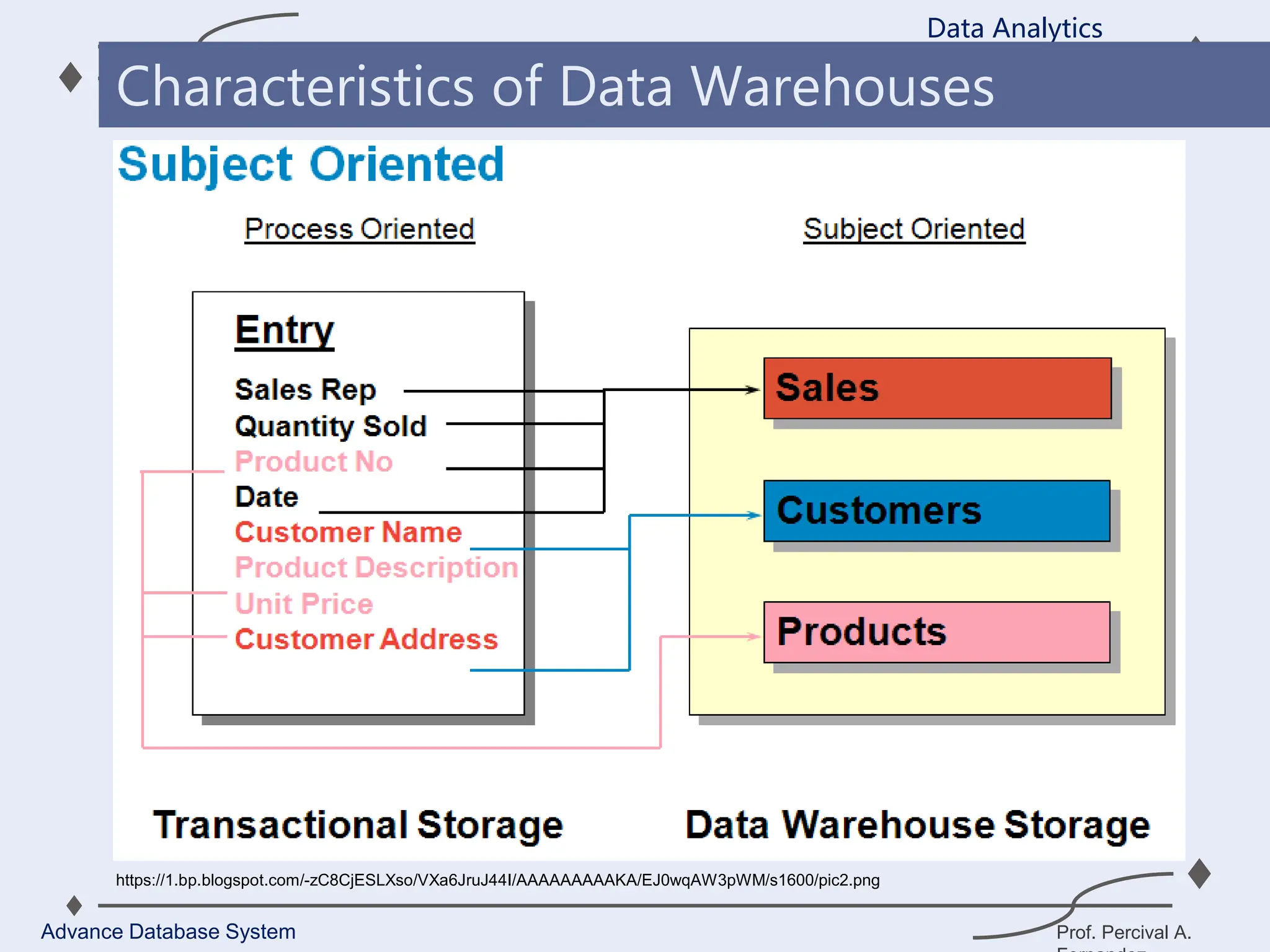
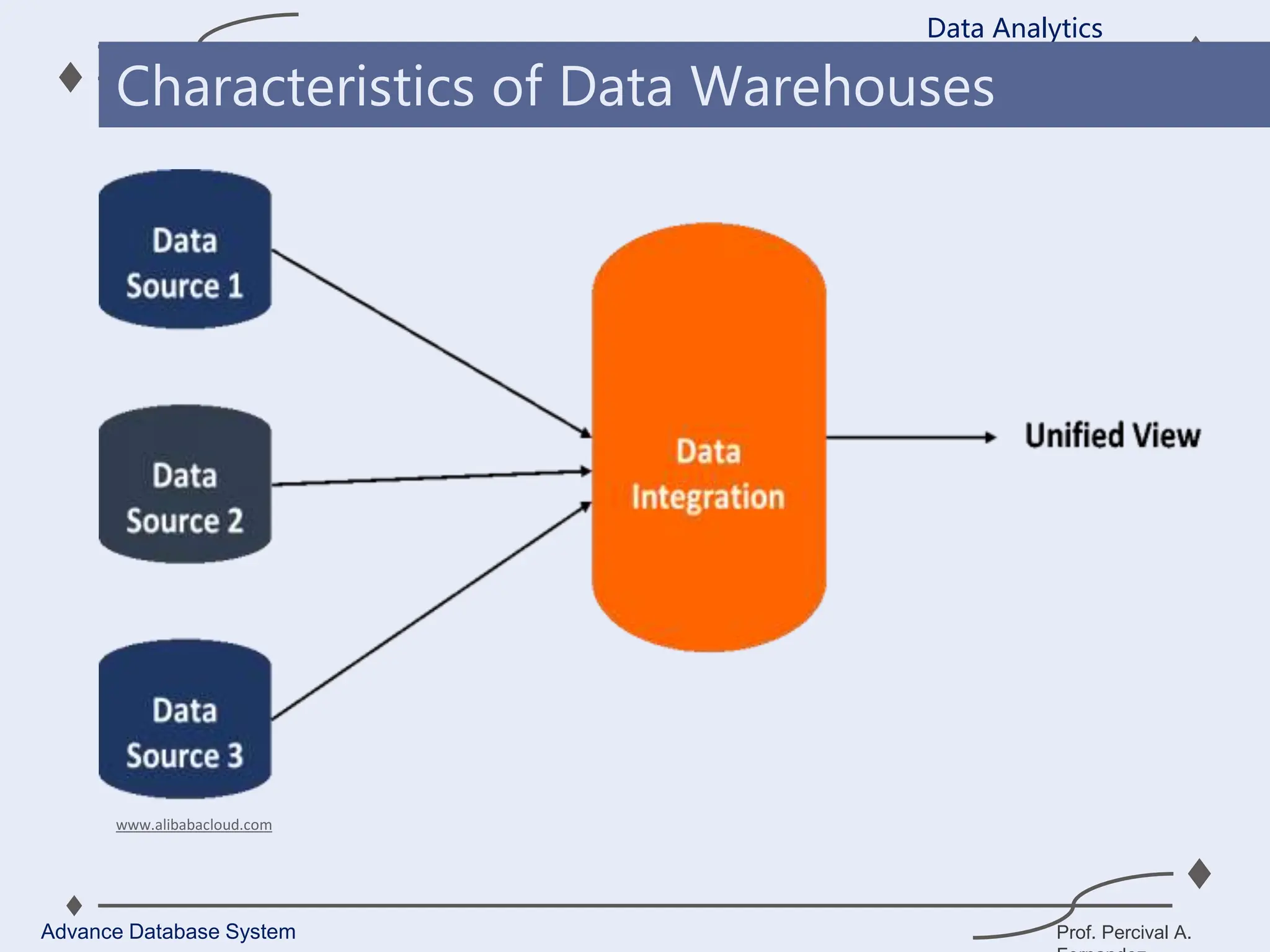
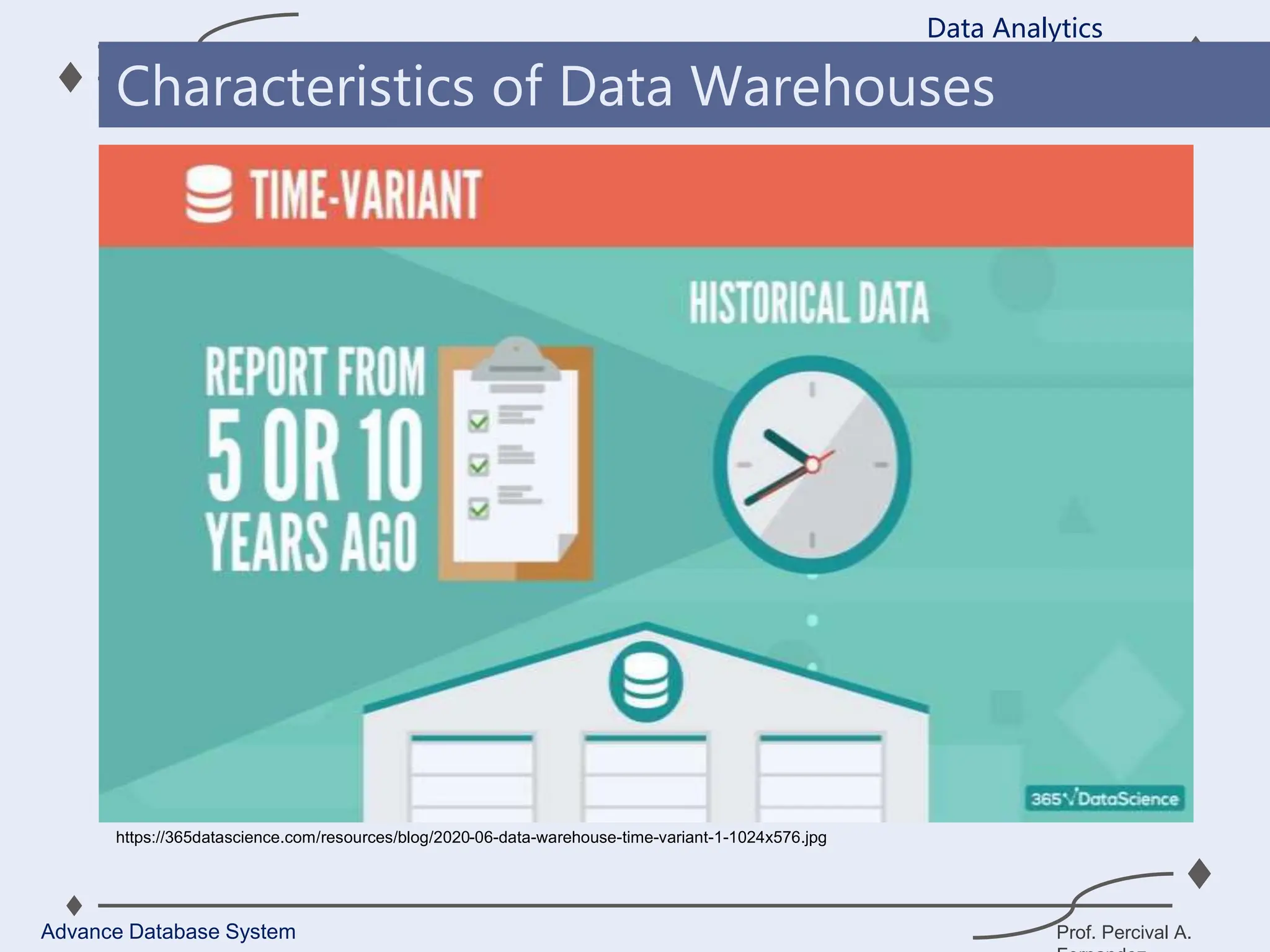
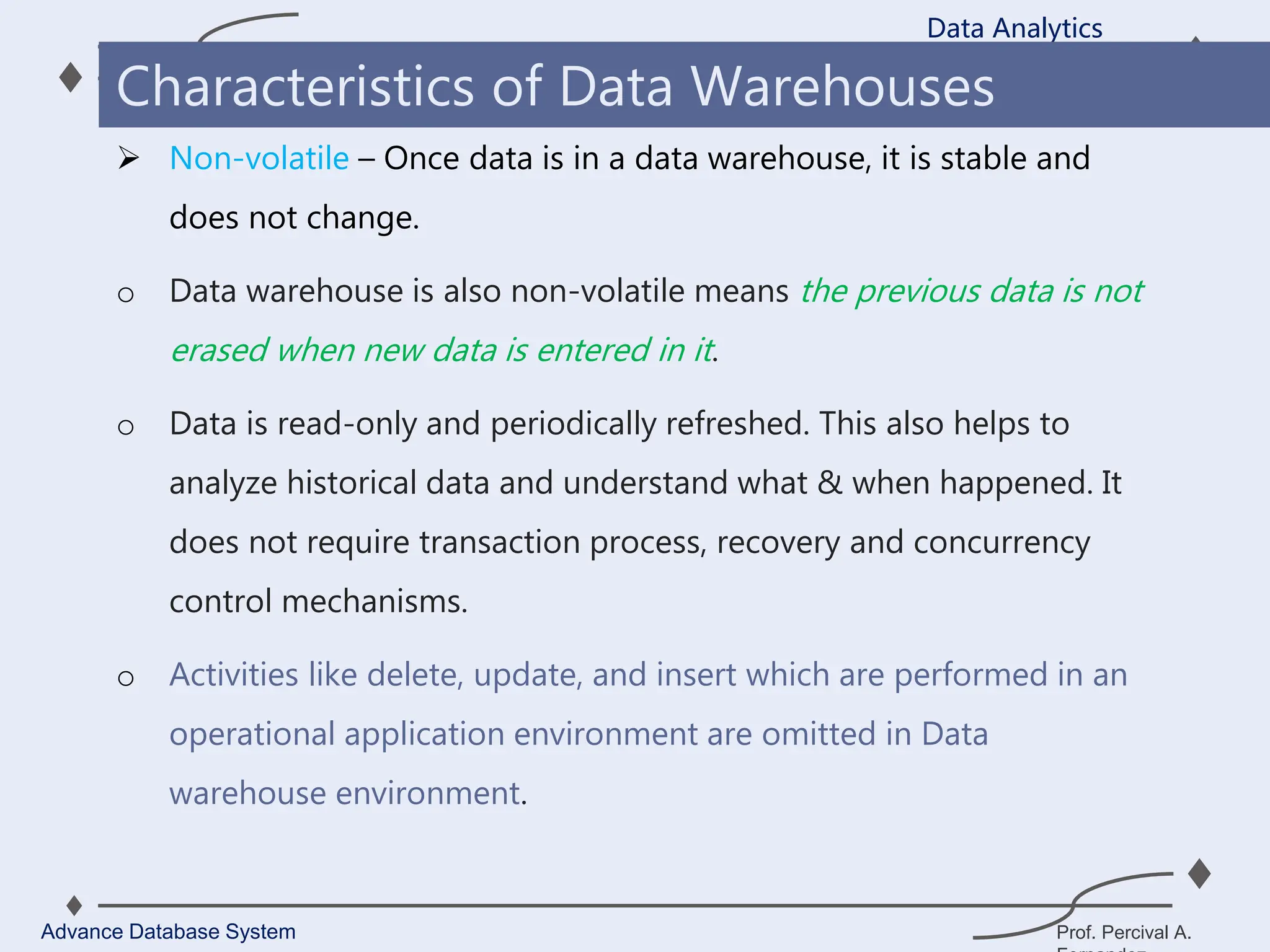
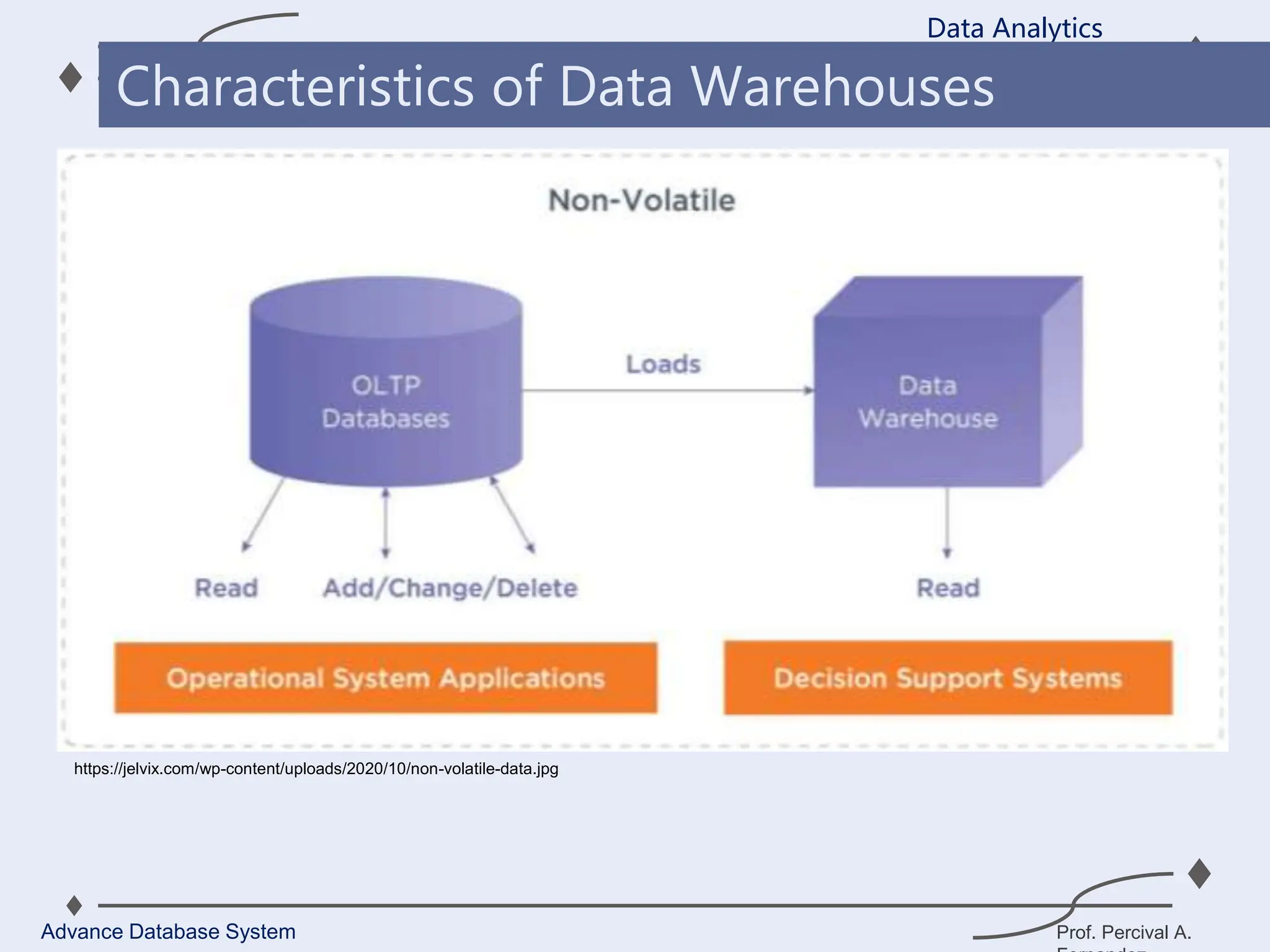
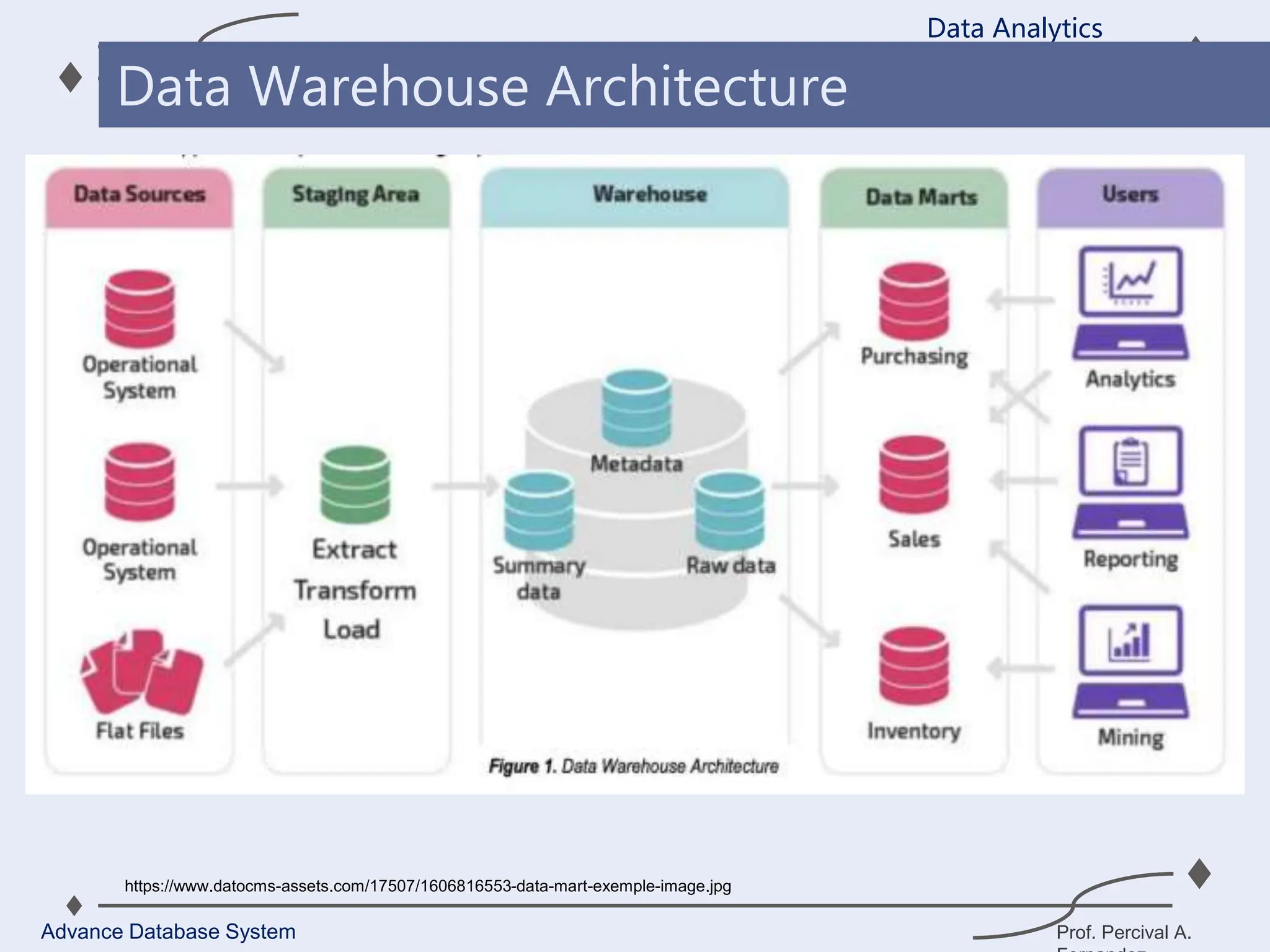
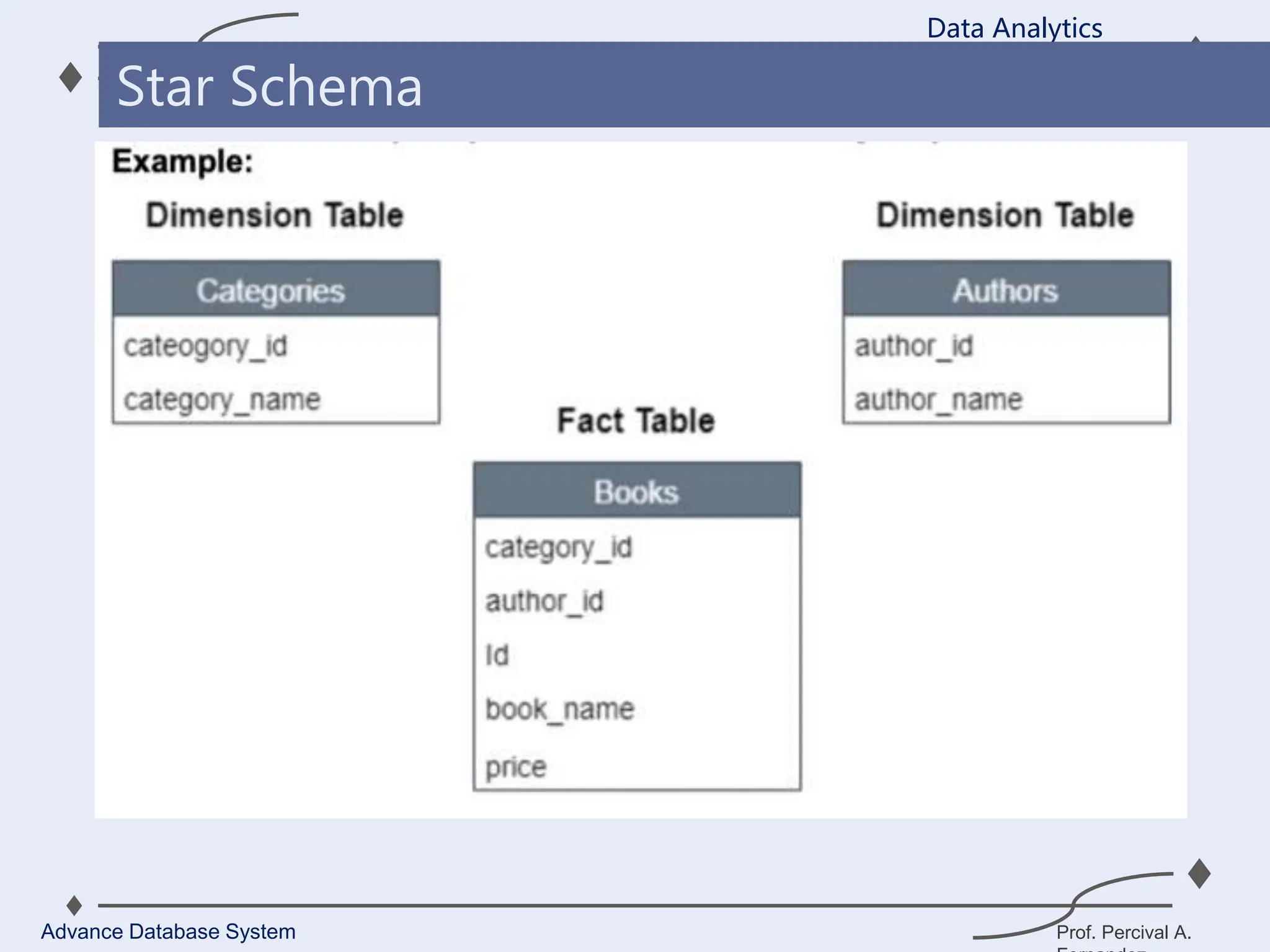
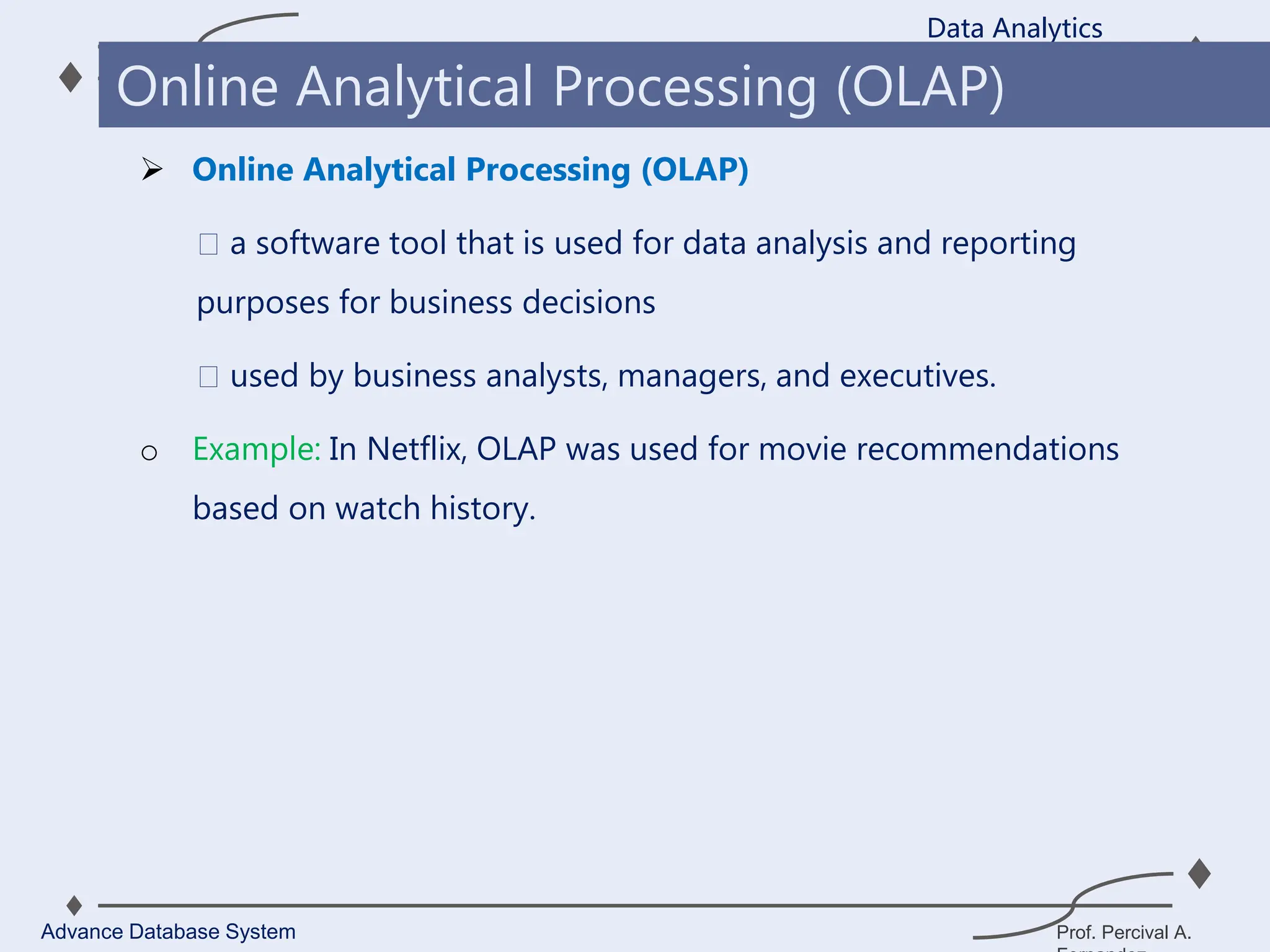
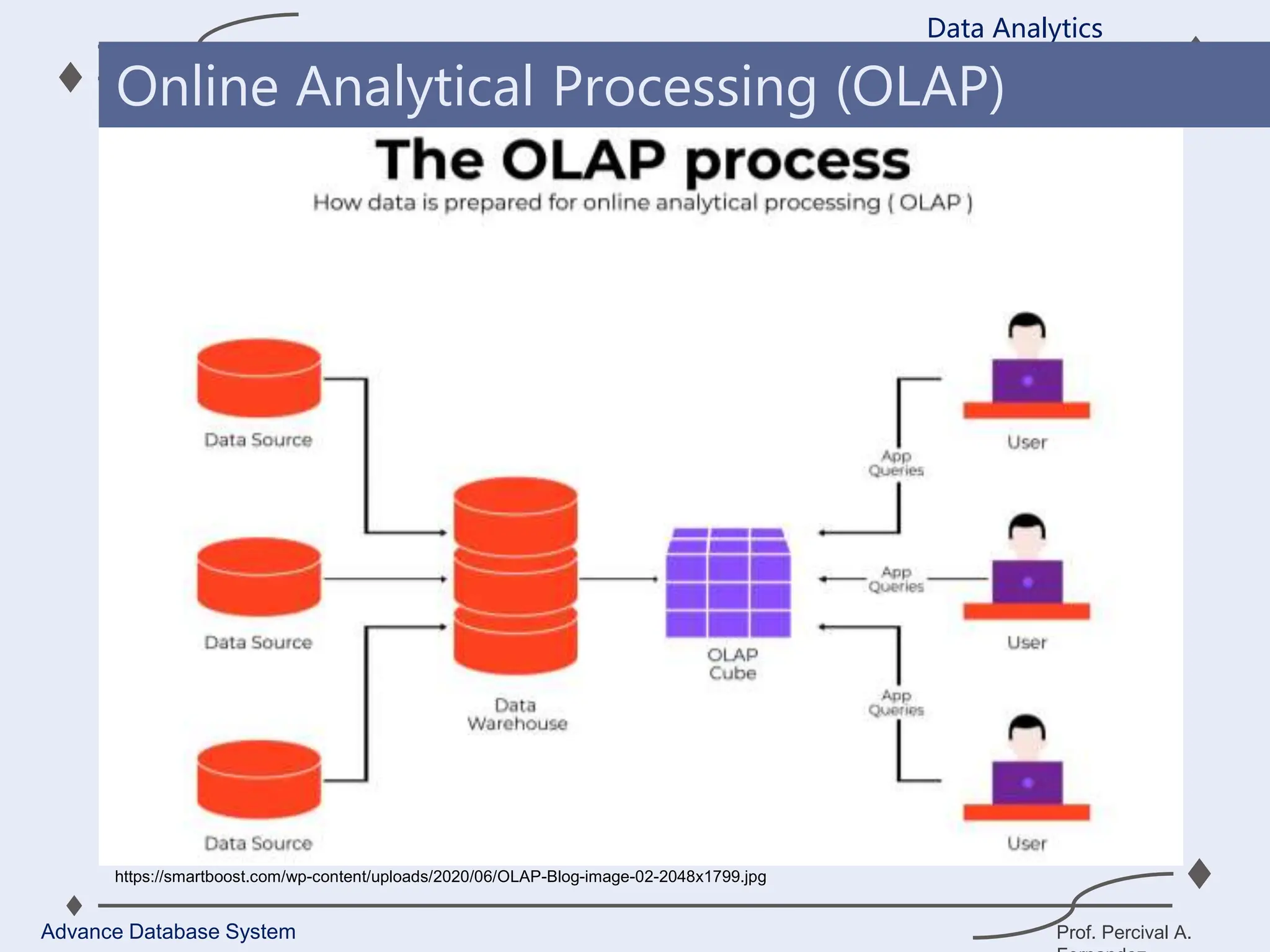
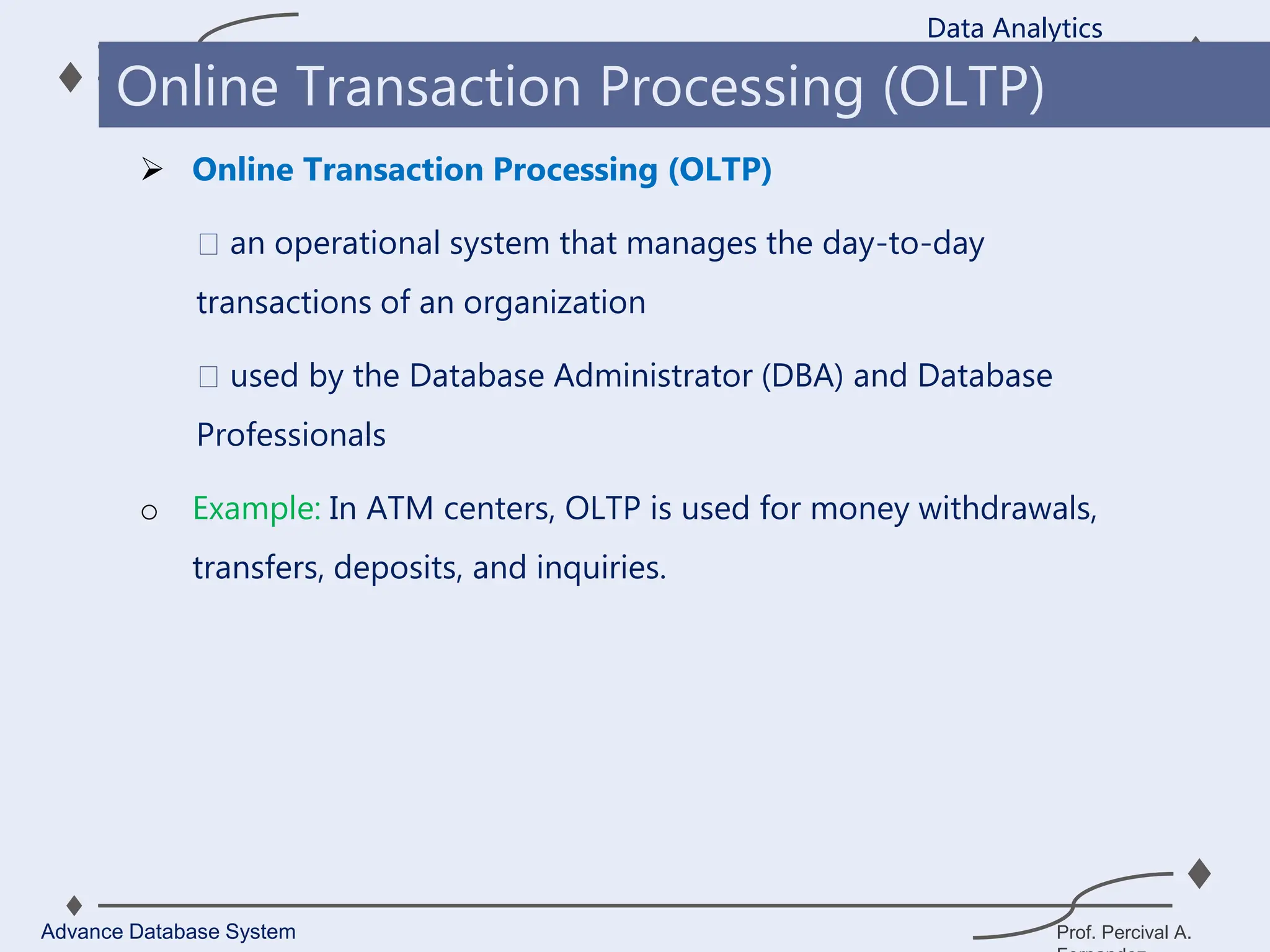
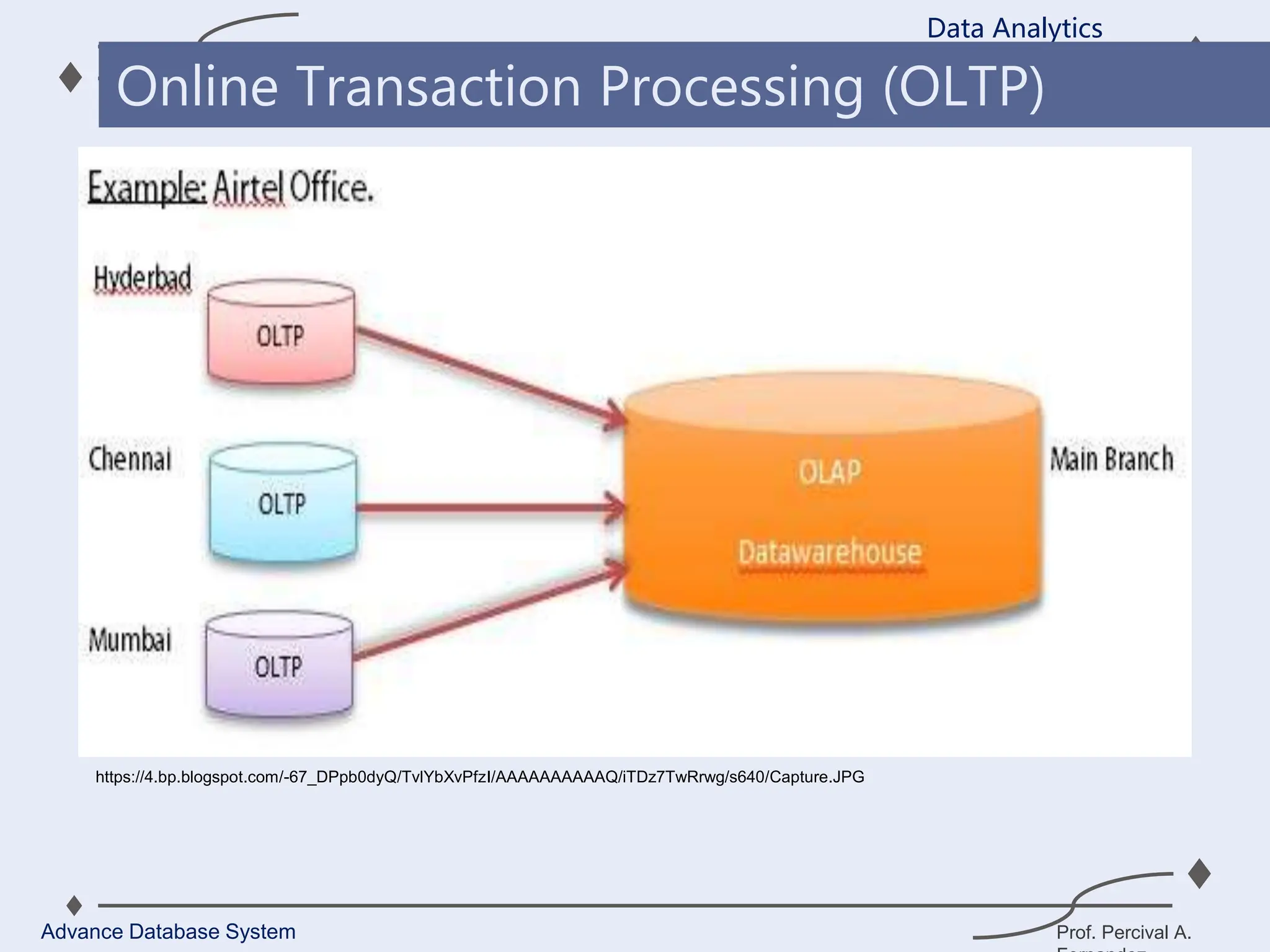
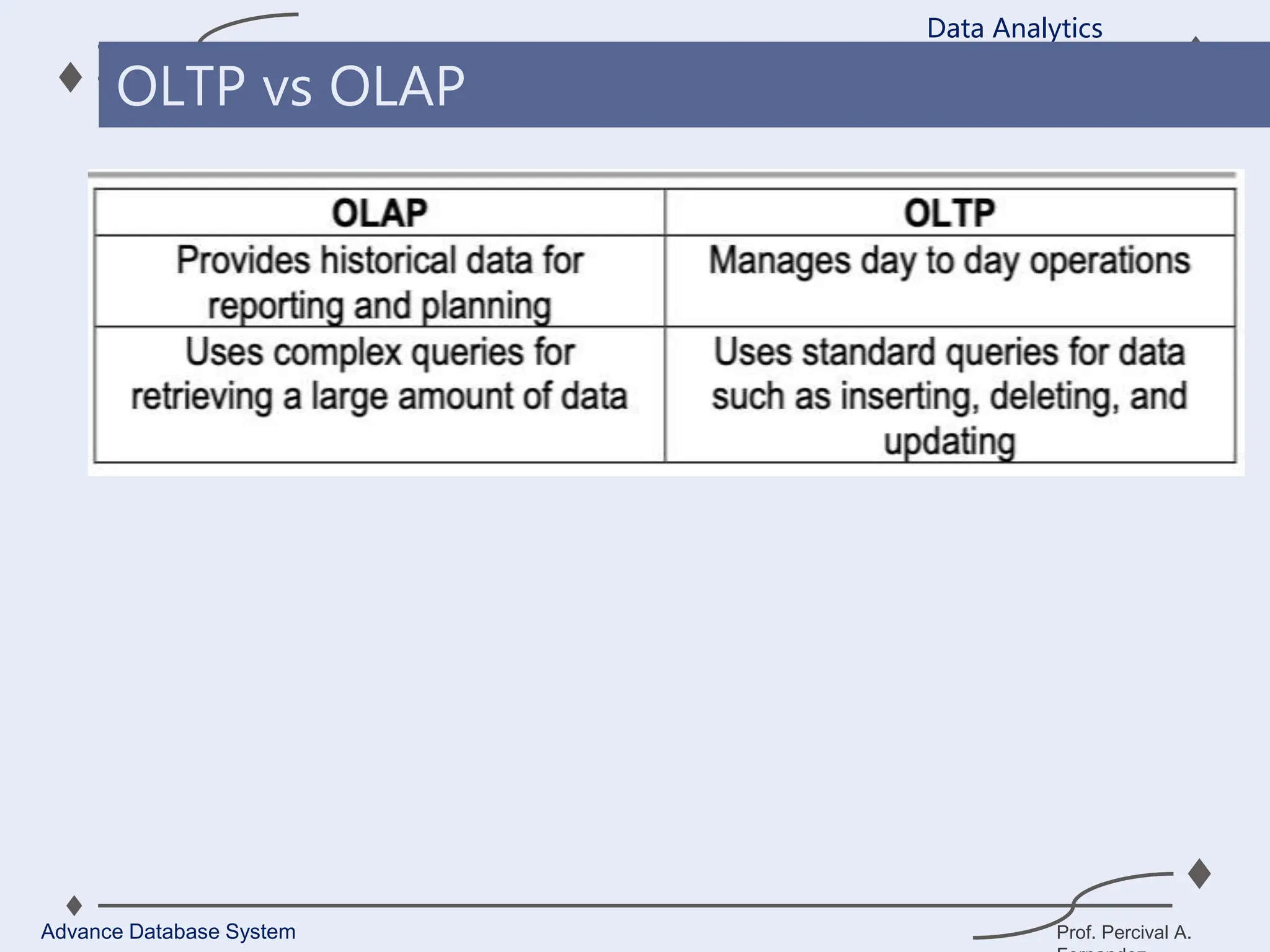
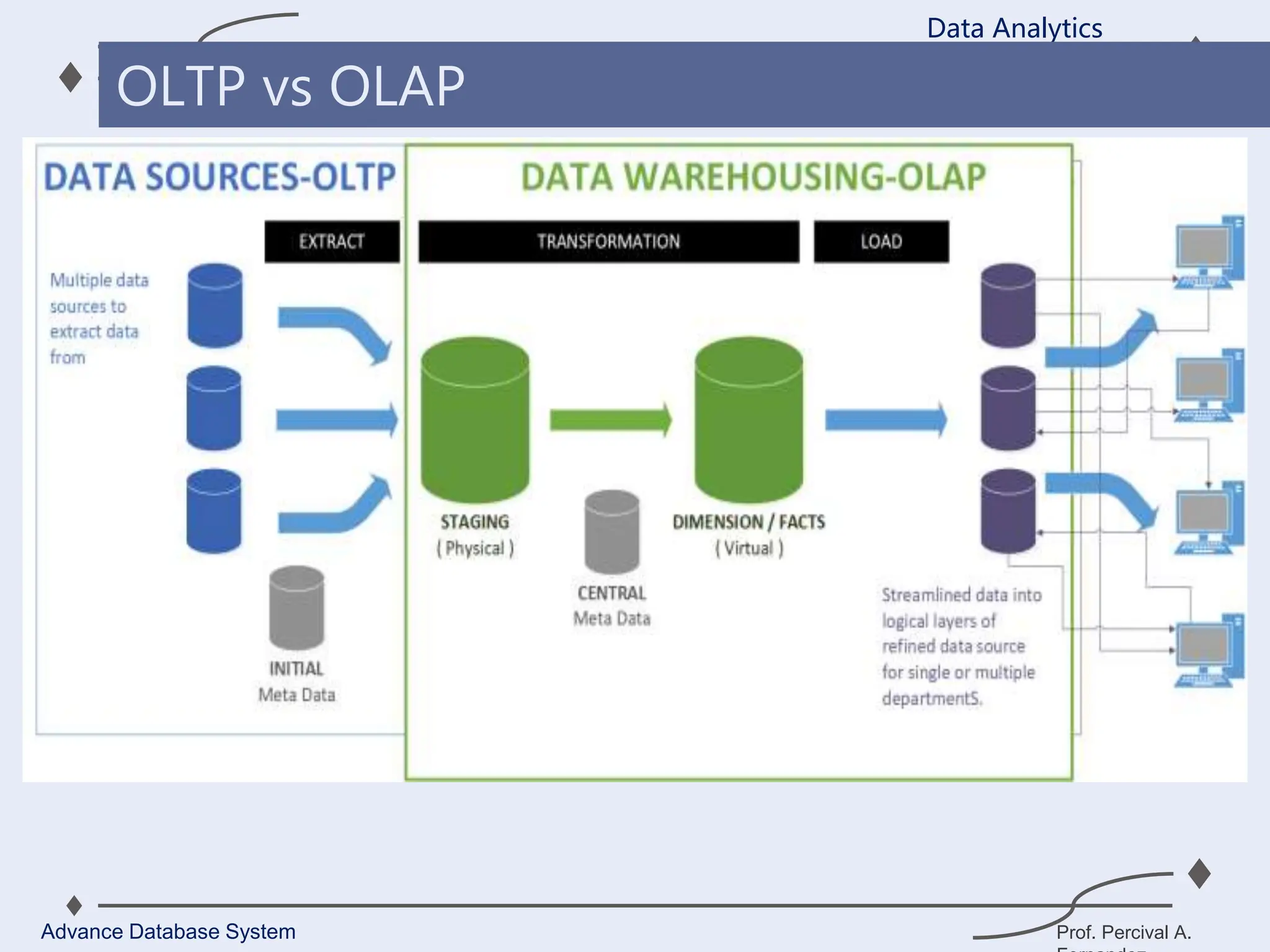
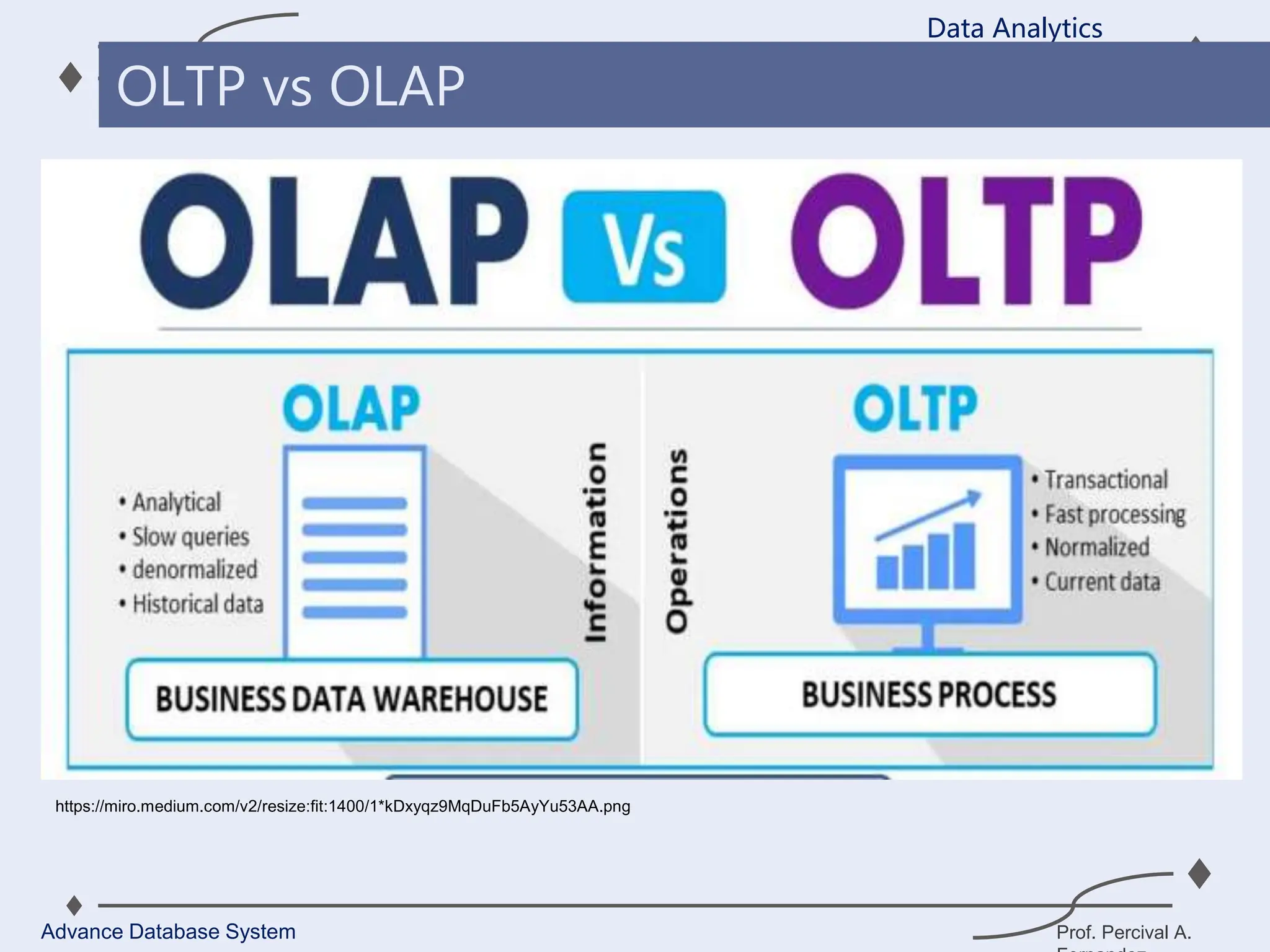
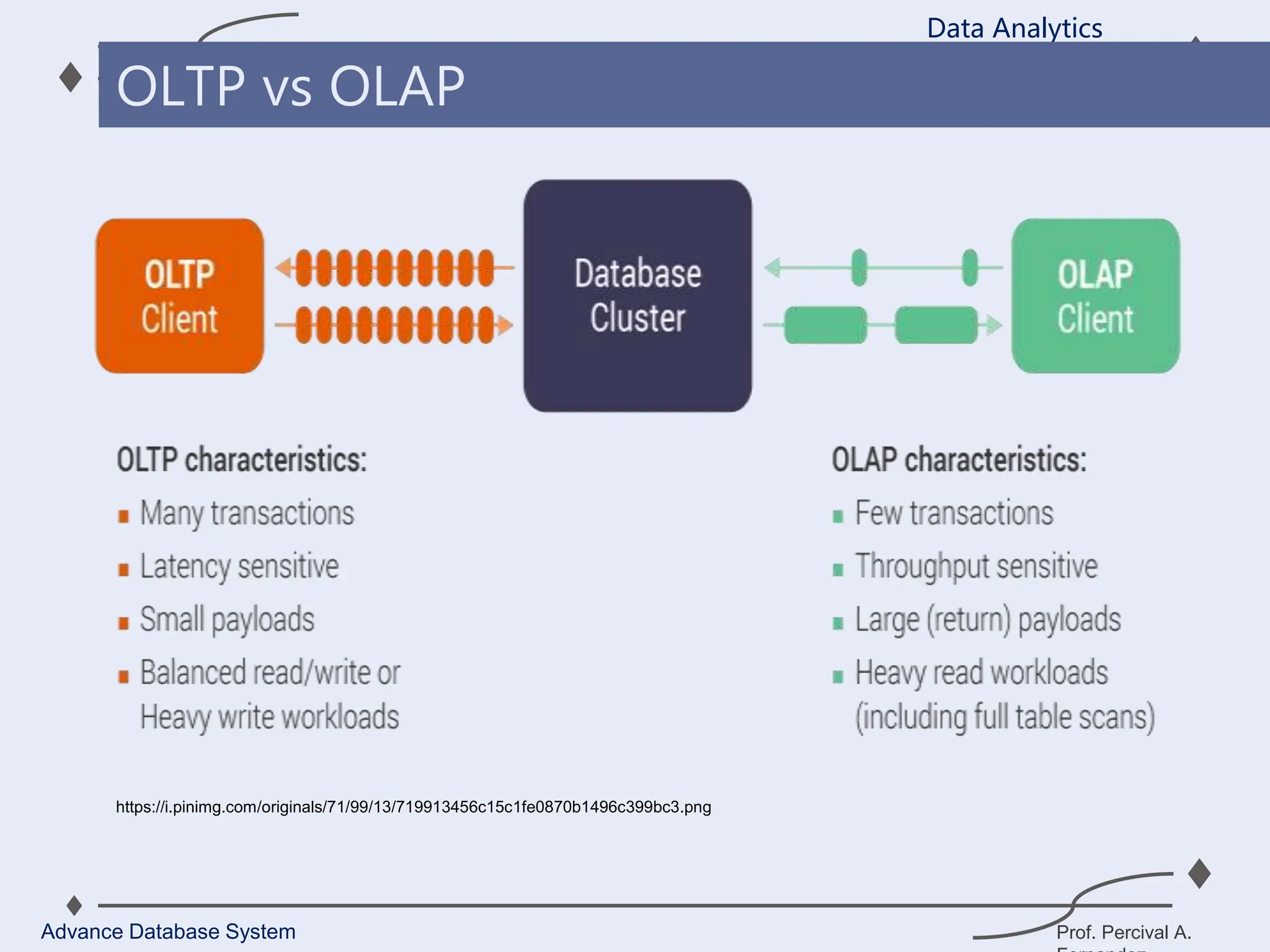
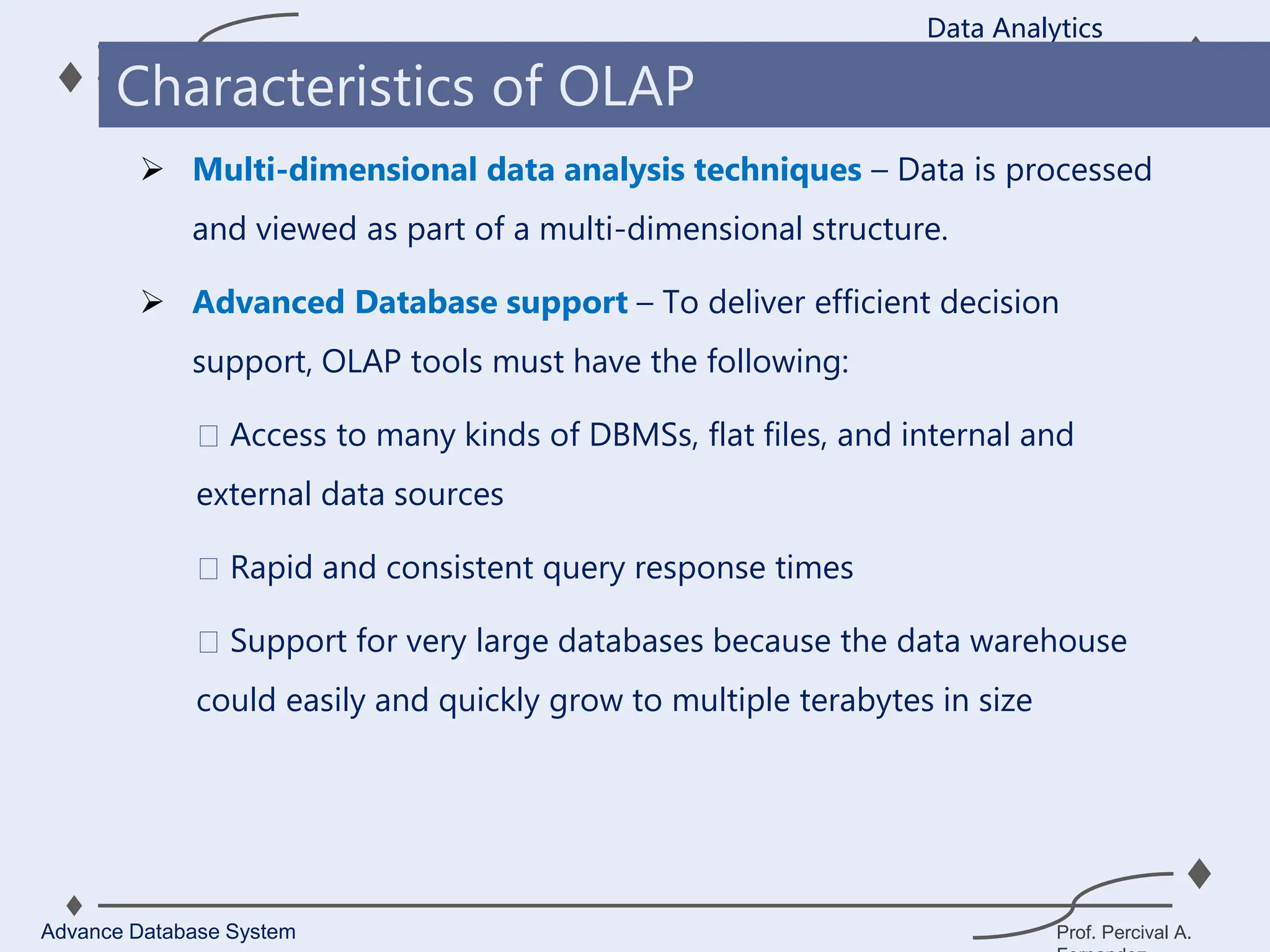
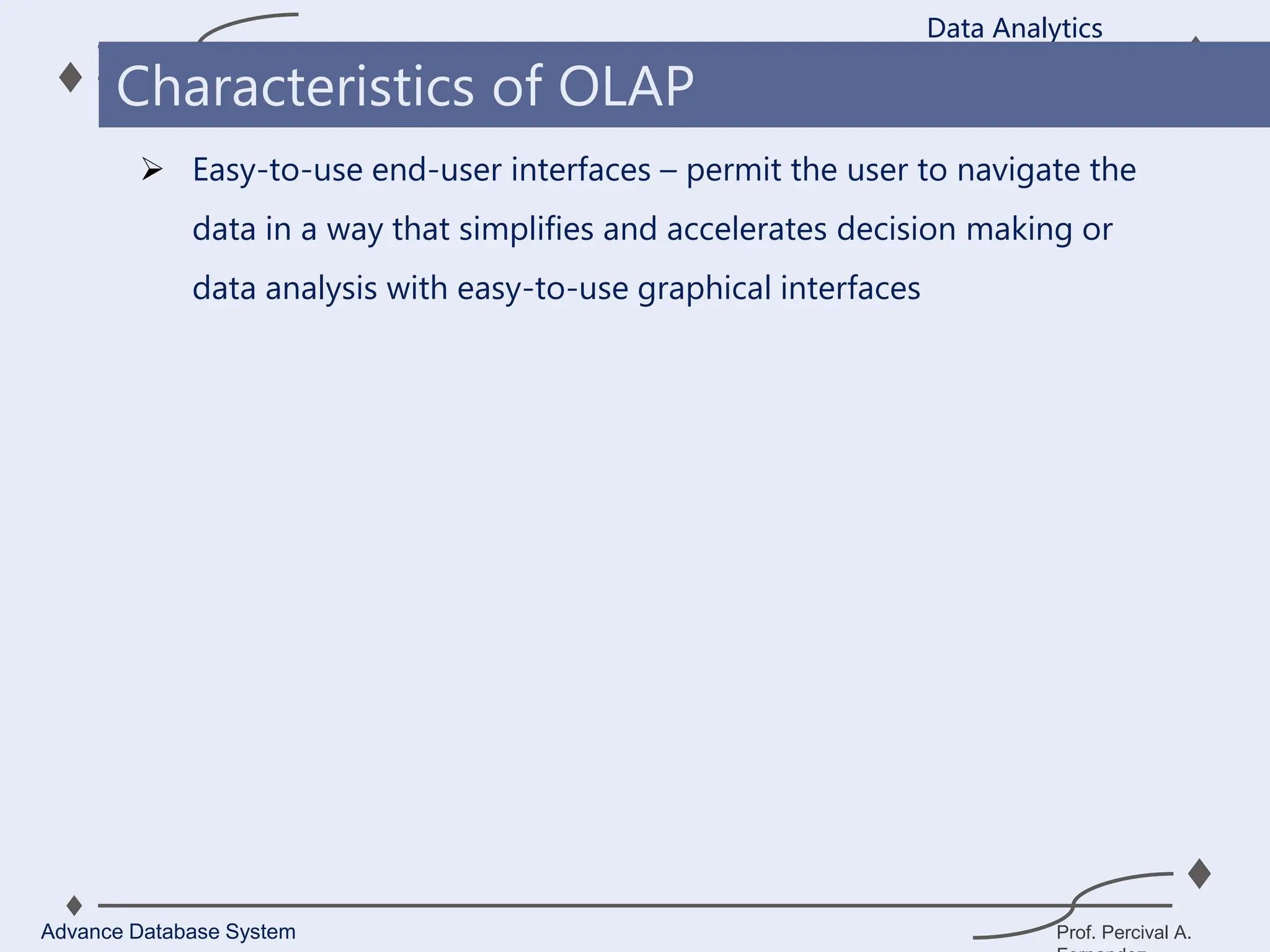
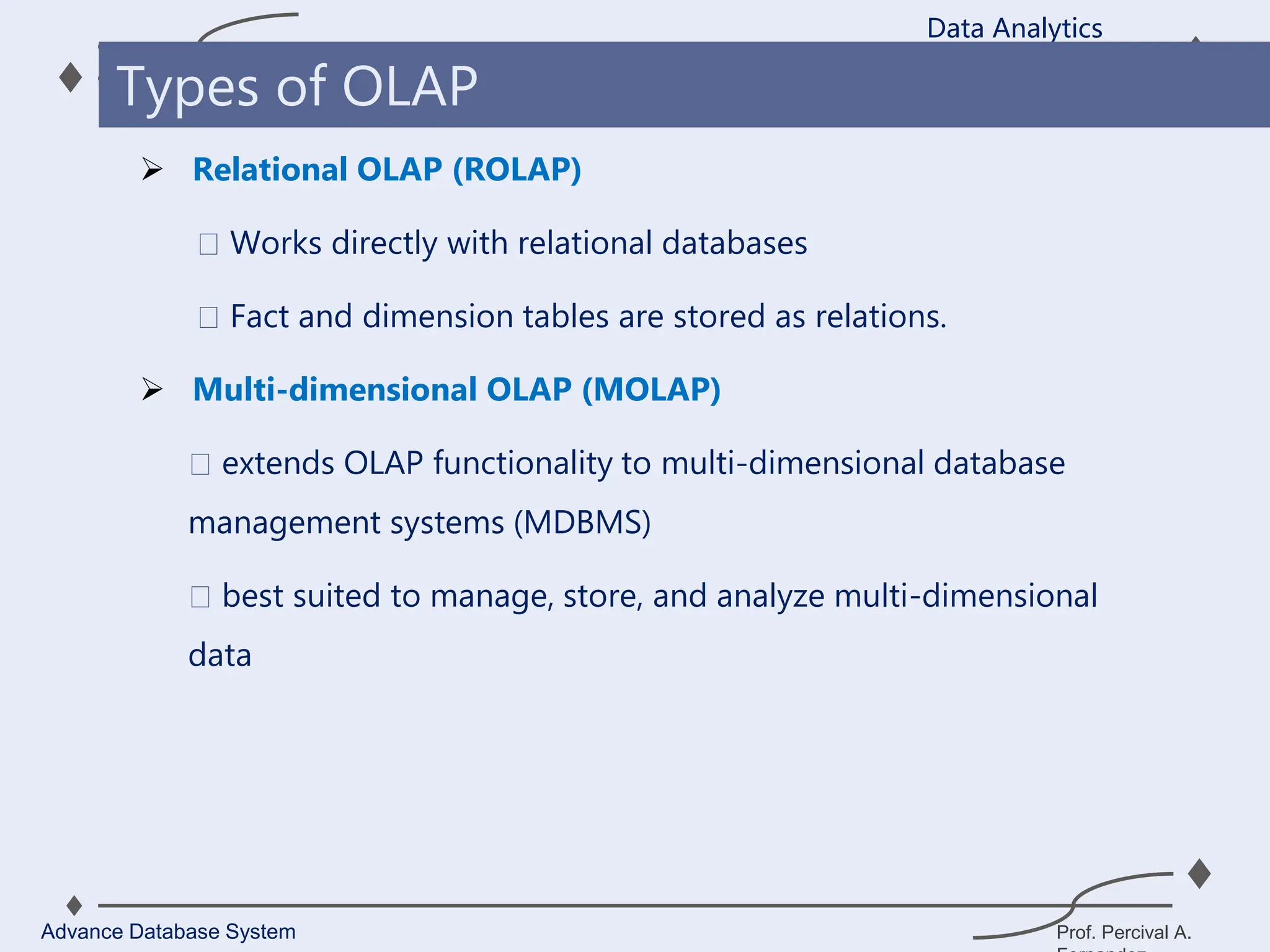
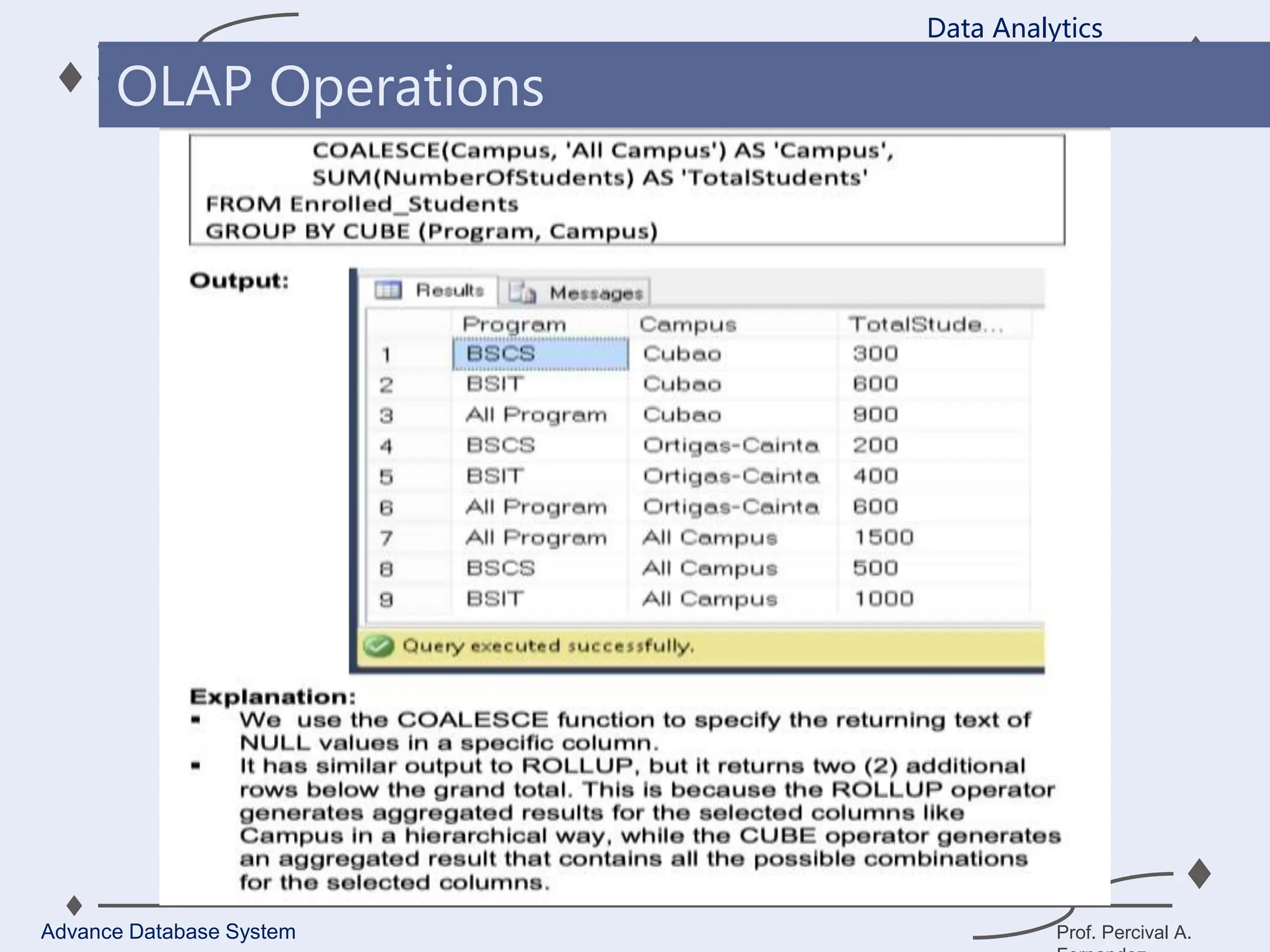
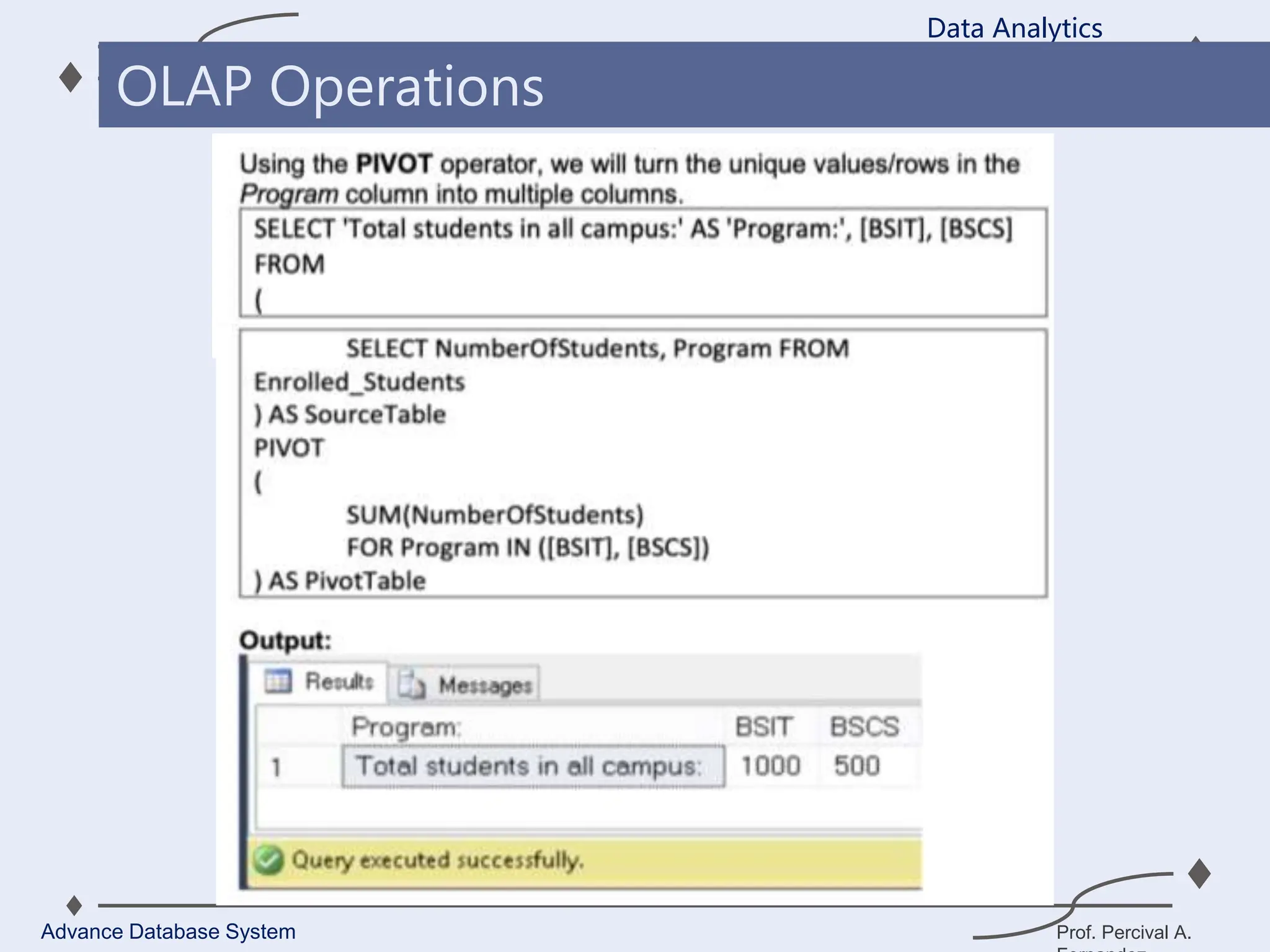
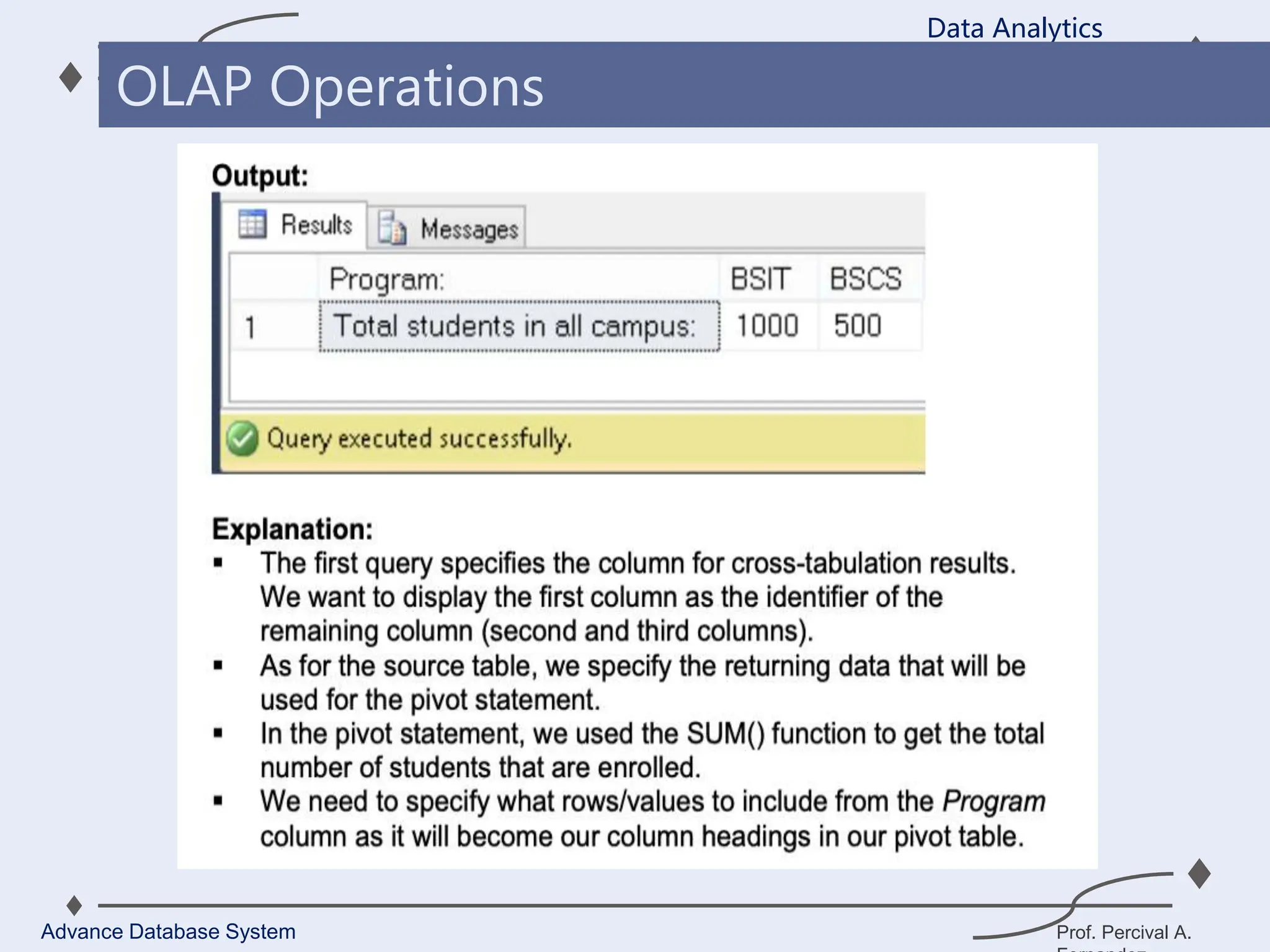
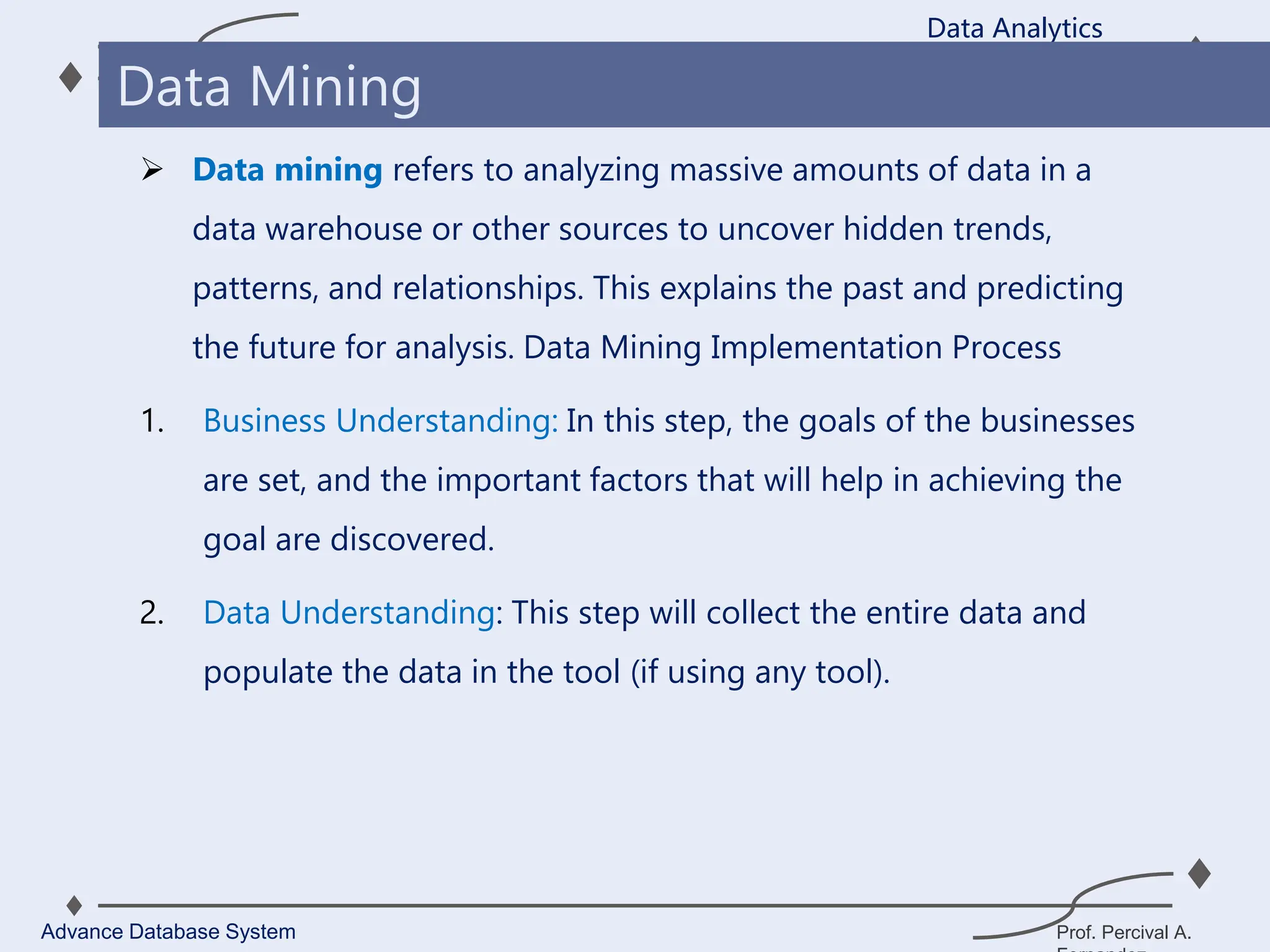
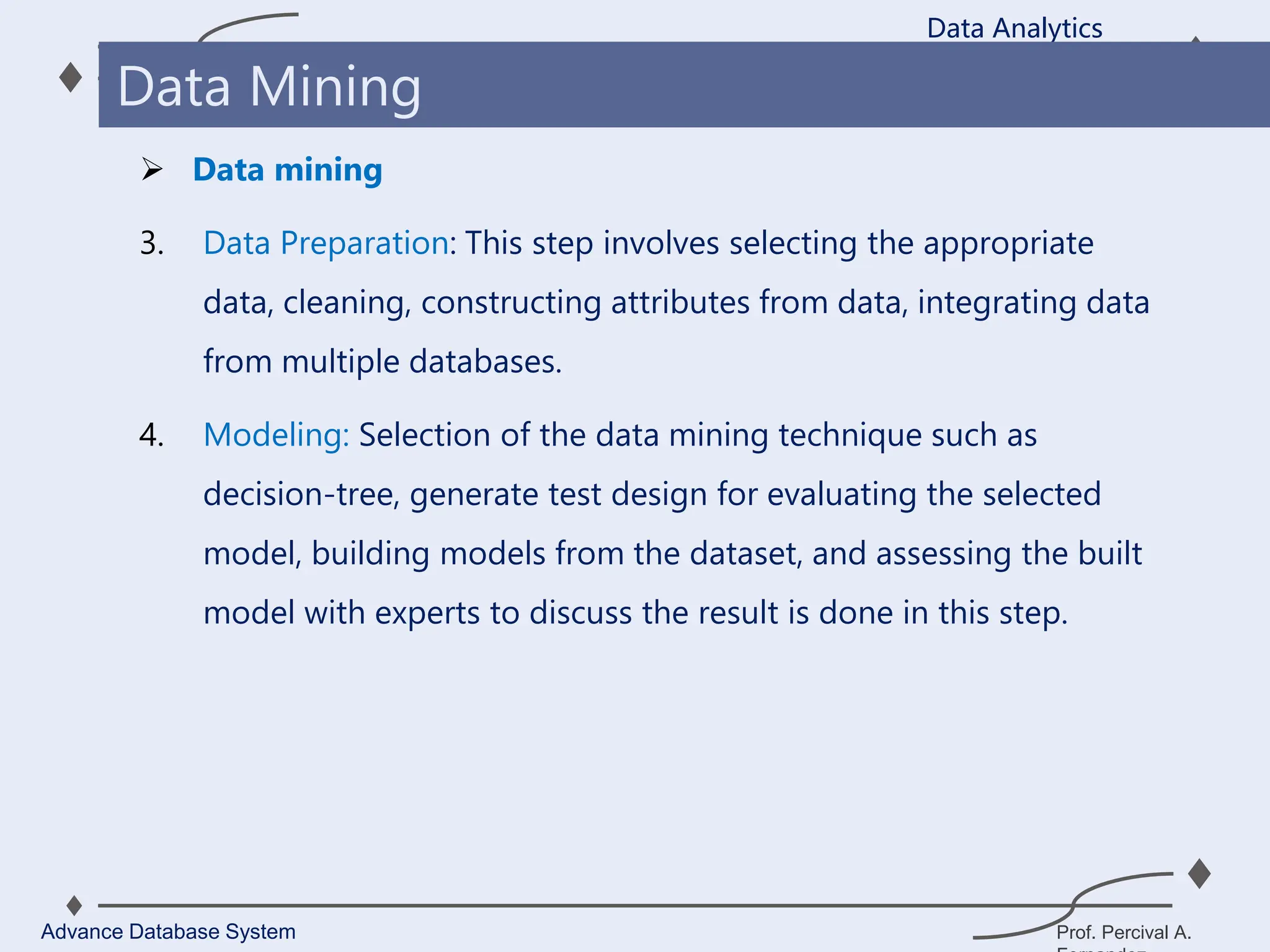
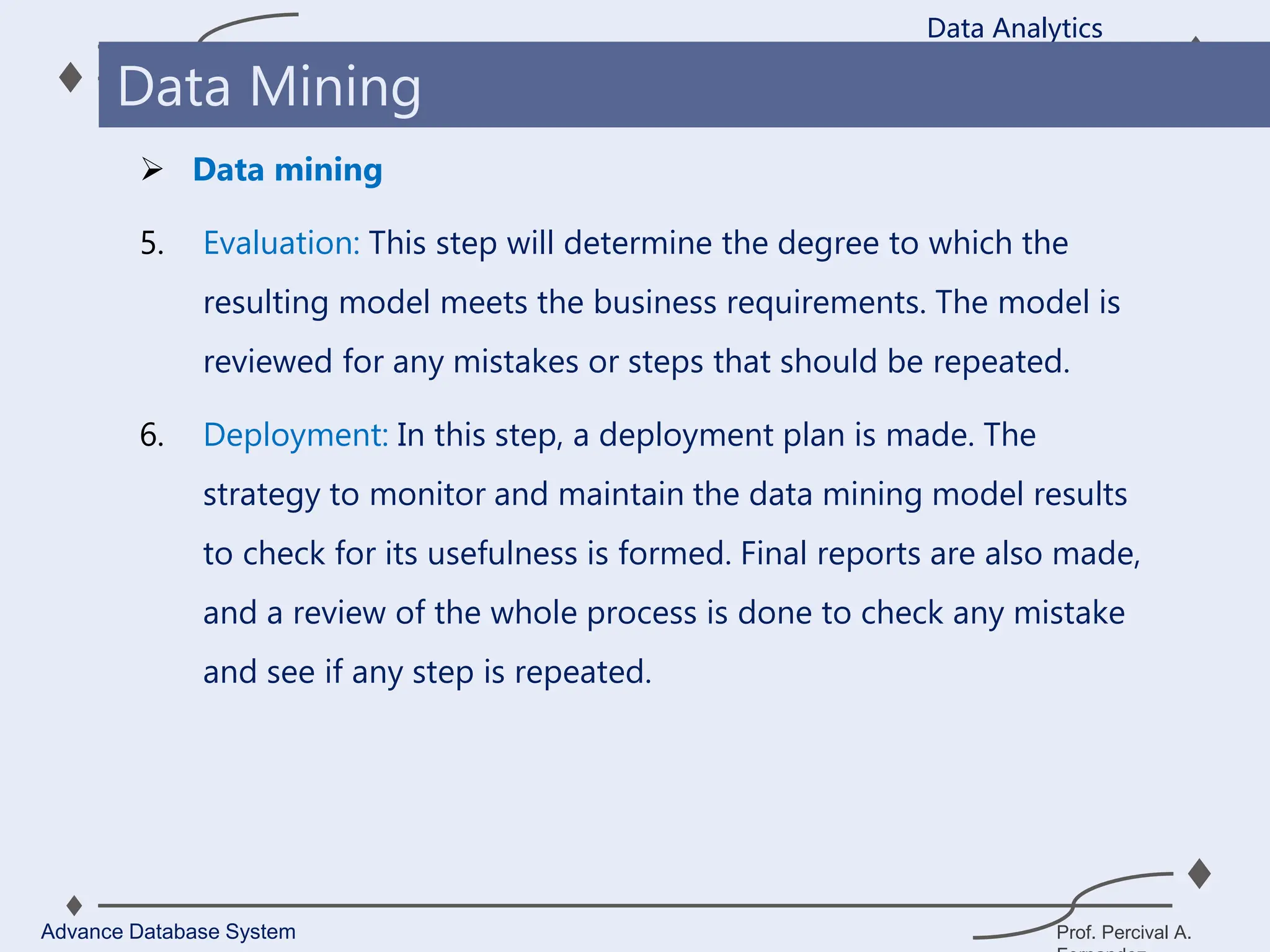
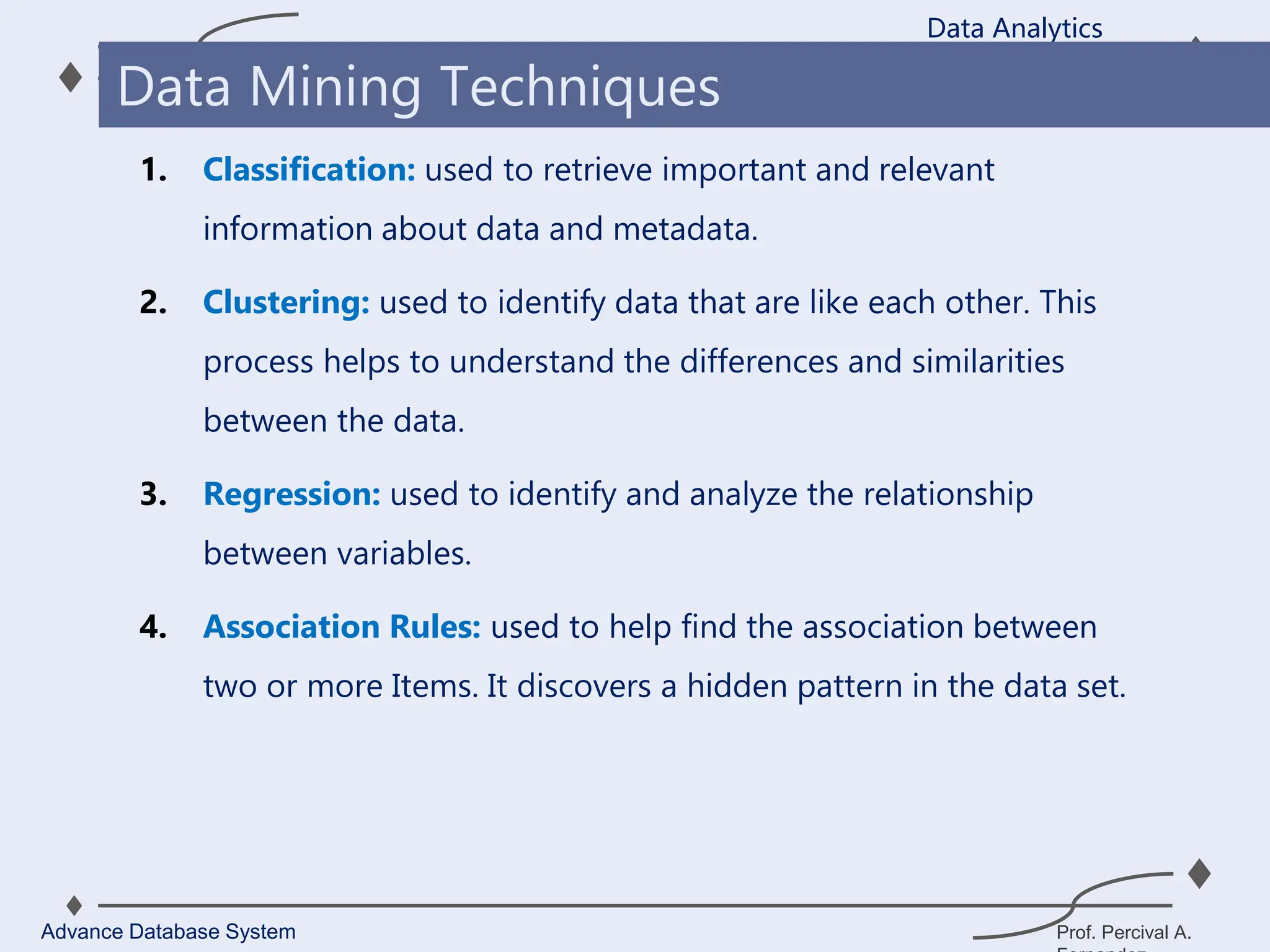
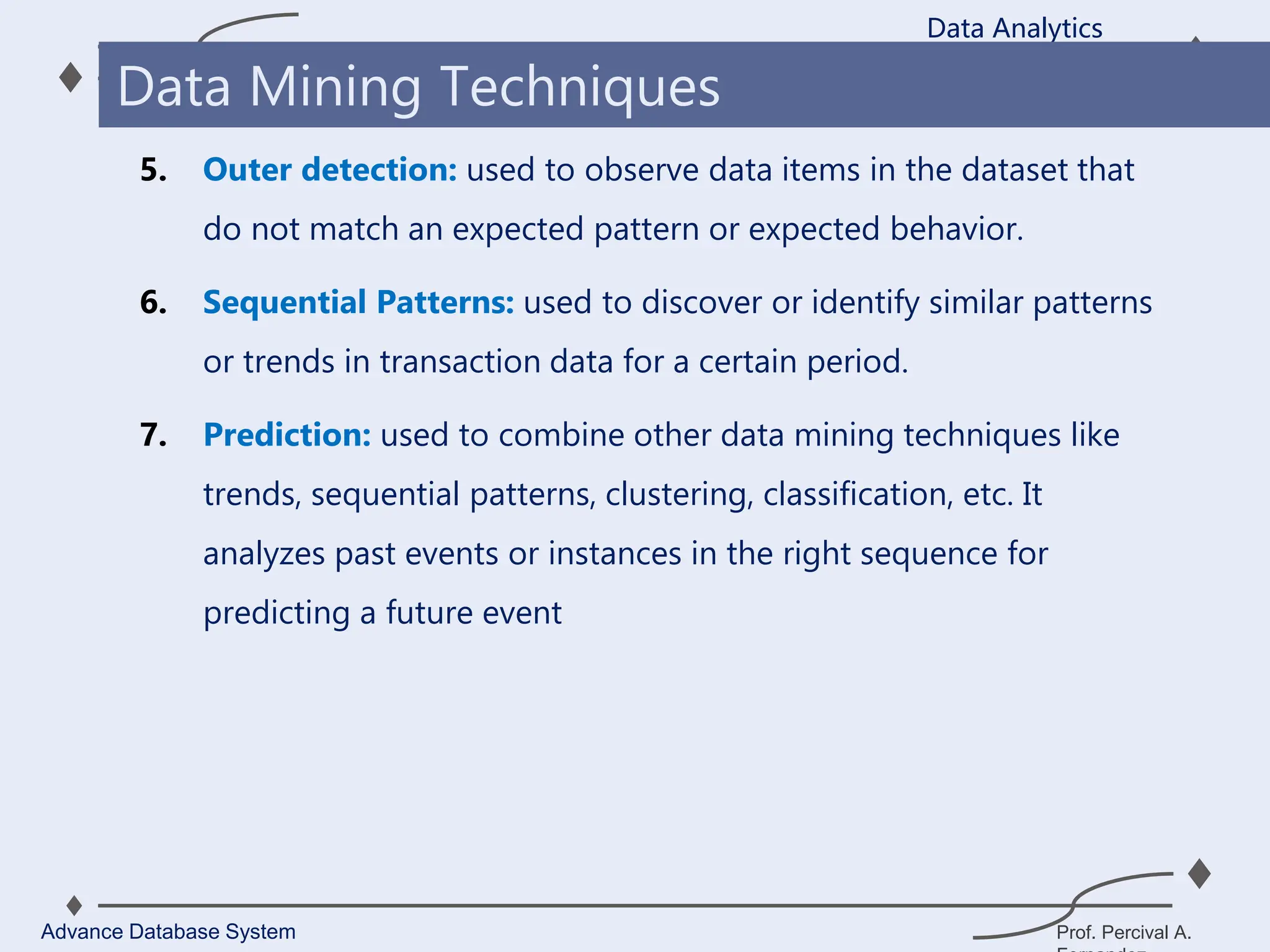
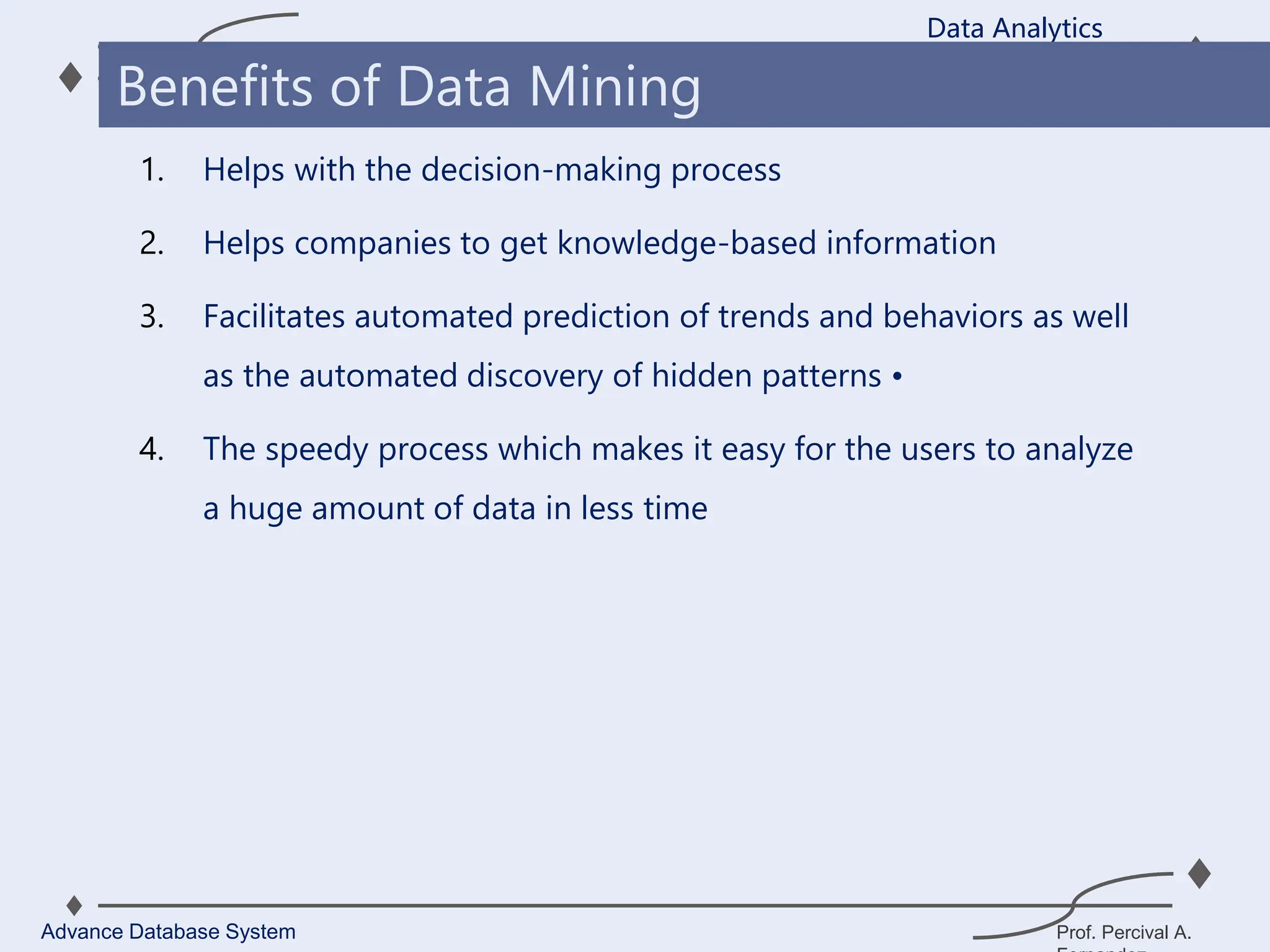
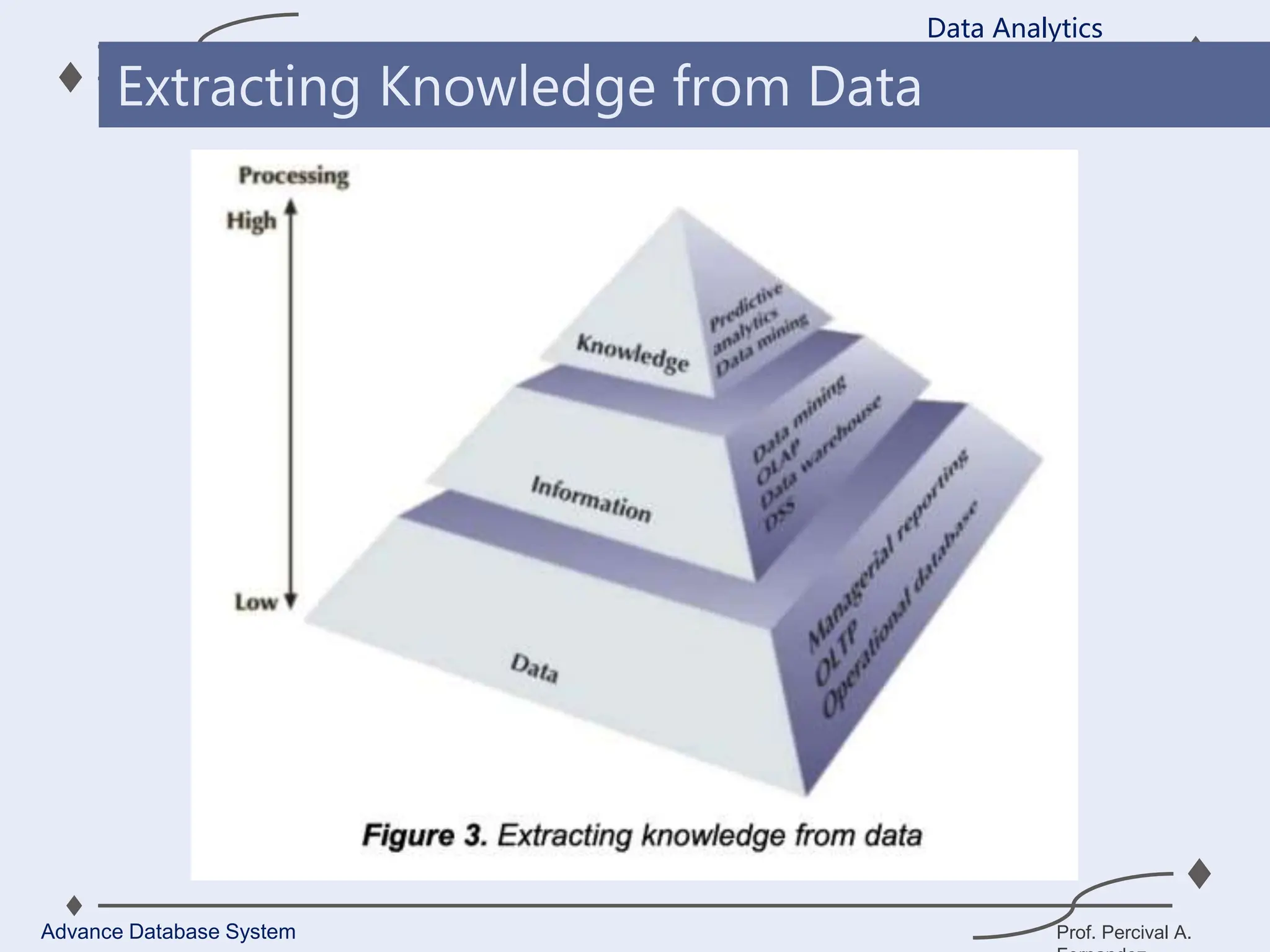
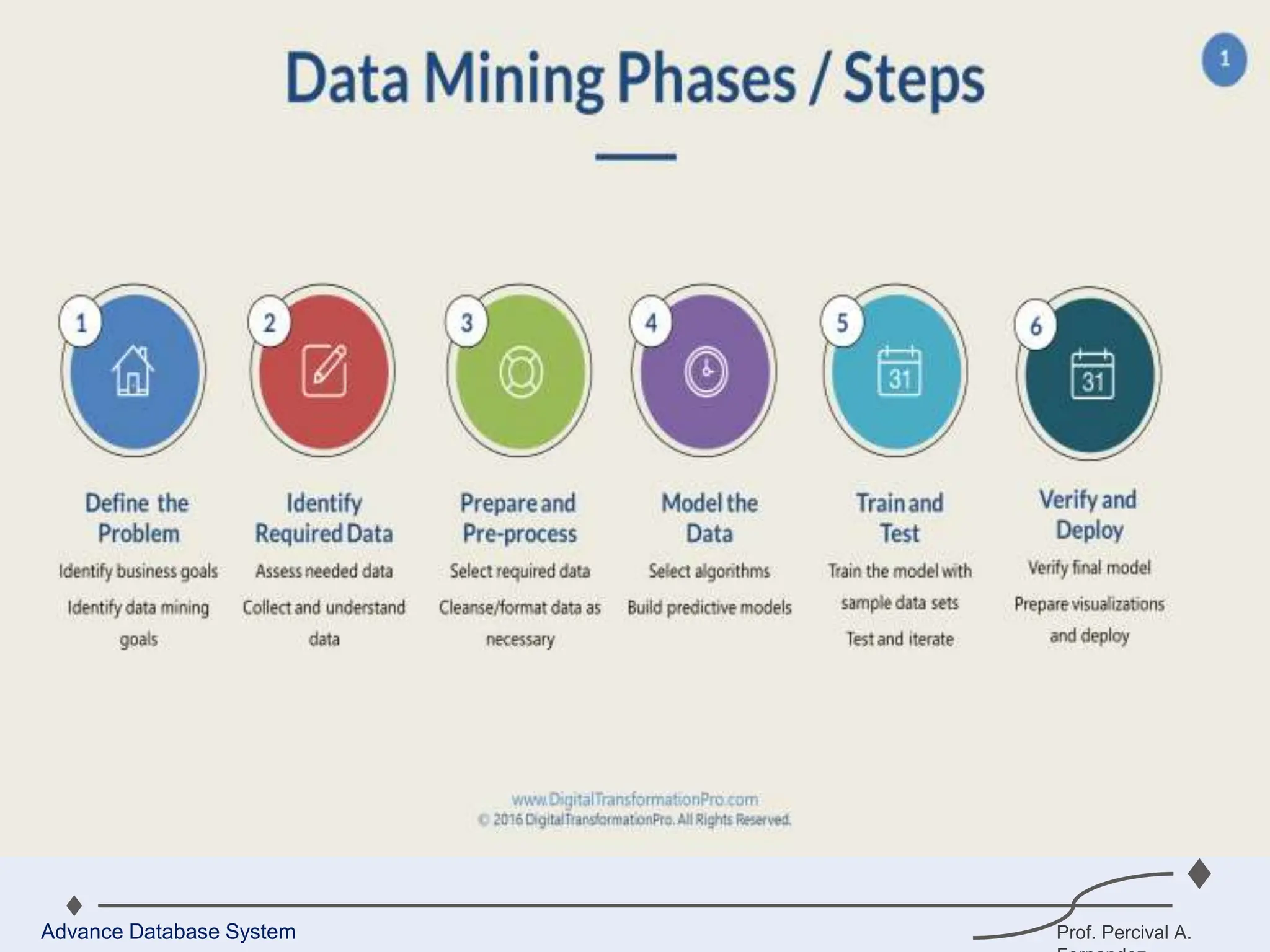
1. A data warehouse is a database designed to support business intelligence and analytics by consolidating large amounts of data from multiple sources into a single repository for analysis and reporting.
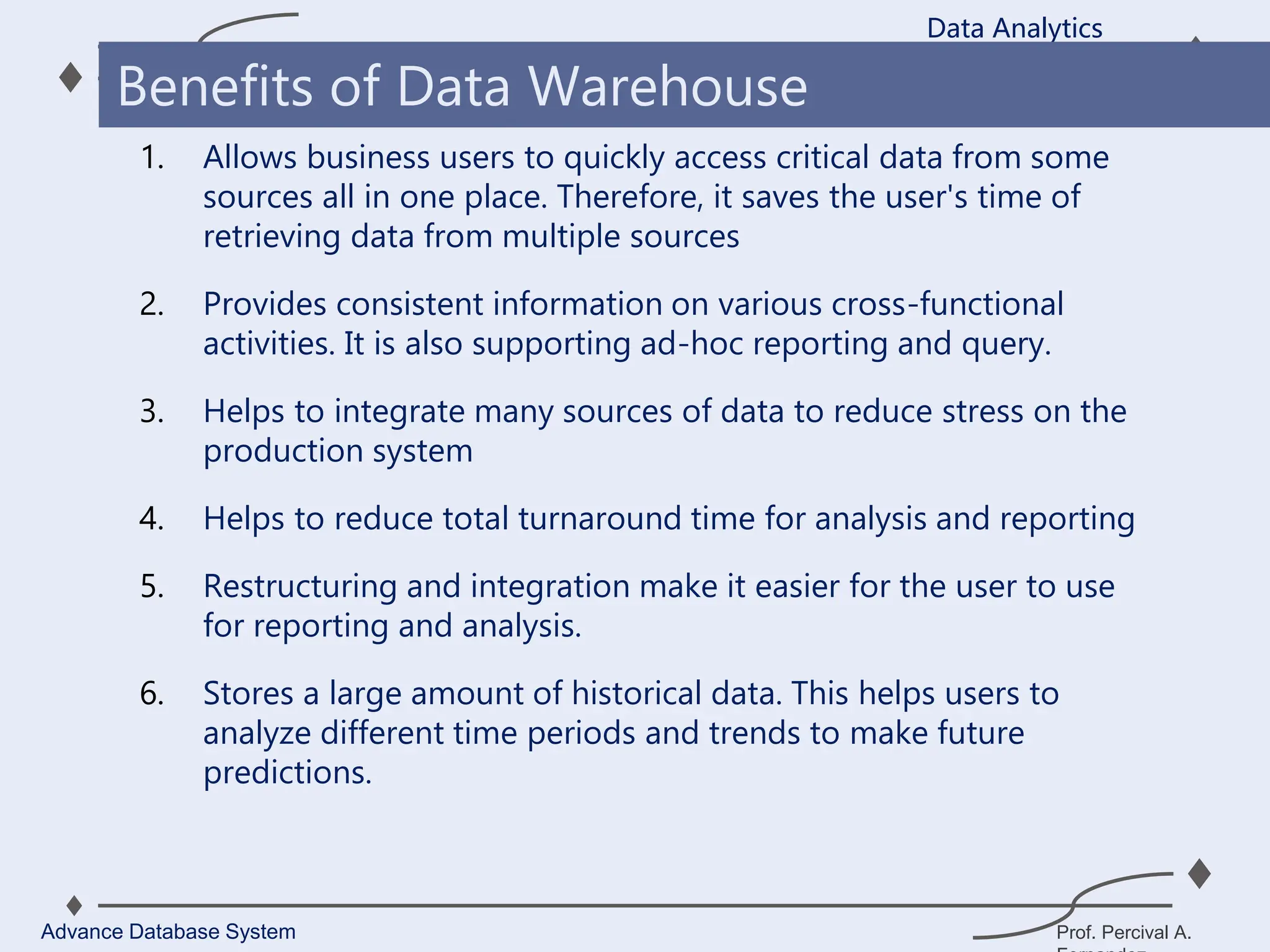
2. It allows organizations to derive valuable insights from their data to improve decision-making and can be considered an organization’s single source of truth.
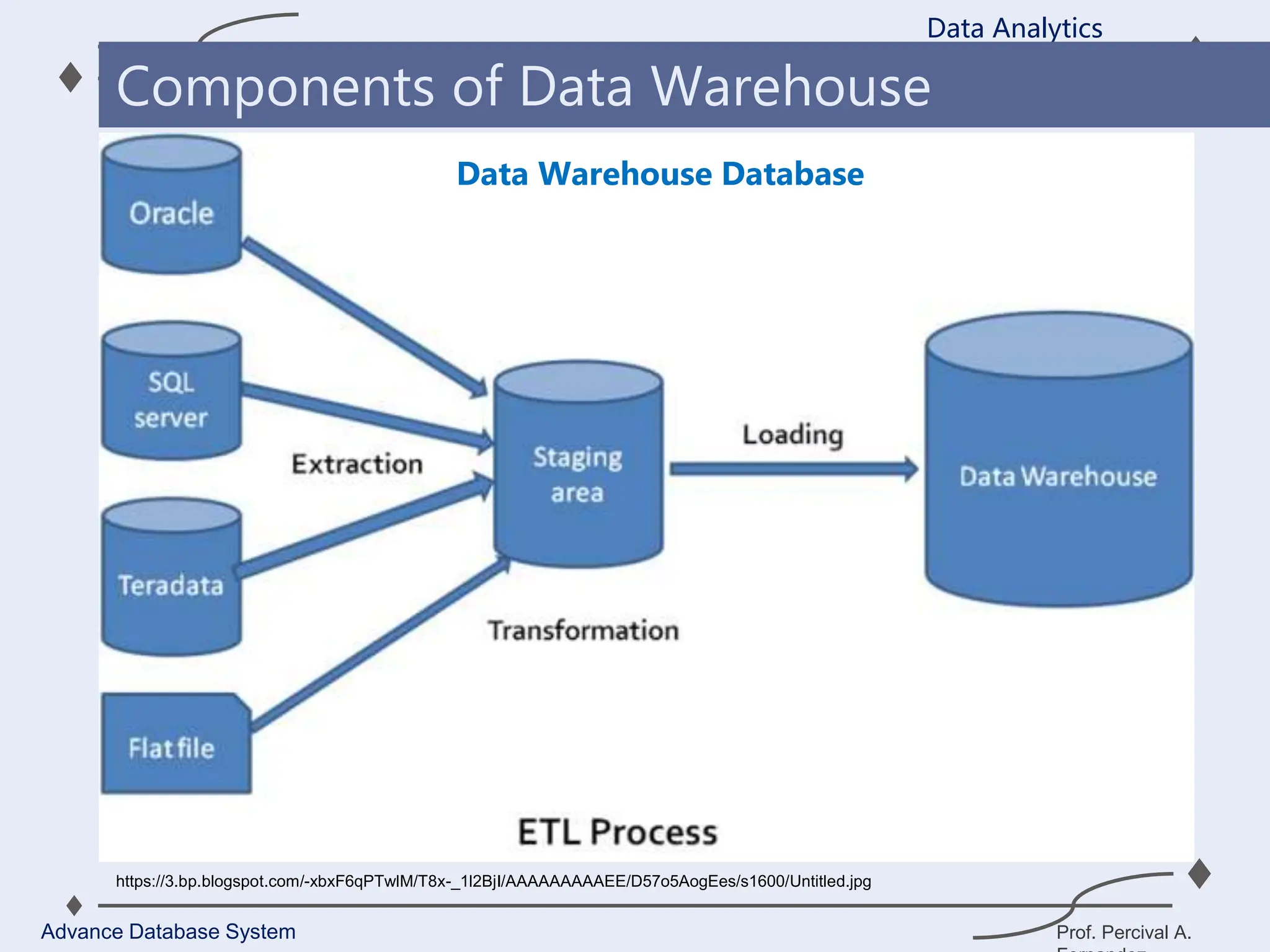
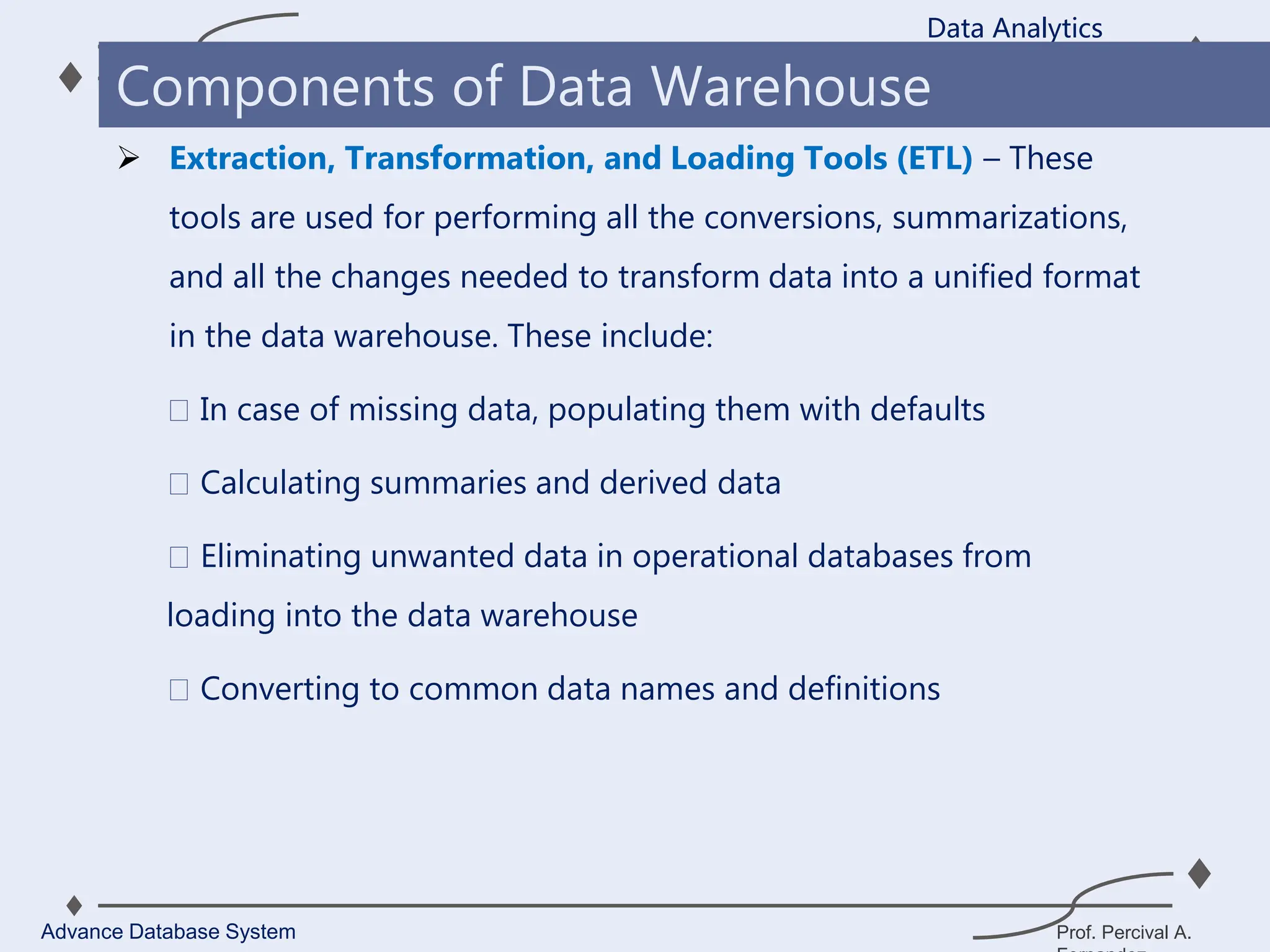
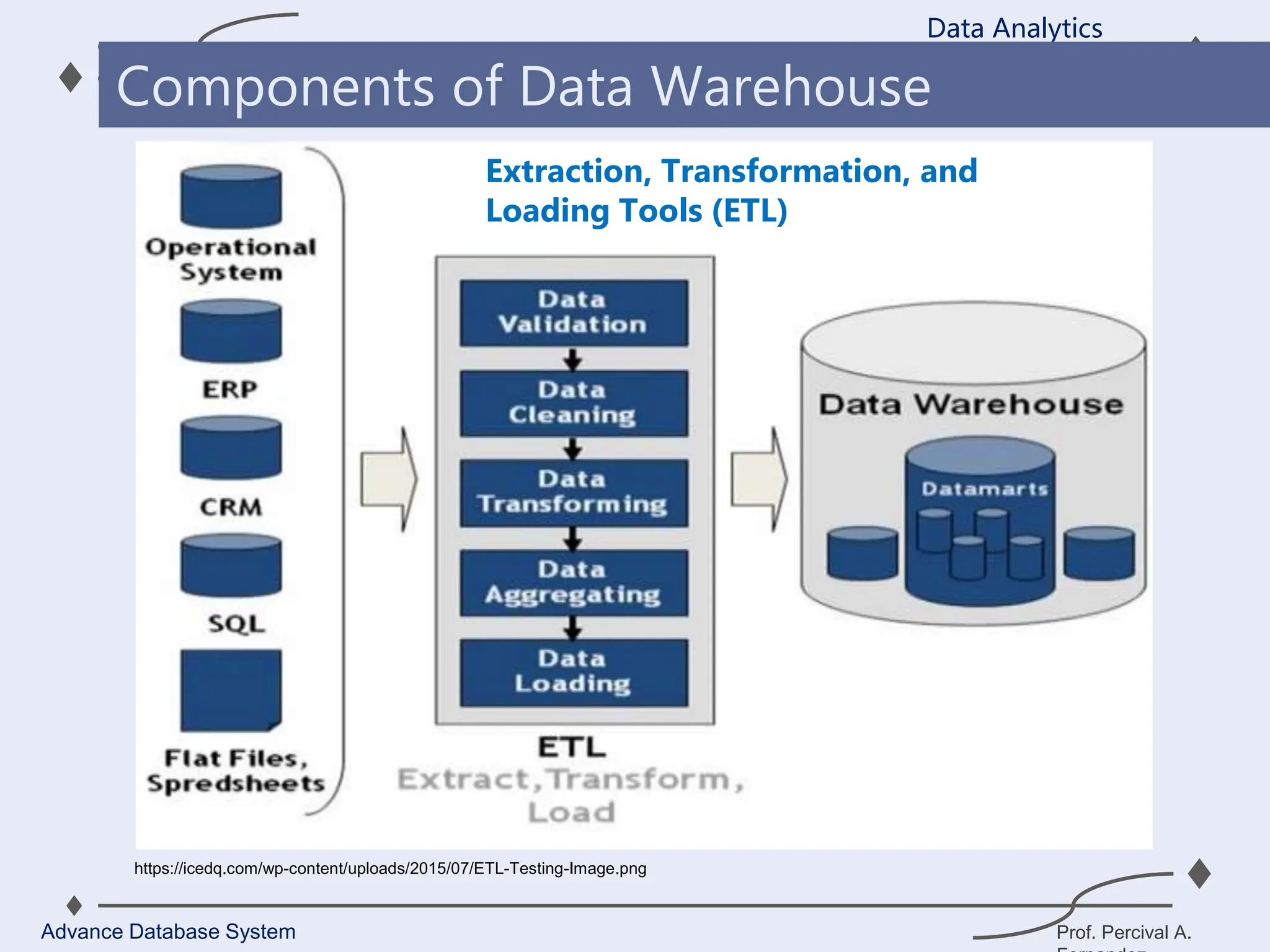
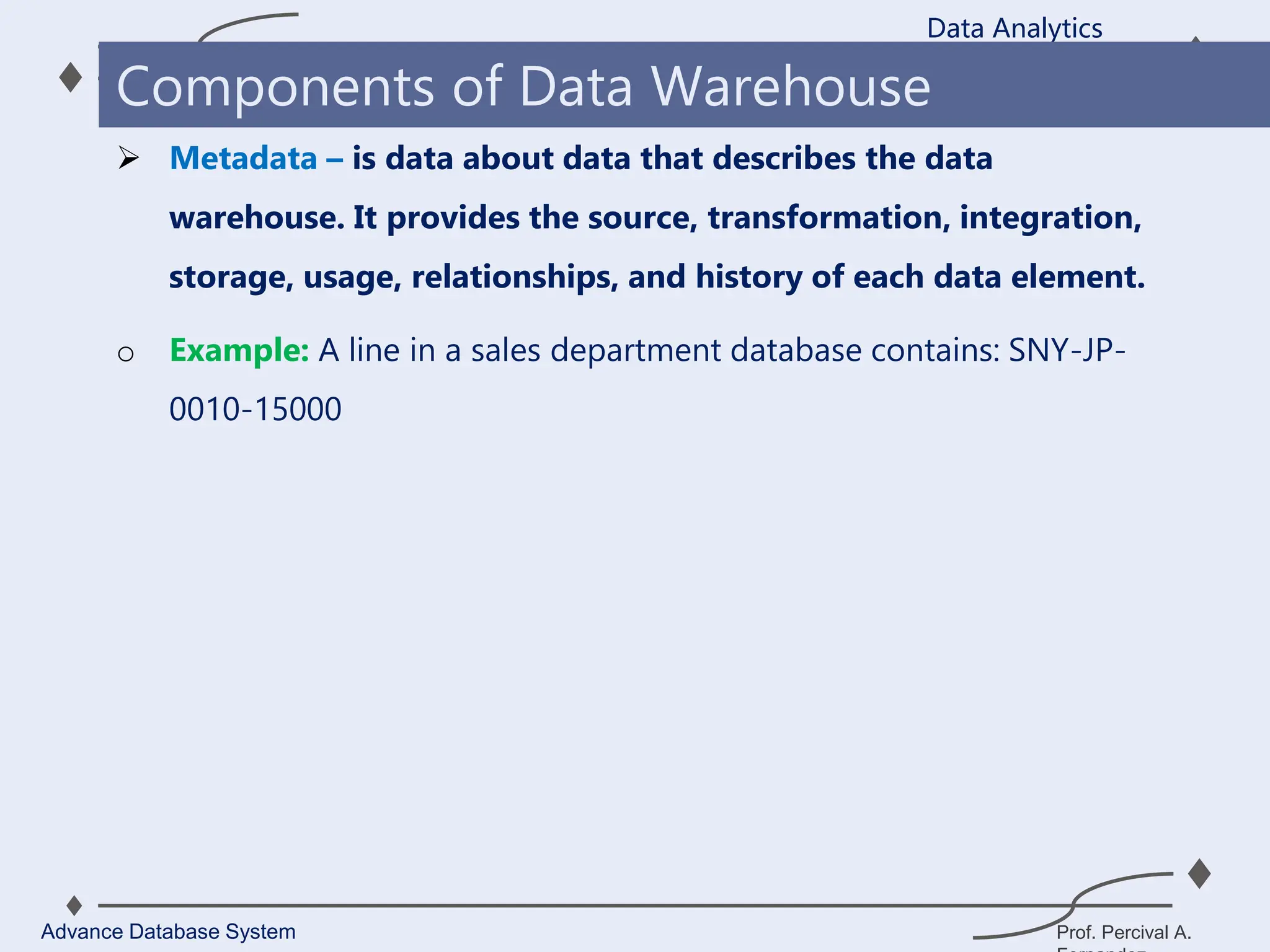
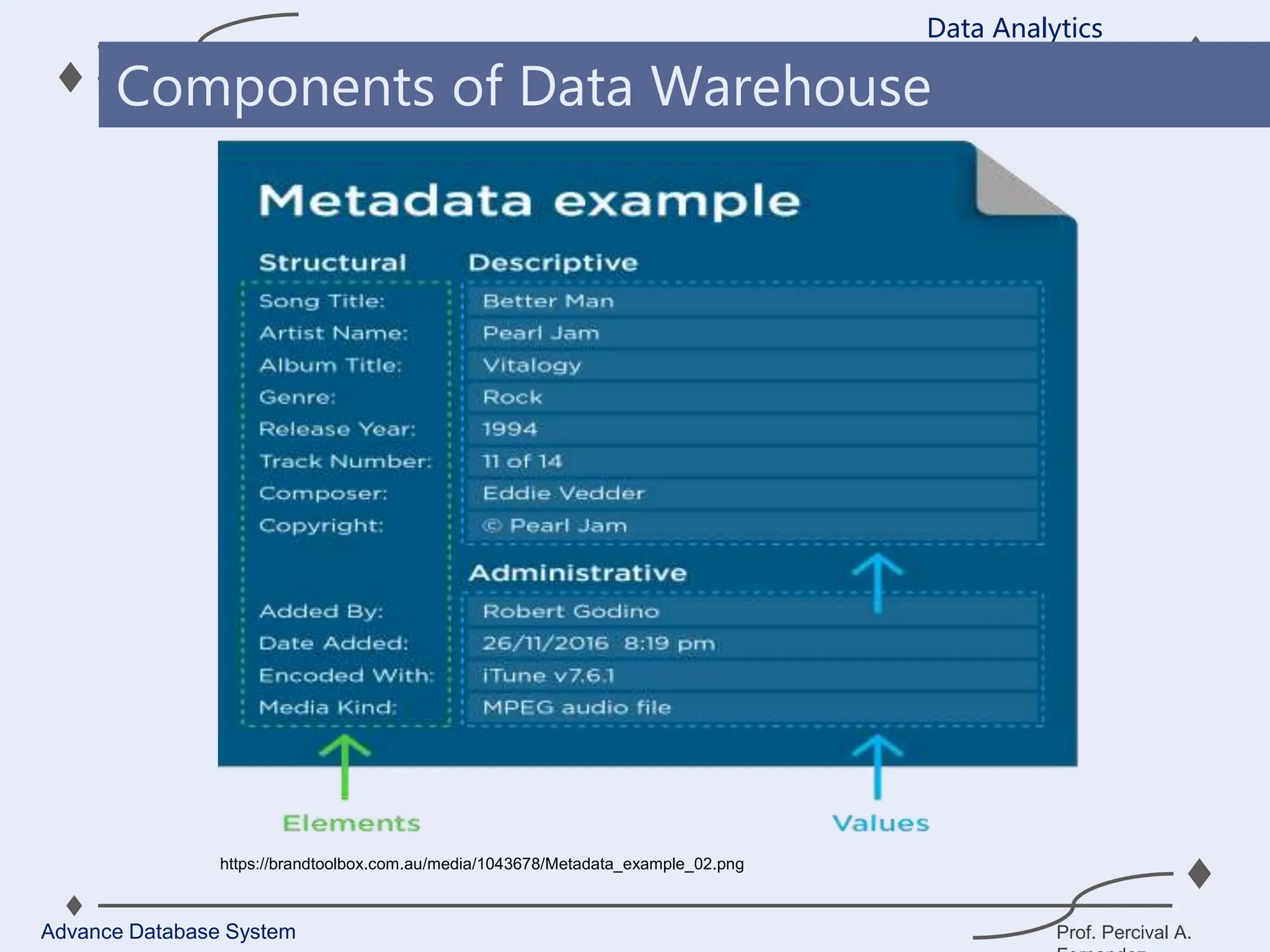
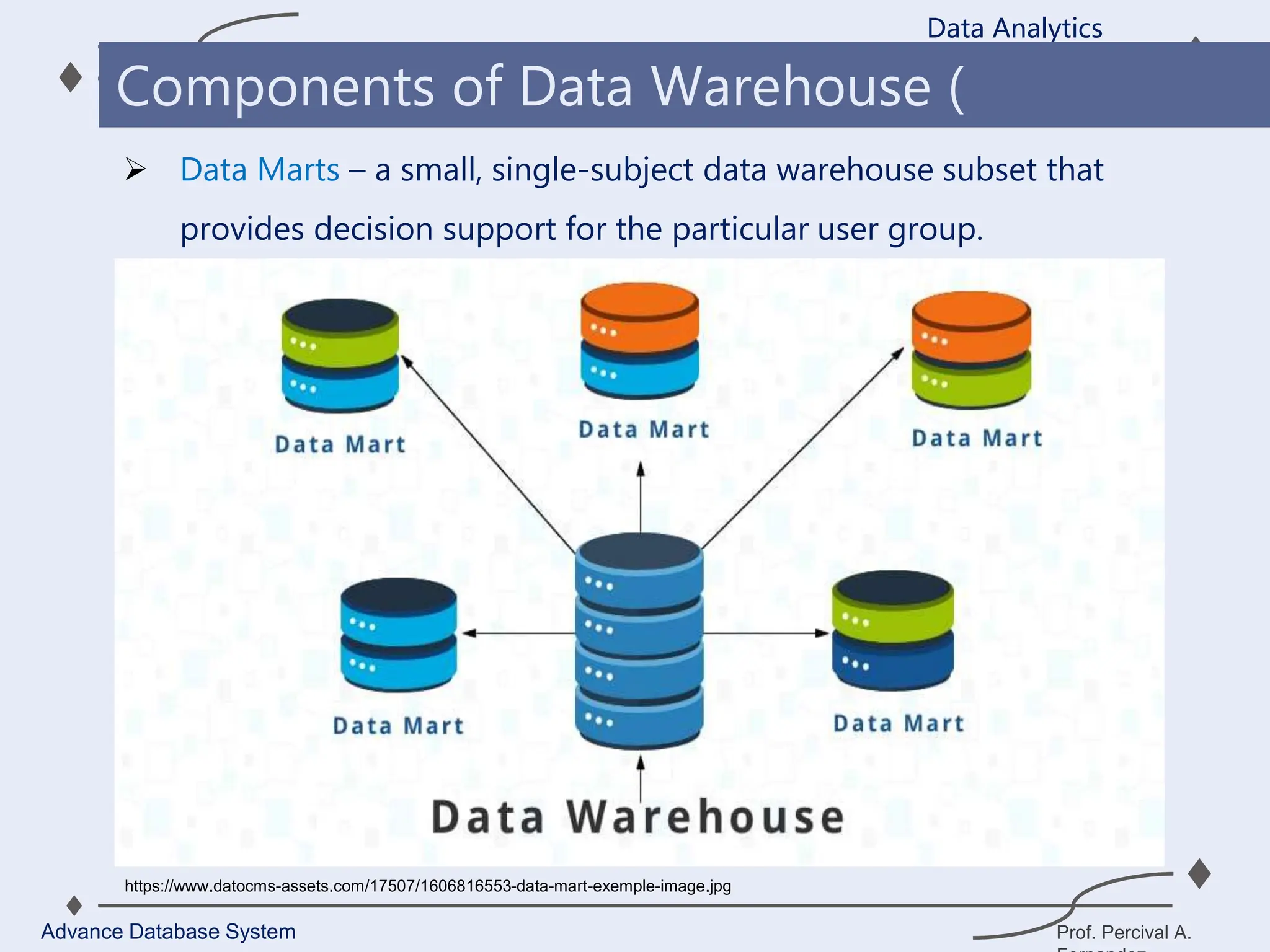
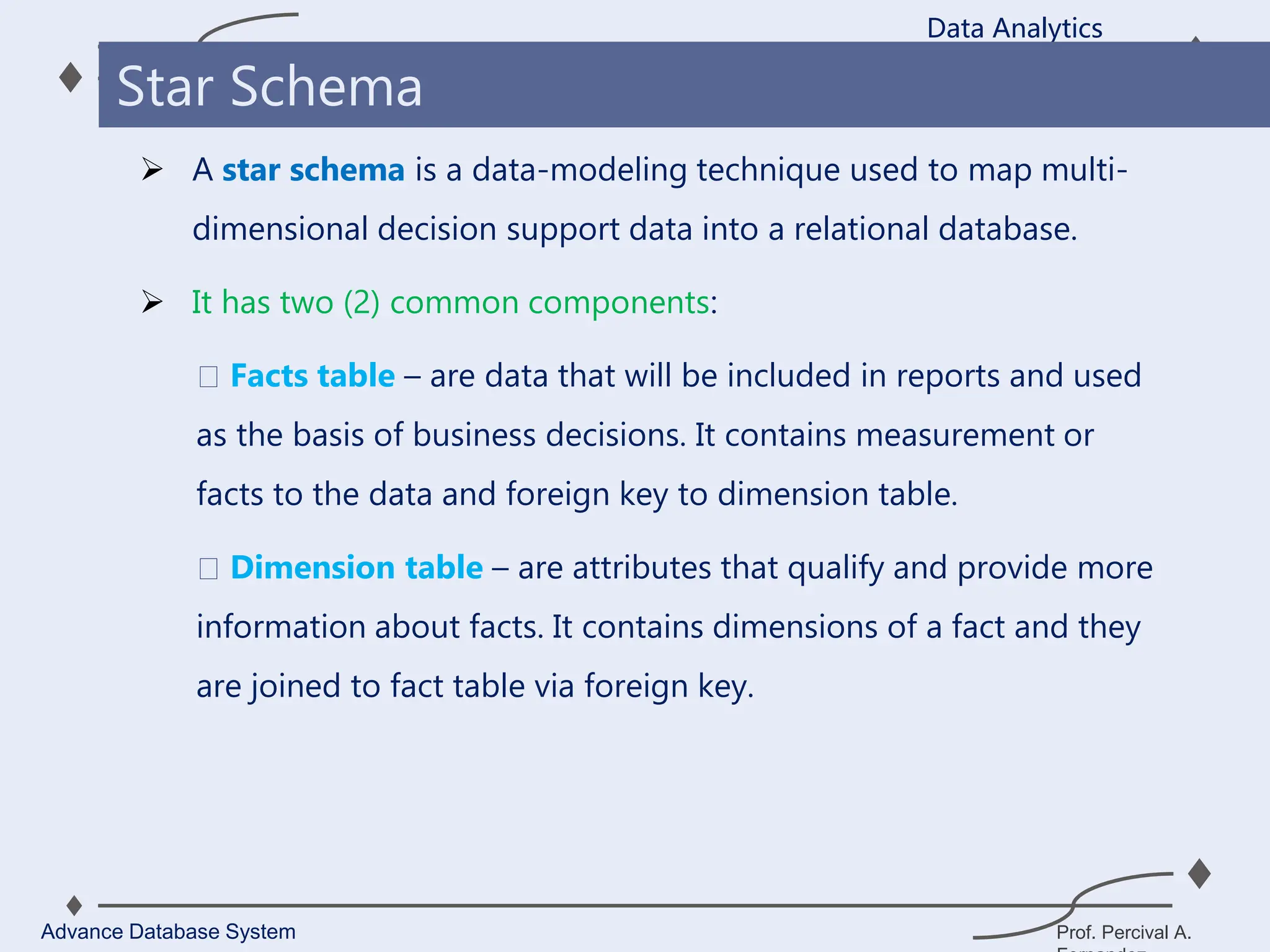
3. Key components of a data warehouse include the data warehouse database, extraction, transformation, and loading tools, metadata, access tools, and data marts.