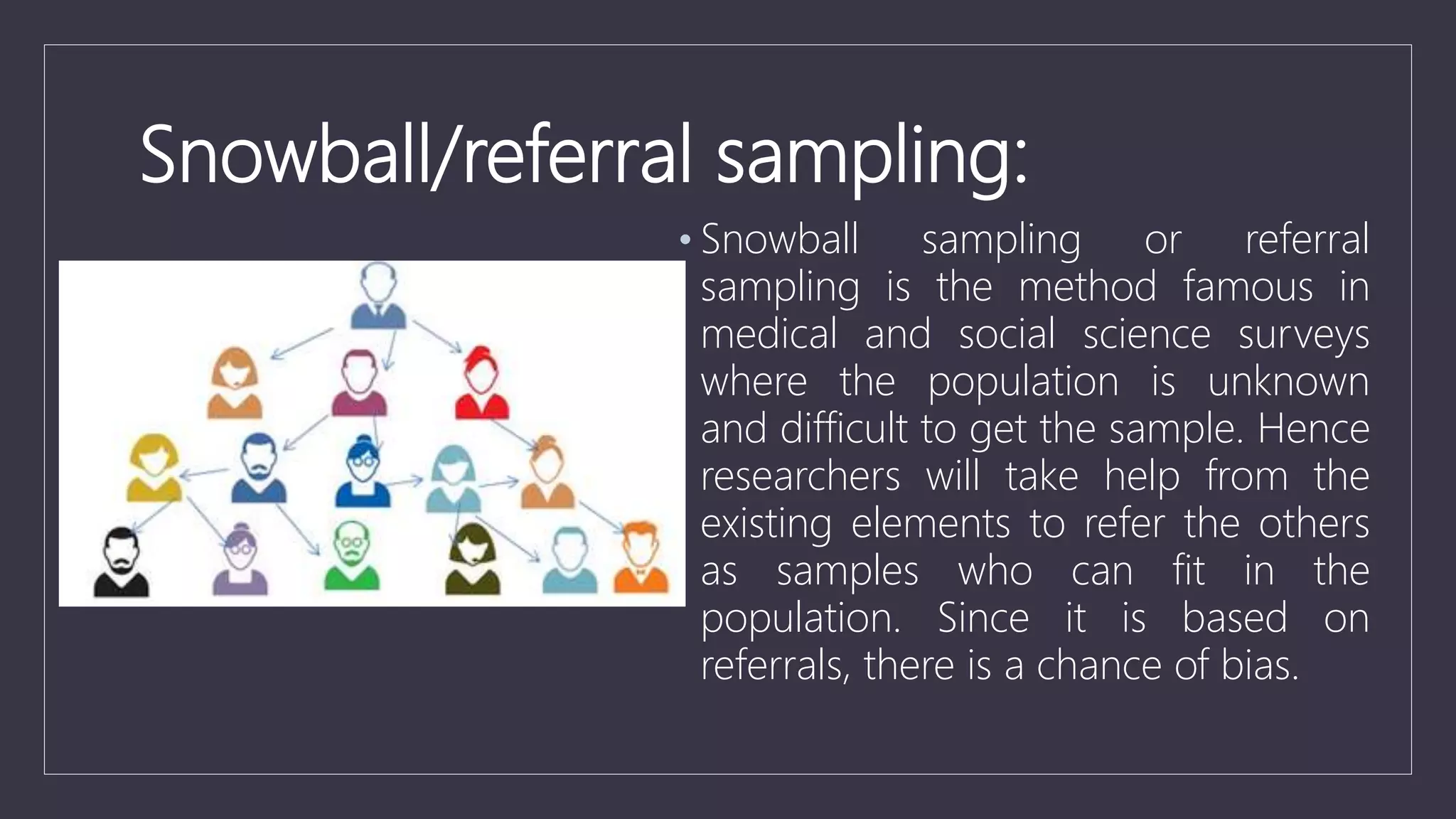
Data sampling is a statistical technique used to select a representative subset of data to identify patterns in a larger dataset. It allows analysts to work with a small, manageable sample while still producing accurate results. Probability sampling methods like simple random sampling aim to give every element an equal chance of selection to avoid bias, while non-probability methods like convenience sampling select available elements. Sample size and method choice impact sampling error and representation of the full data.