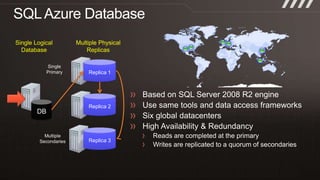
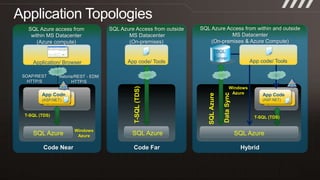
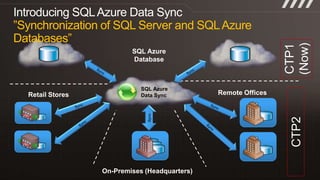
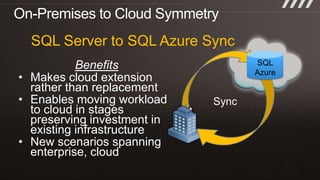
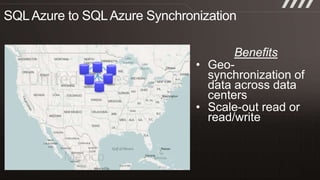
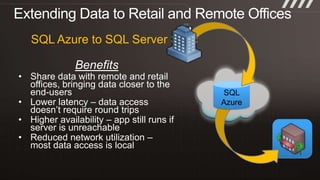
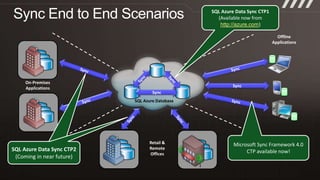
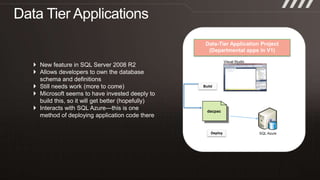
The document provides an overview of migrating SQL Server applications to SQL Azure Cloud Database, highlighting the benefits of cloud-based solutions with SQL Azure's relational database as a service. It discusses database migration processes, application topologies, and synchronization features, emphasizing developer agility and flexibility. Additional topics include data-tier applications, auto high-availability, and advantages of utilizing SQL Azure for enterprise synchronization and scalability.