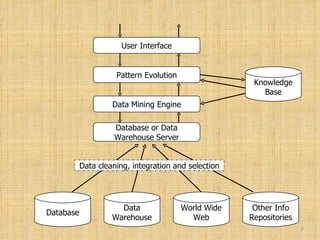
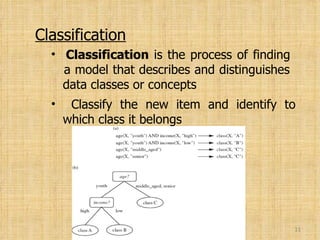
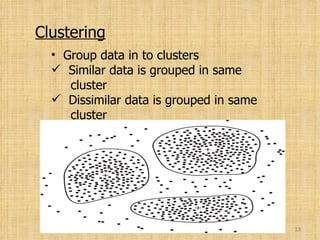
This document provides an overview of data mining. It introduces data mining and its goals, which include prediction, identification, classification, and optimization. The typical architecture of a data mining system is explained, including its major components. Common data mining techniques like classification, clustering, and association are also outlined. Examples are provided to illustrate techniques. The document concludes by discussing advantages and uses of data mining along with some popular data mining tools.










![A 1% support means that 1% of all of the transactions under analysis showed that computer and software were purchased together. Association rules “ An association algorithm creates rules that describe how often events have occurred together.” Example: buys(X, “computer”)=> buys(X, “software”) [support=1%, confidence=50%] Where X is a variable representing a customer. A confidence, or certainty, of 50% means that if a customer buys a computer, there is a 50% chance that they will buy software as well.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datamining-111122073050-phpapp01/85/Data-mining-14-320.jpg)






