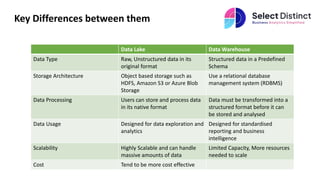
Data lakes and data warehouses are distinct data storage solutions with different structures and use cases. Data lakes handle unstructured data and offer scalability, while data warehouses are designed for structured data, optimized for reporting and analytics. Choosing between them depends on the data type and organizational needs.