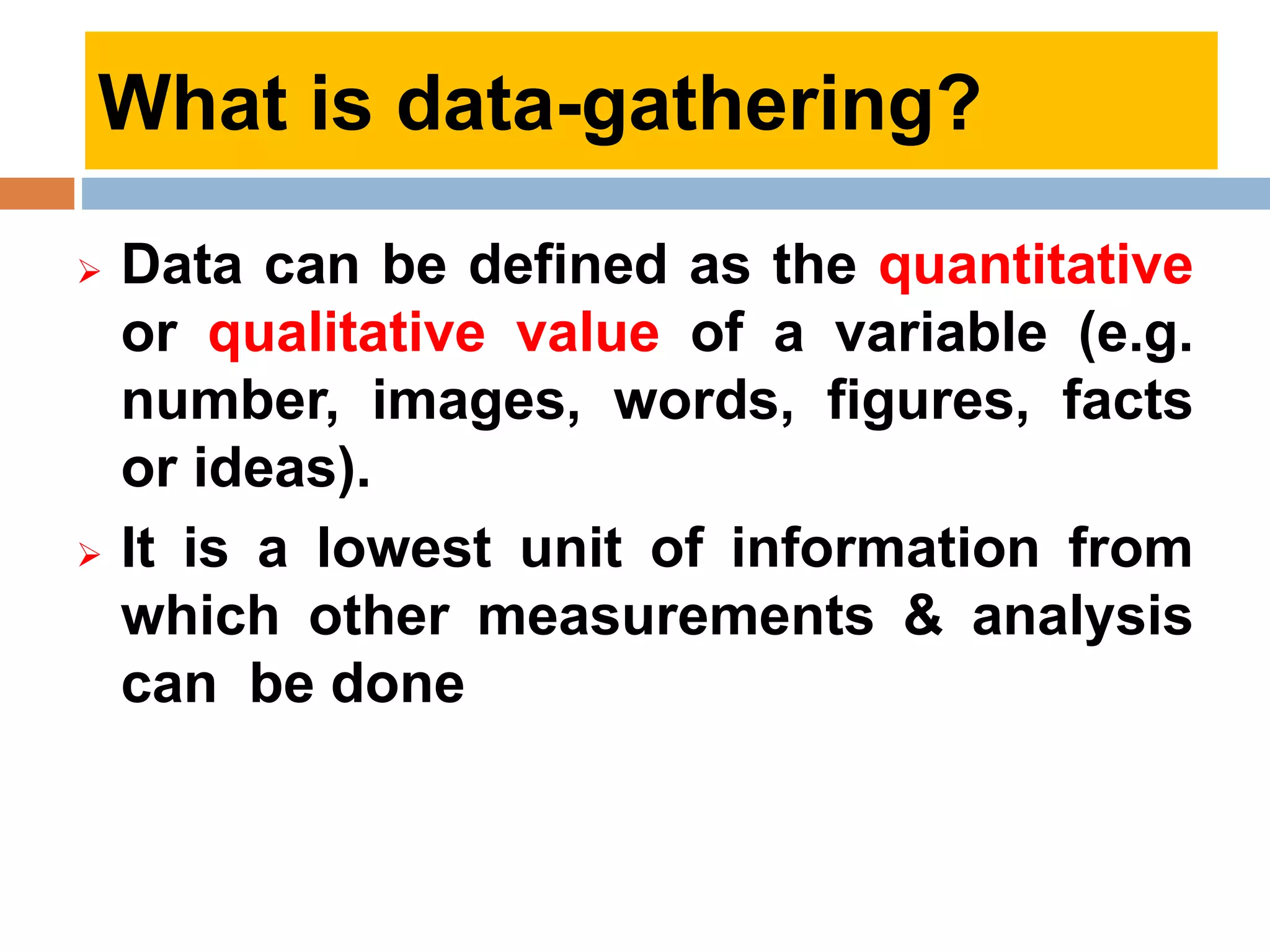
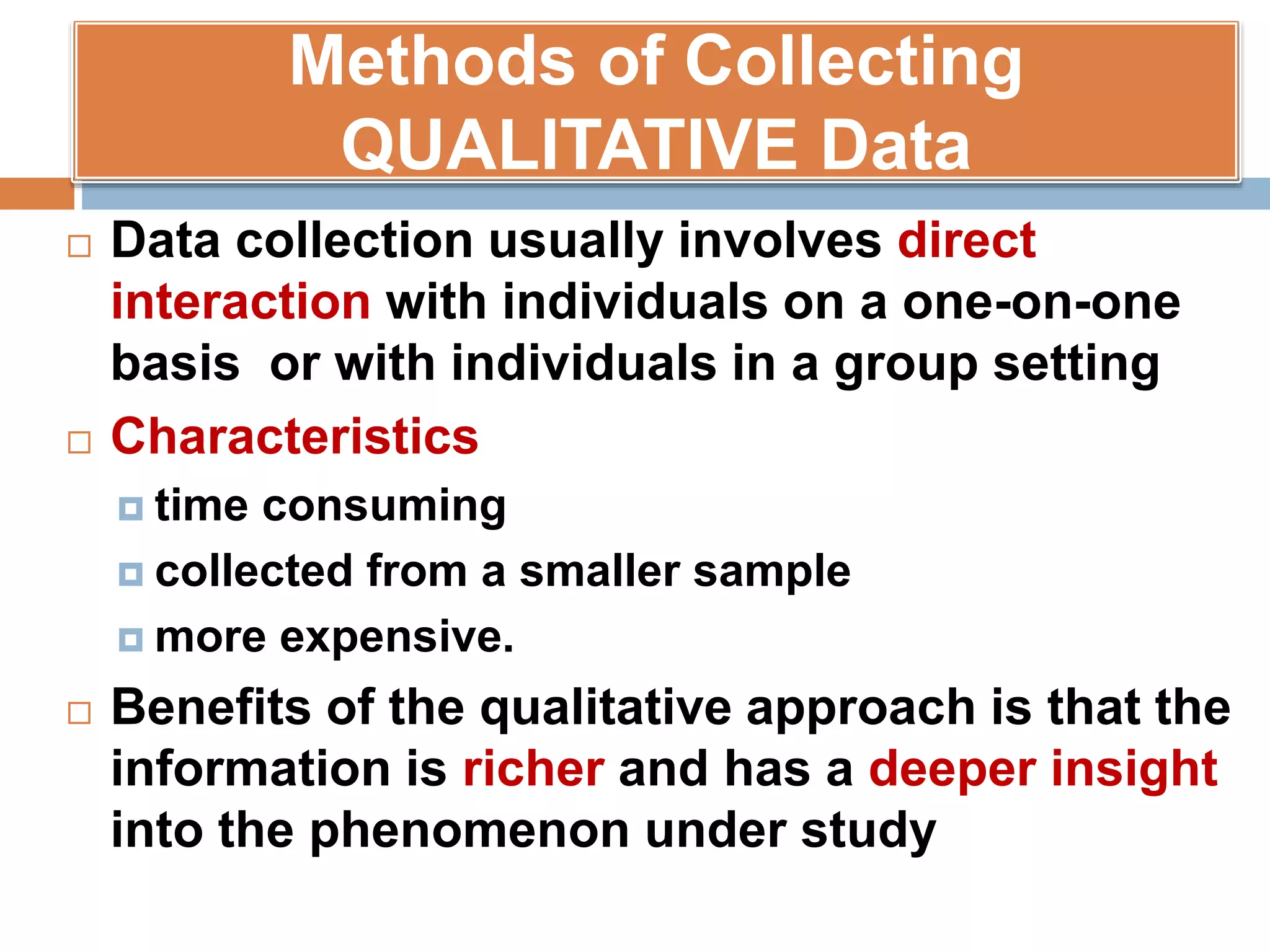
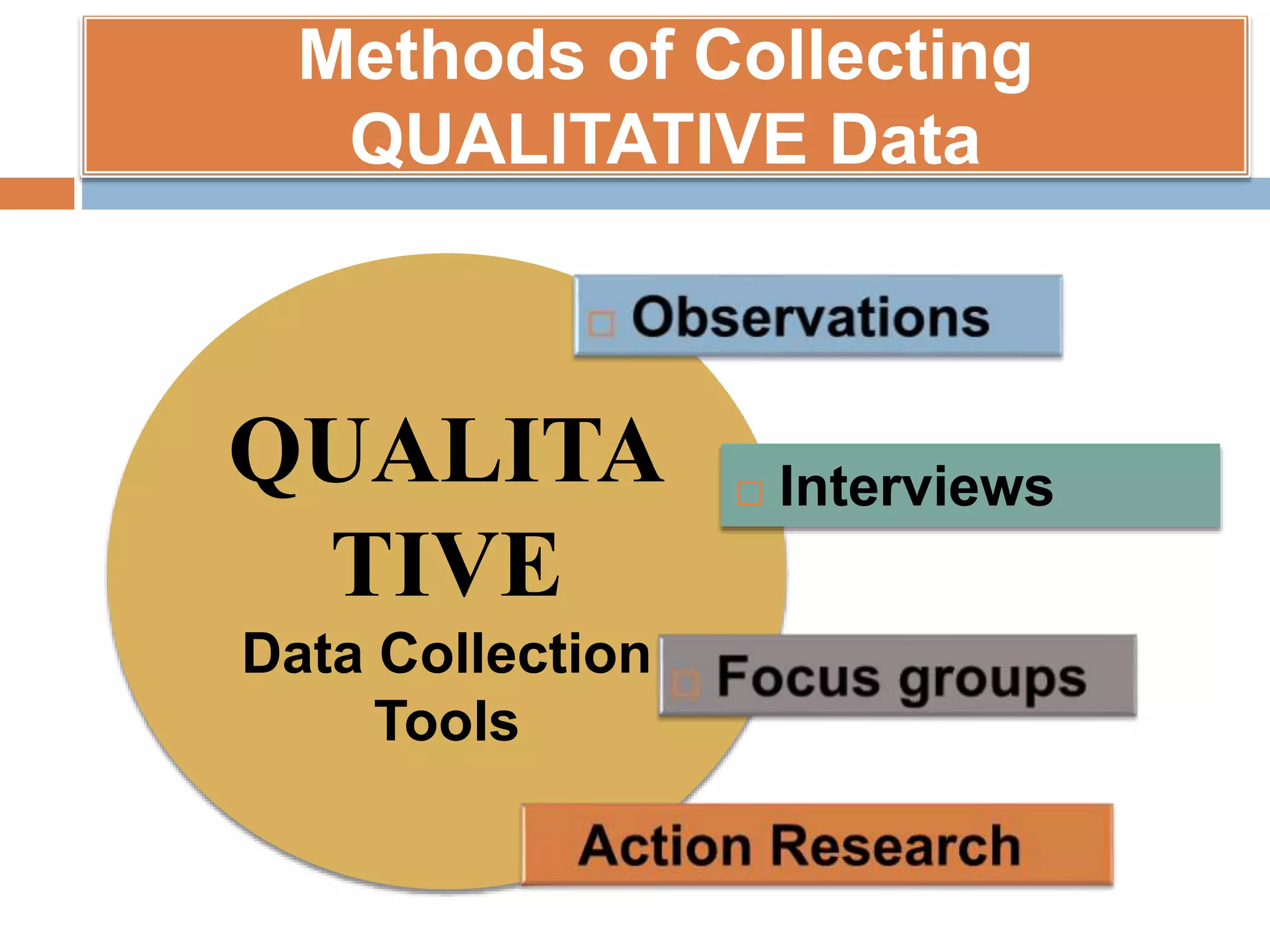
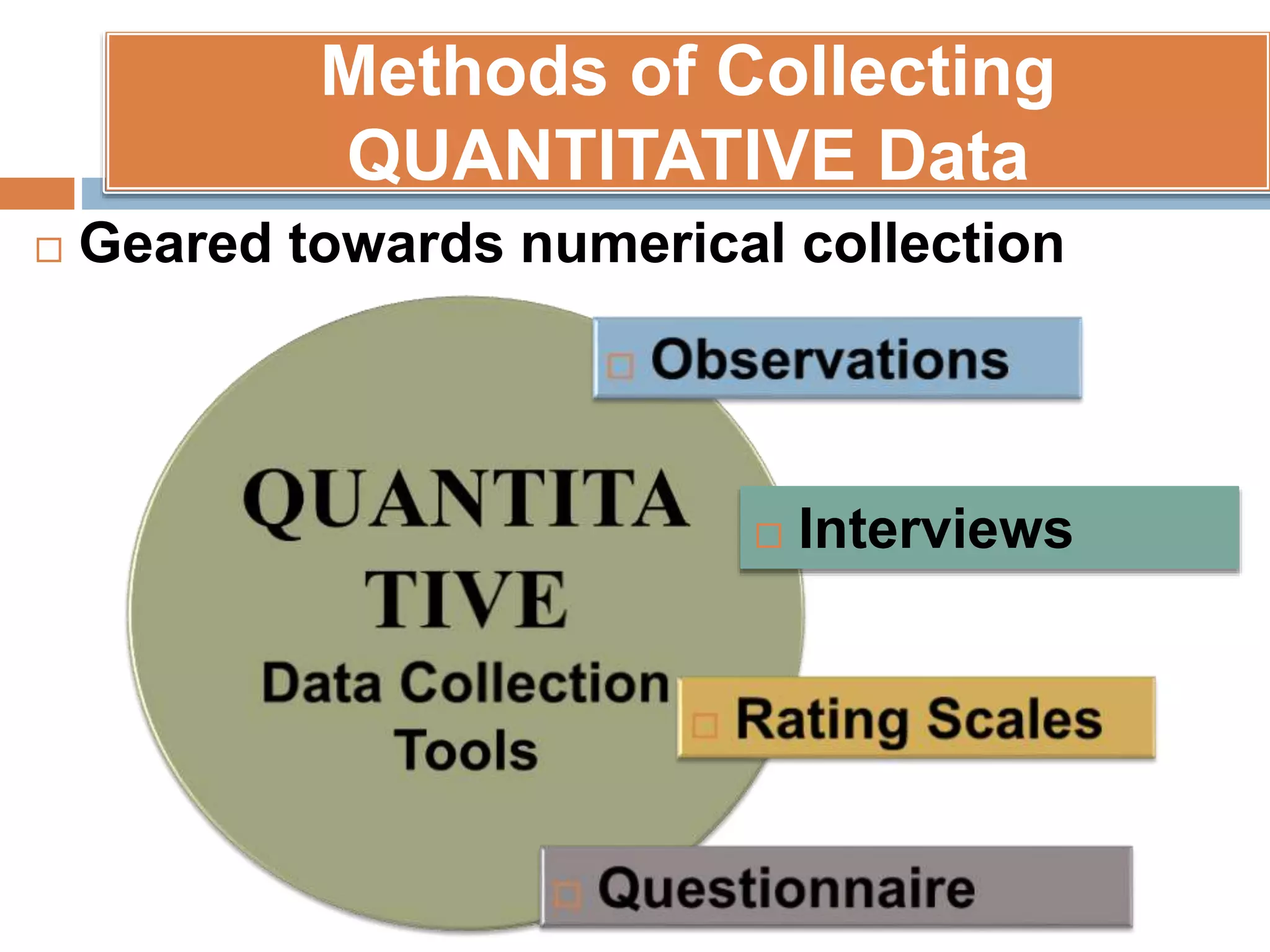
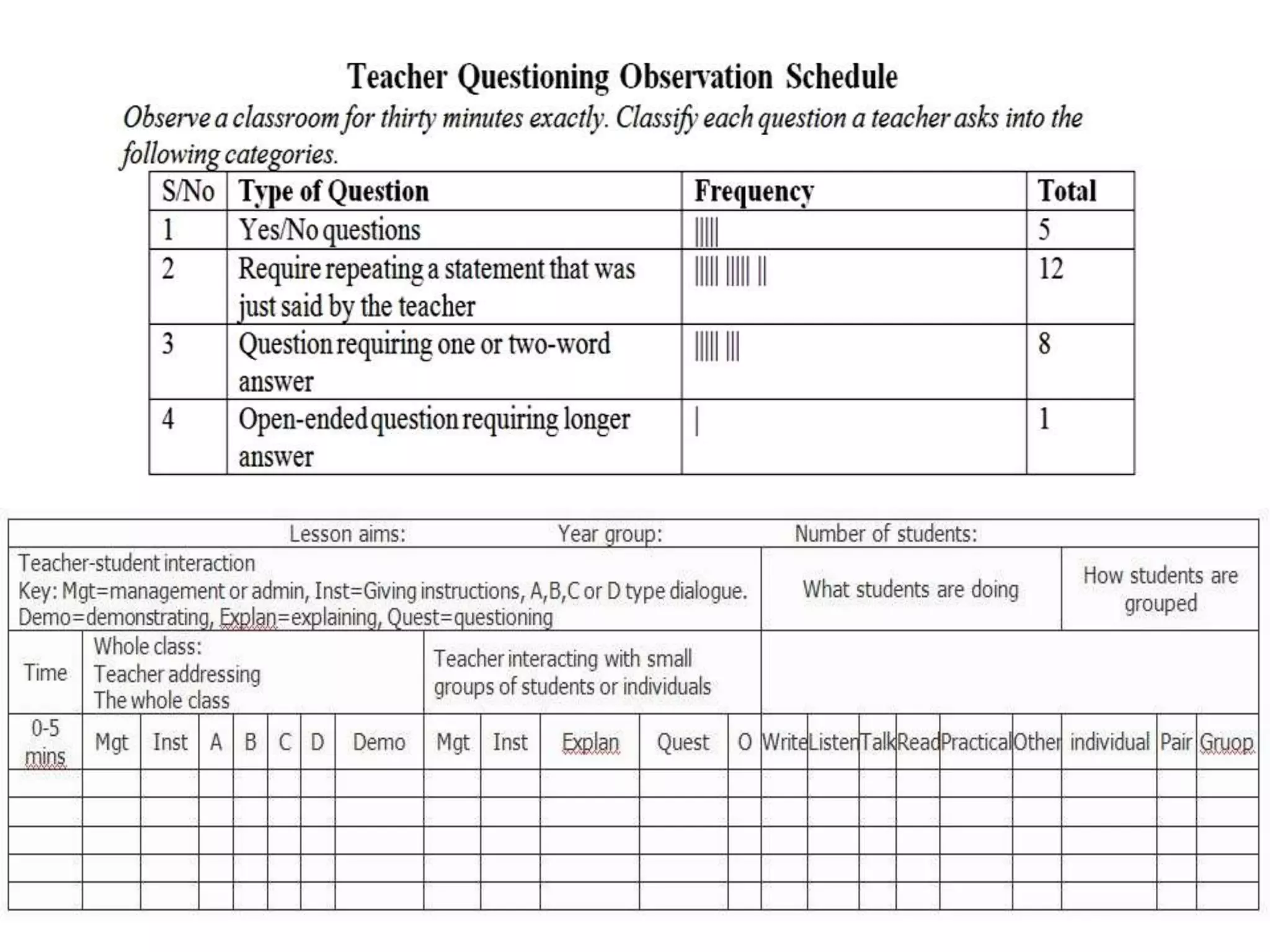
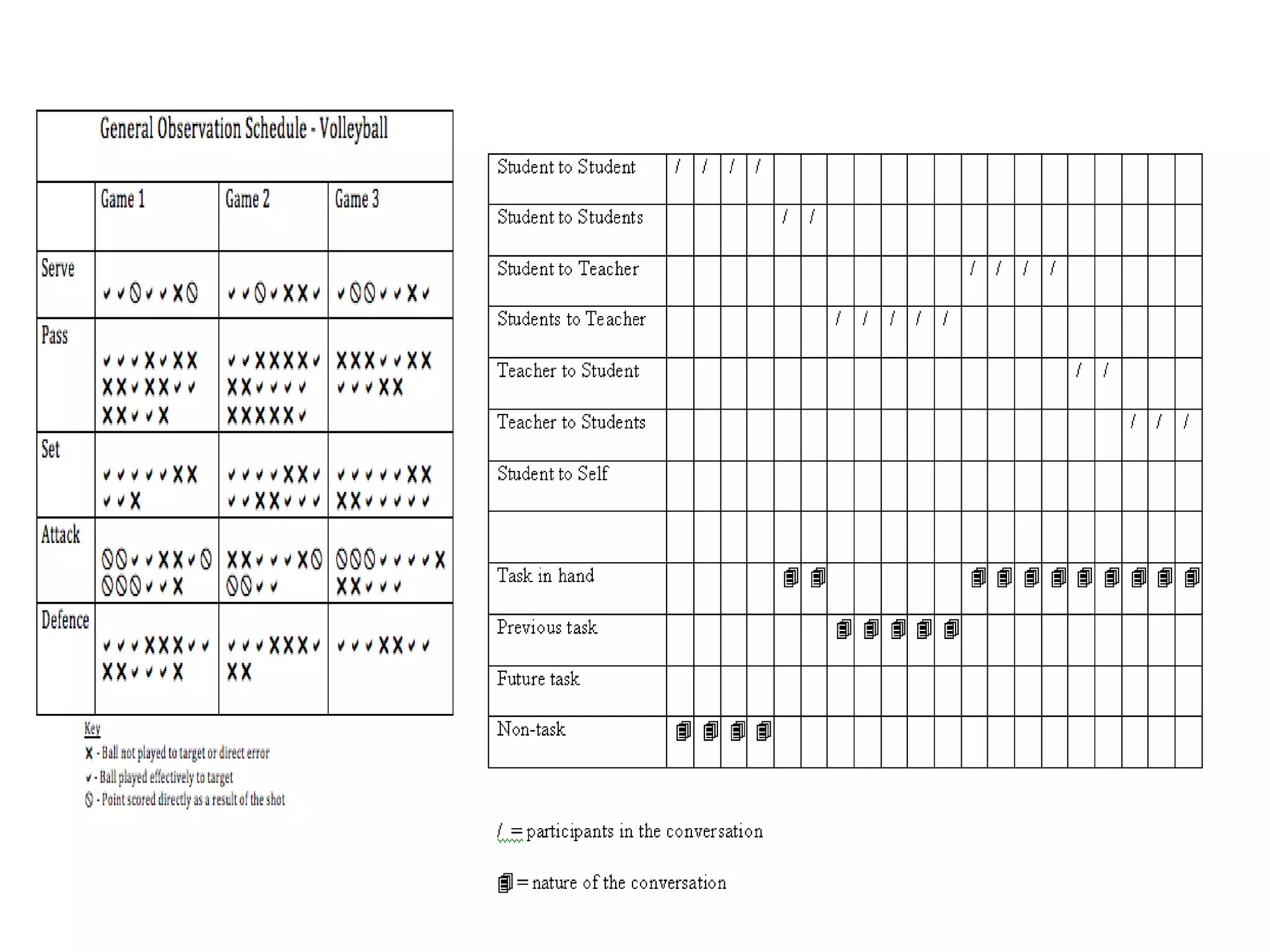
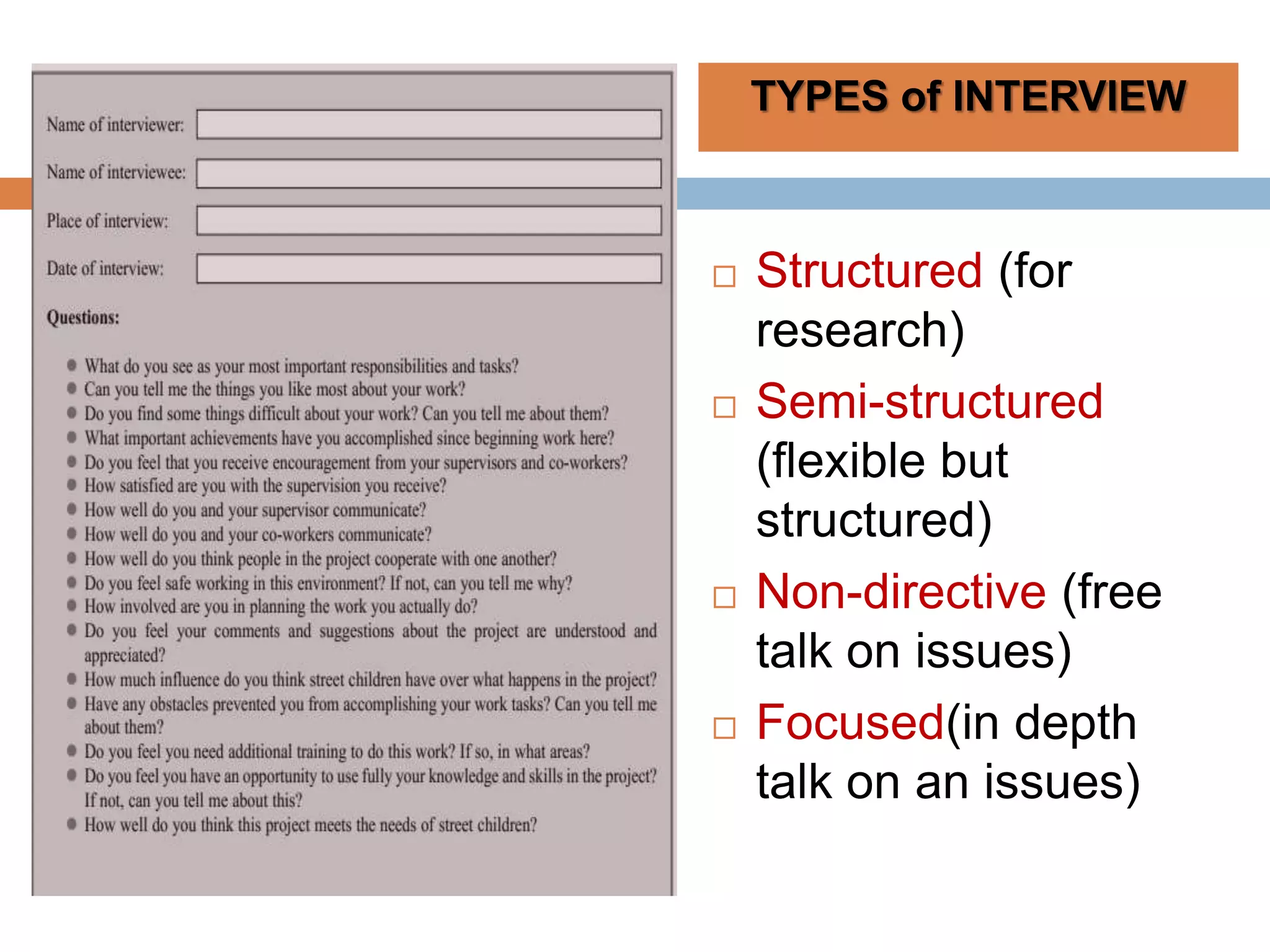
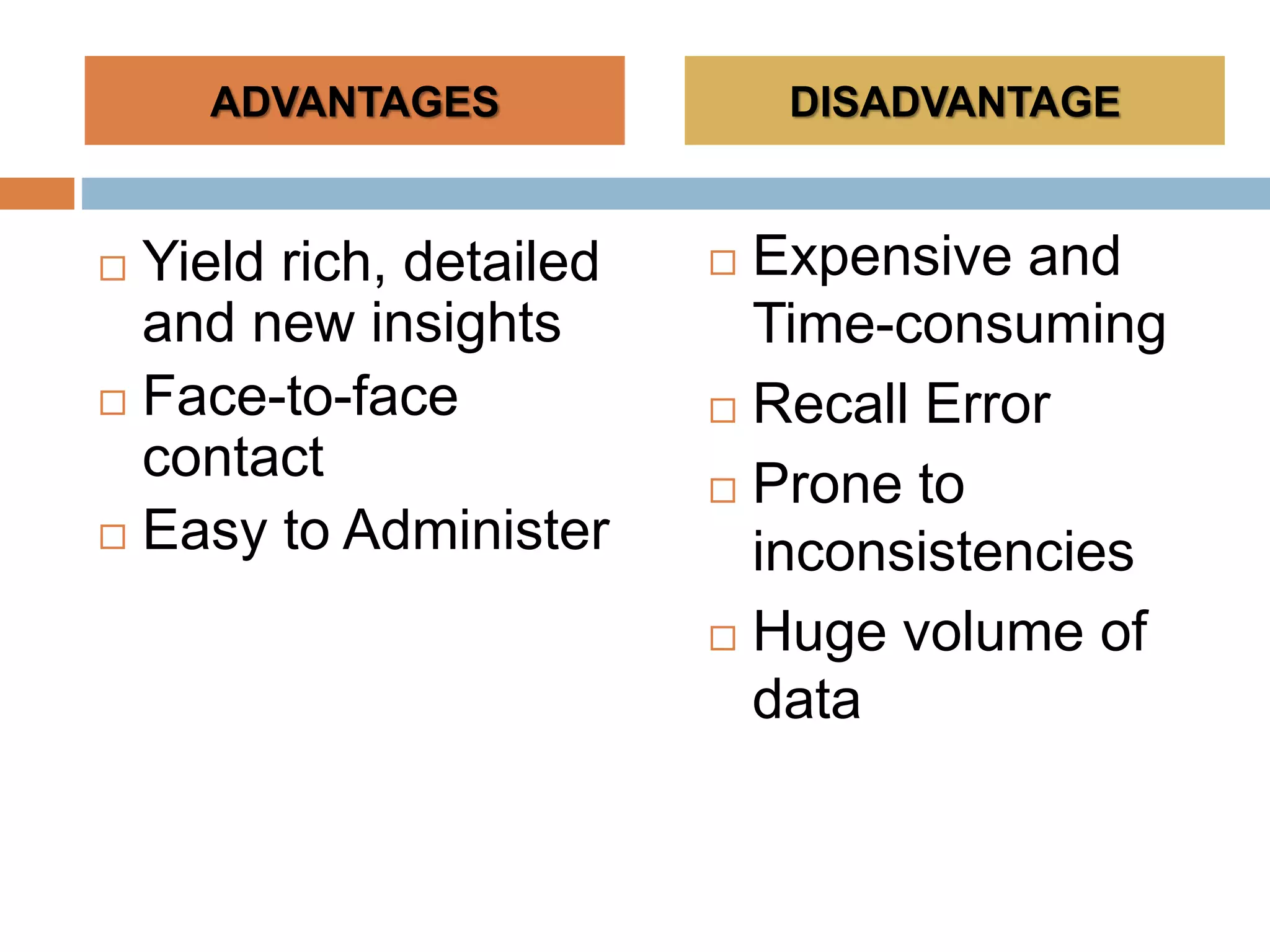
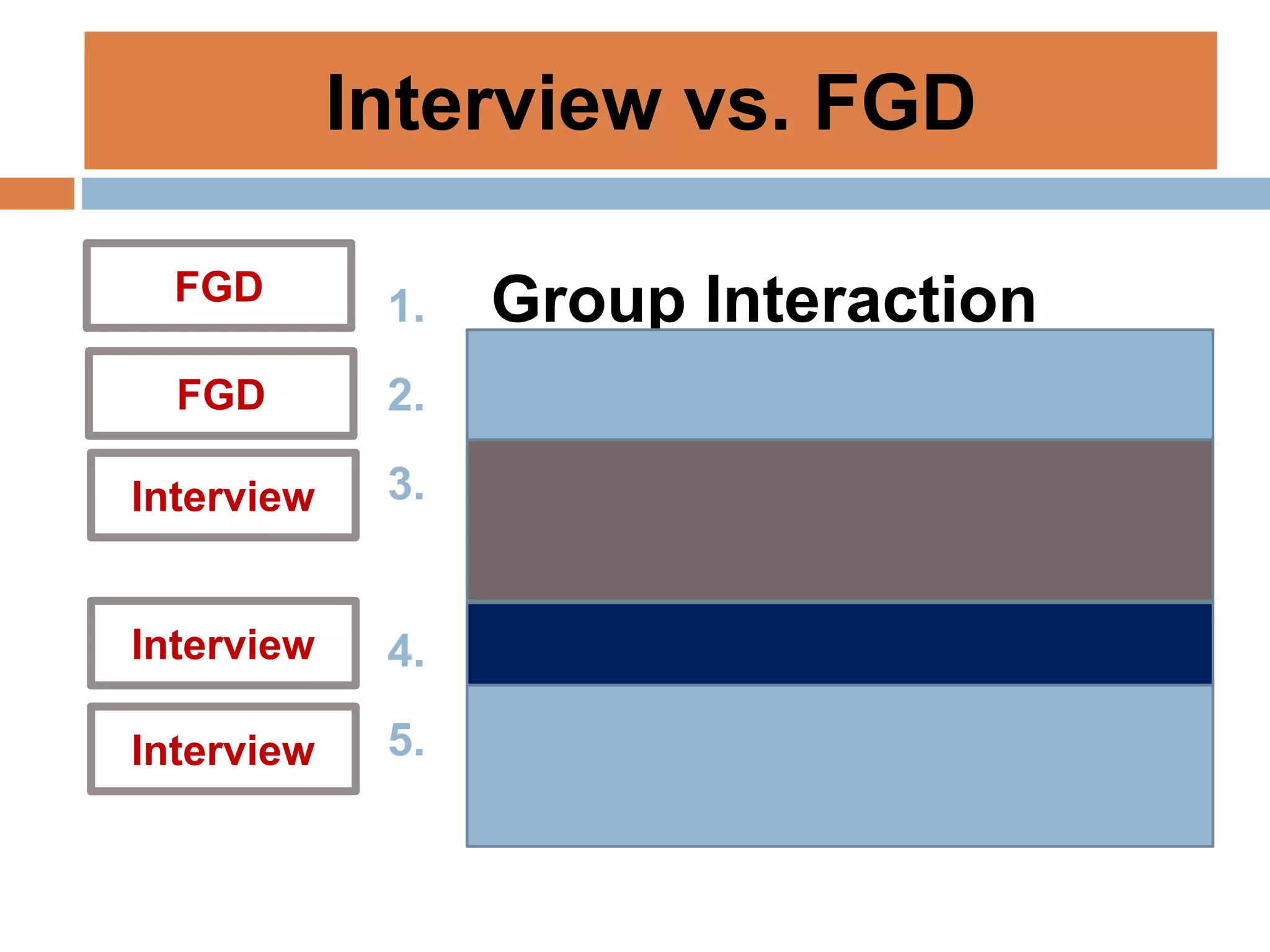
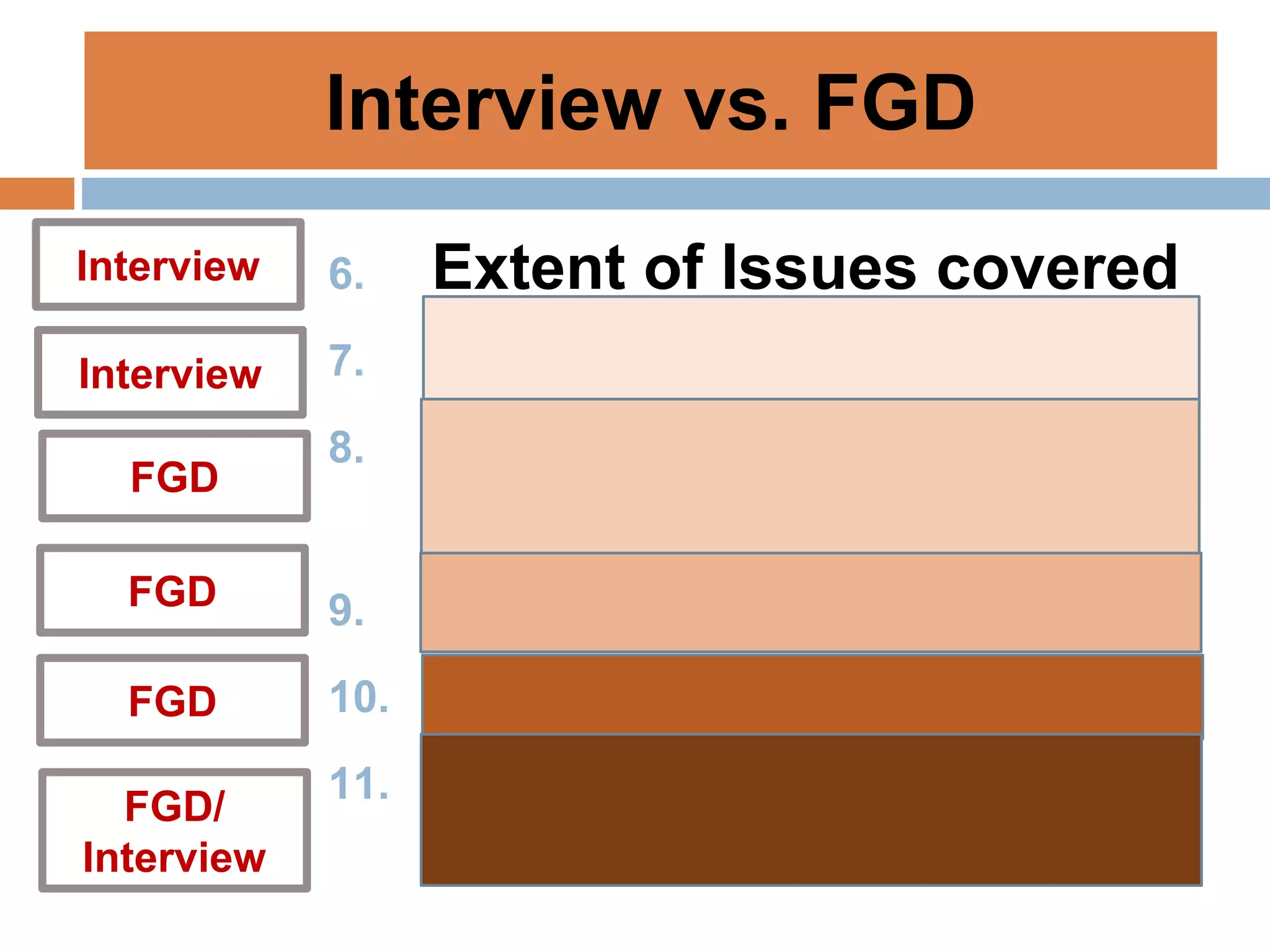
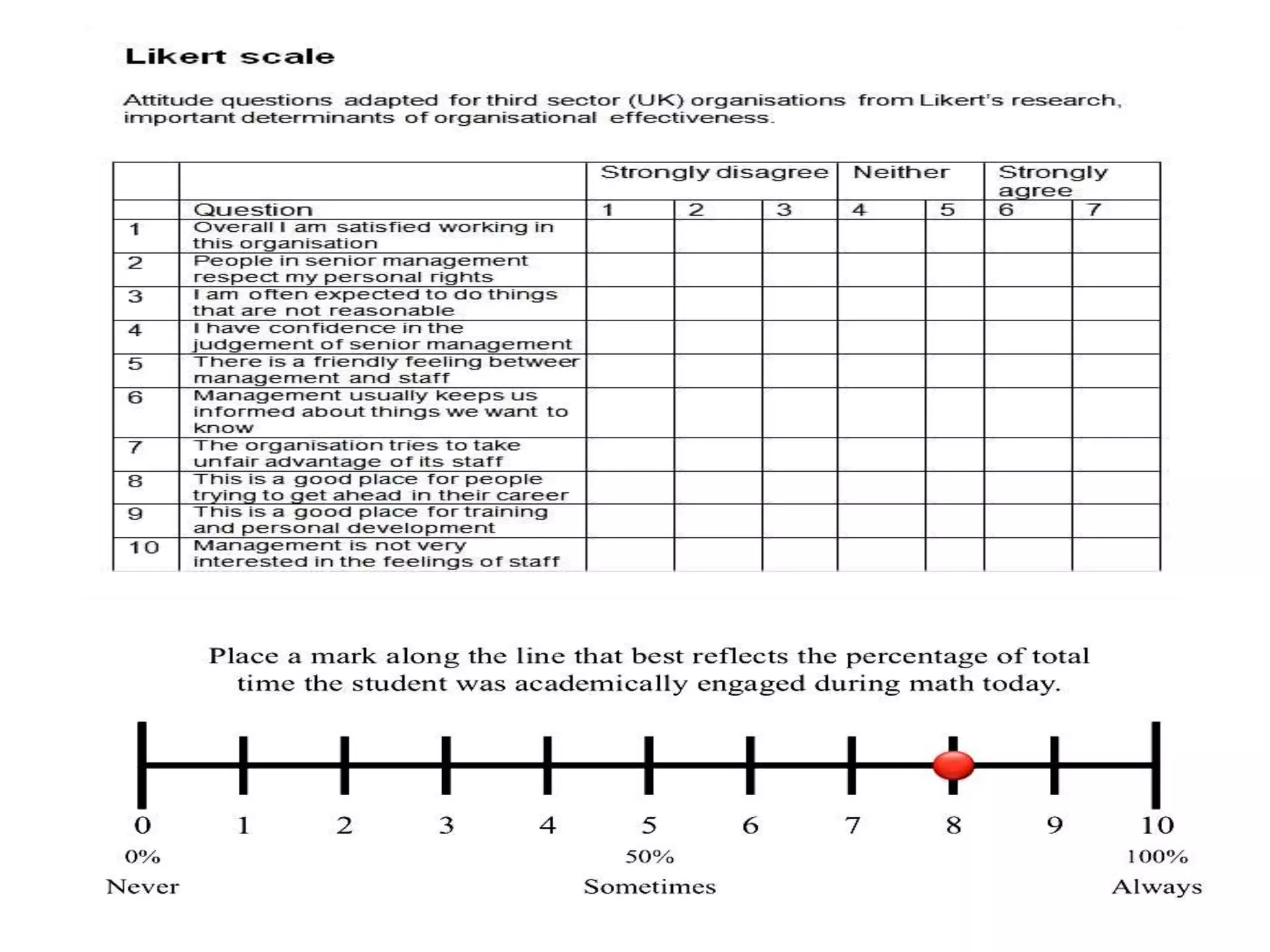
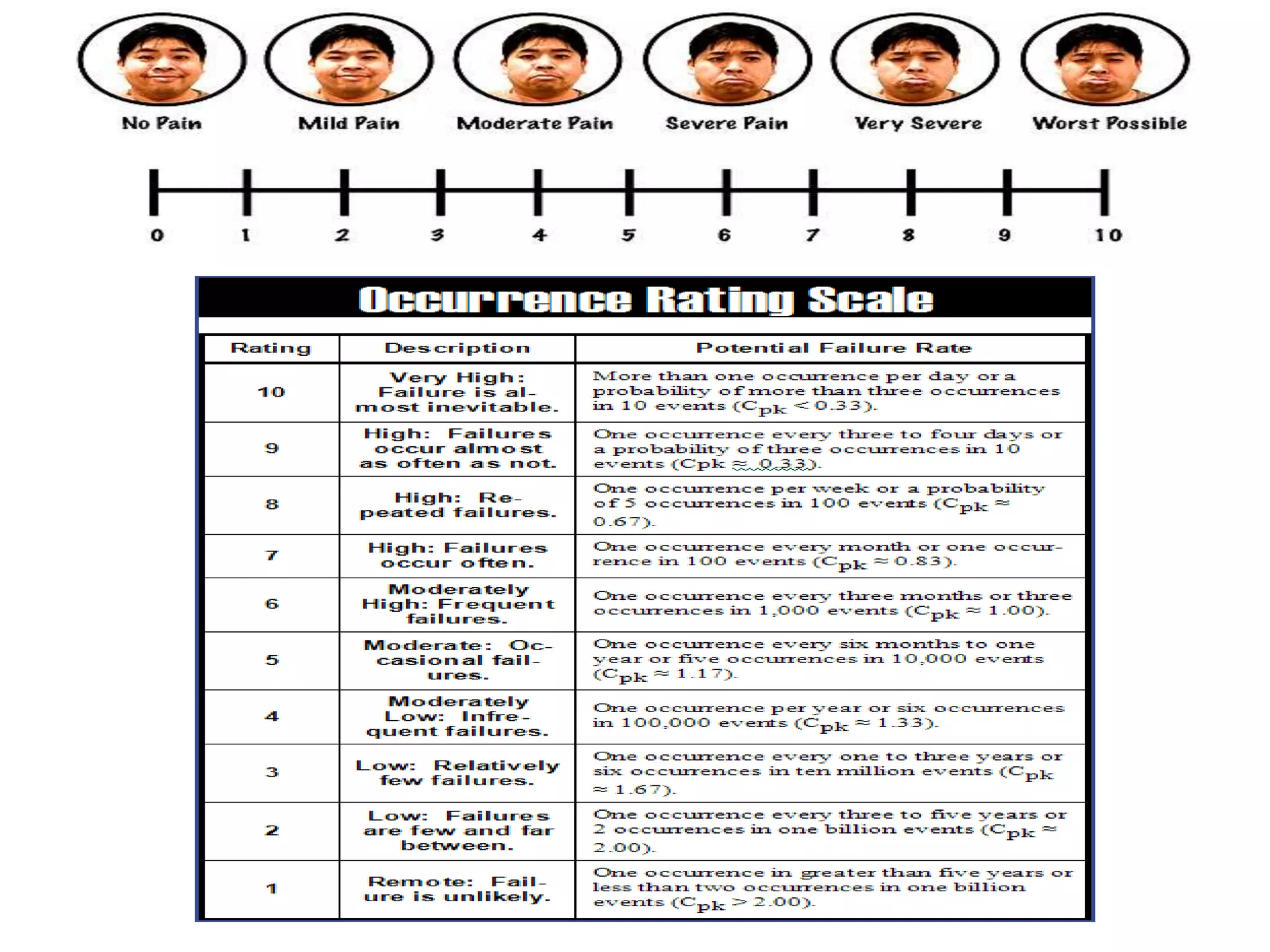
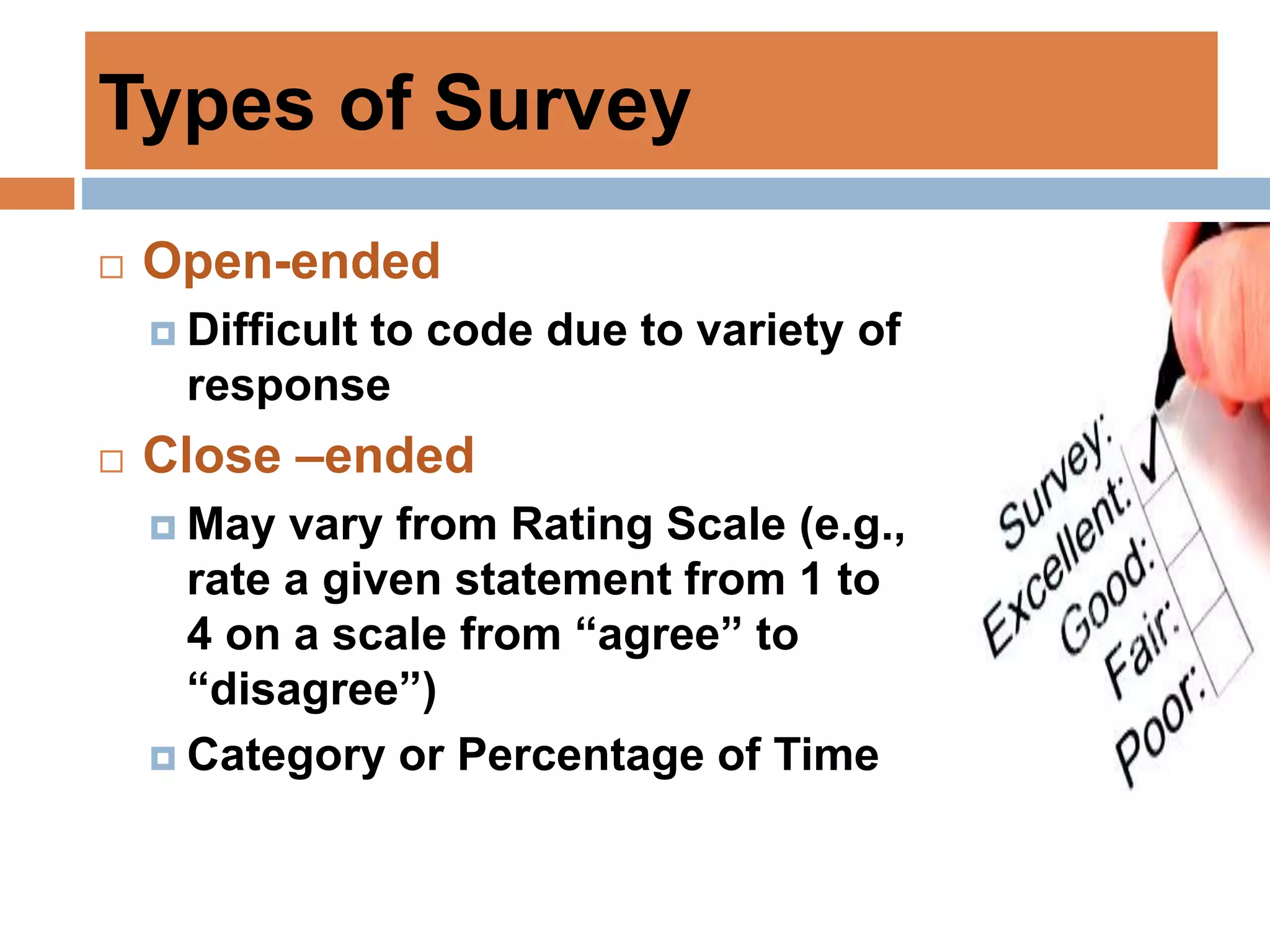
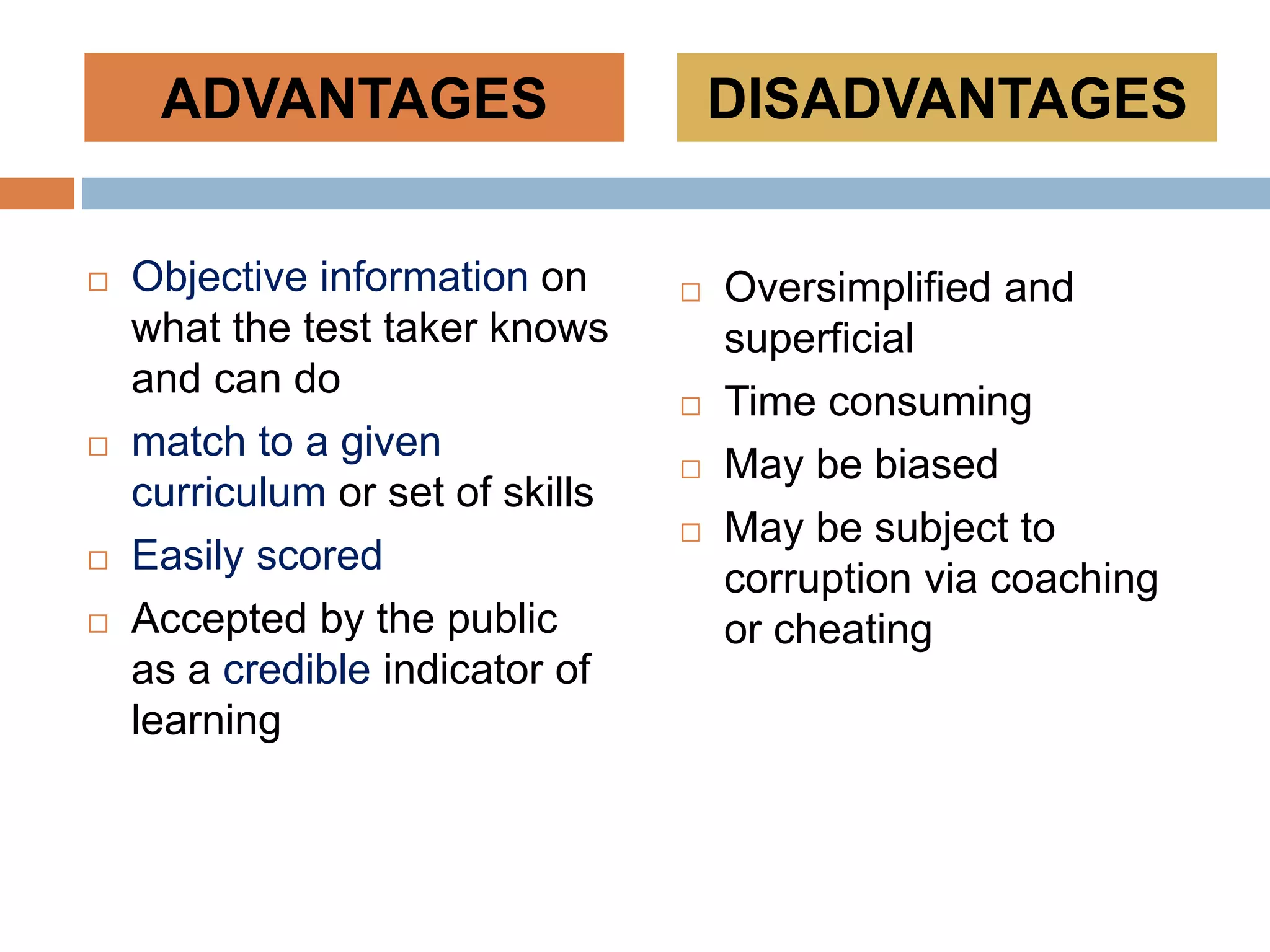
This document discusses various tools that can be used for data gathering in qualitative and quantitative research. It begins by stating the objectives of understanding what data gathering is, being able to select appropriate tools, and choosing tools for specific research topics. It then defines data and data gathering. The rest of the document discusses different tools for collecting qualitative data, like interviews and focus groups, and quantitative data, like questionnaires and tests. For each tool, it provides details on what it is, how it is used, and advantages and disadvantages. The goal is to help participants in selecting the right data collection methods for their research needs.