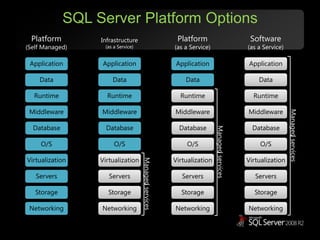
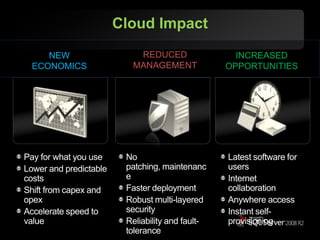
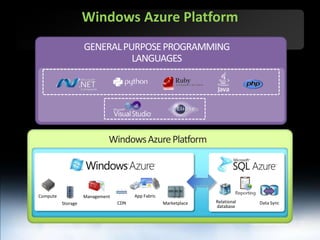
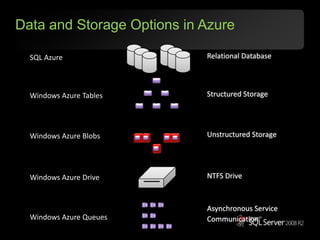
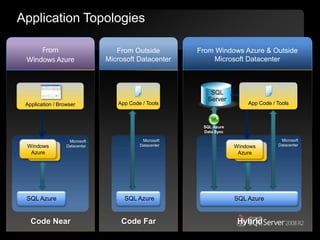
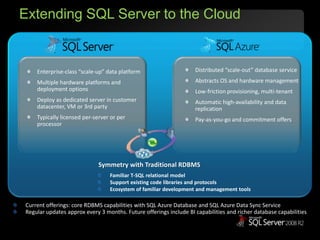
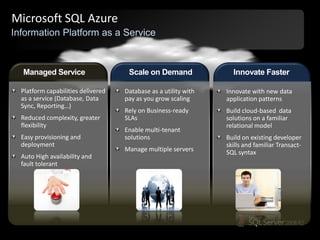
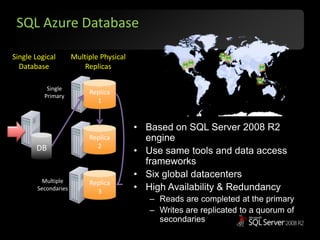
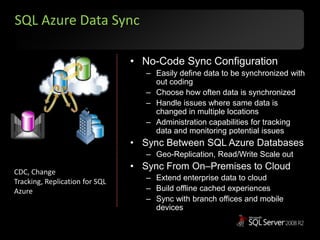
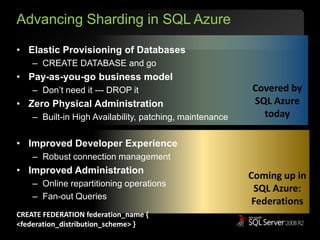
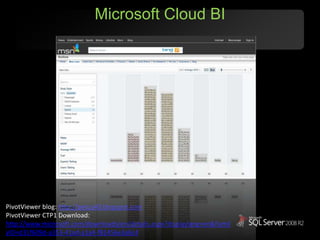
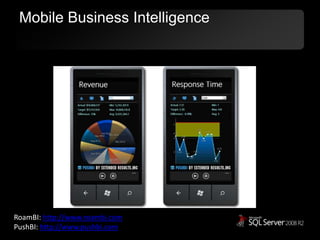
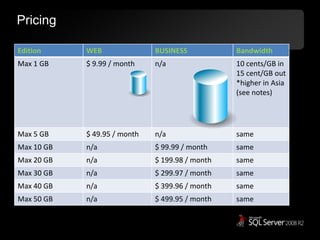
The document outlines Microsoft SQL Azure as part of the Azure cloud platform, highlighting its capabilities for database management, business intelligence, and cloud solutions. It emphasizes the benefits of cloud computing, such as reduced costs, flexibility, and improved scalability, as well as future offerings and developments in SQL Azure. The document also provides resources for further information and potential use cases in enterprise applications and BI solutions.