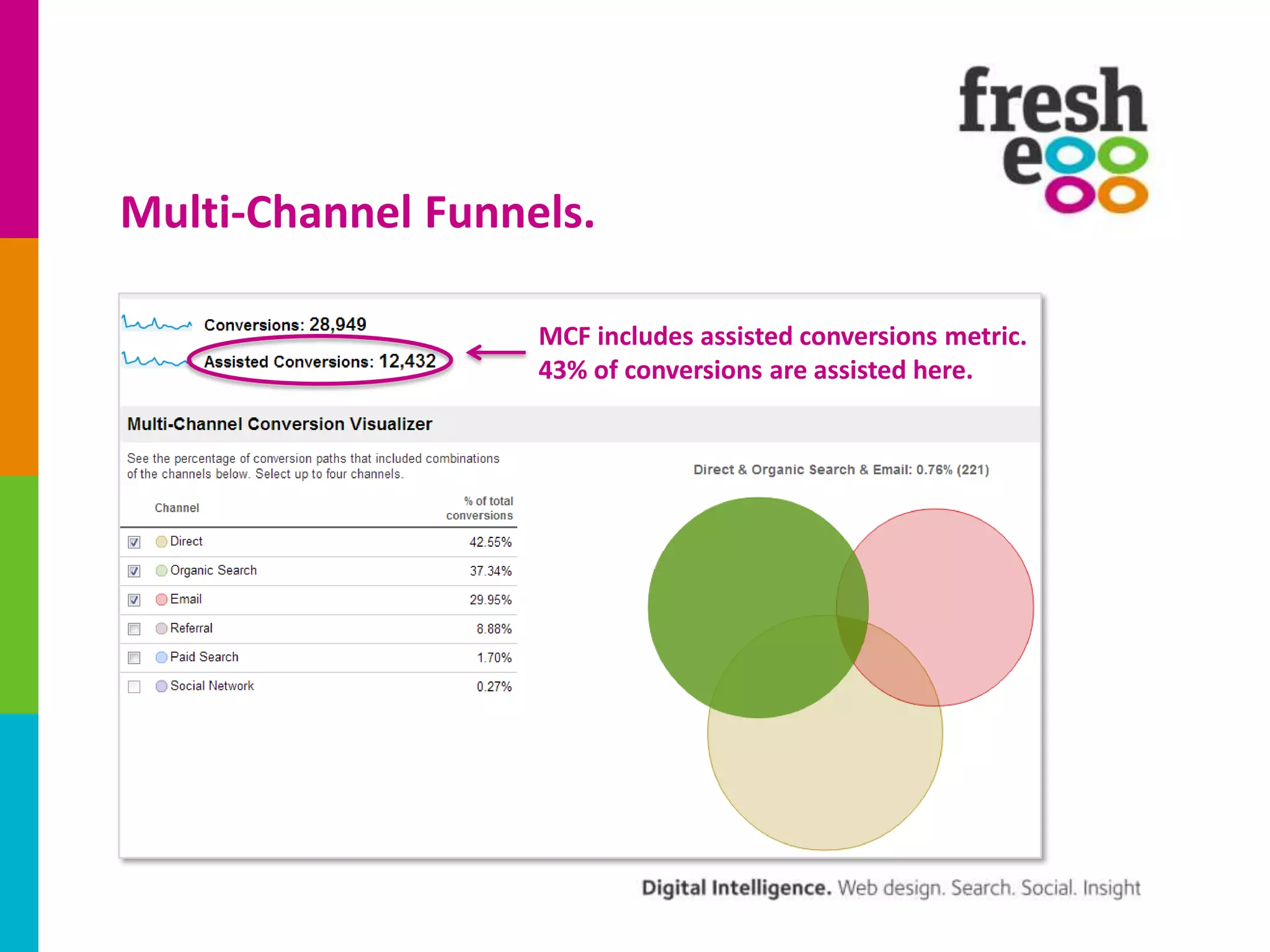
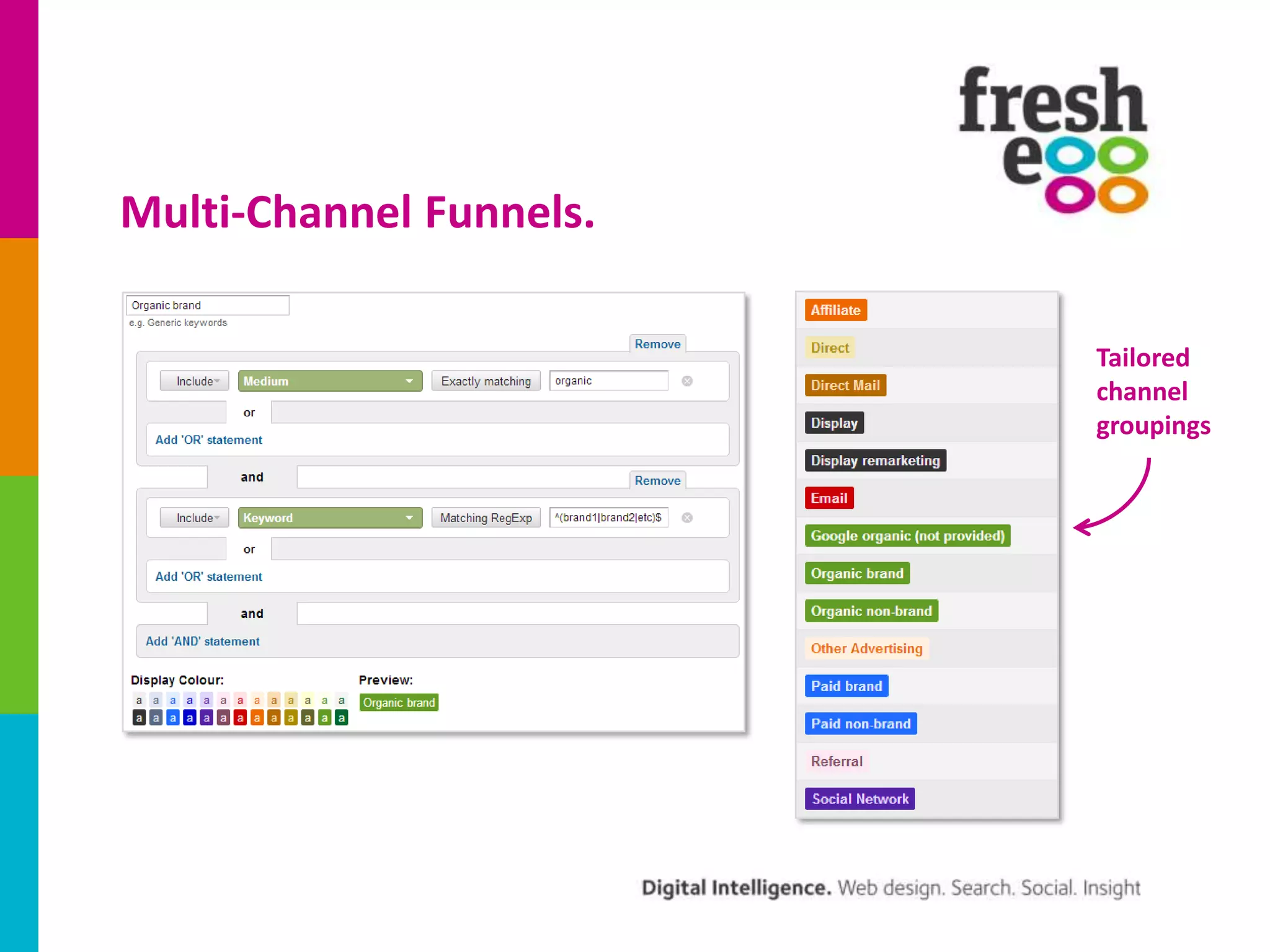
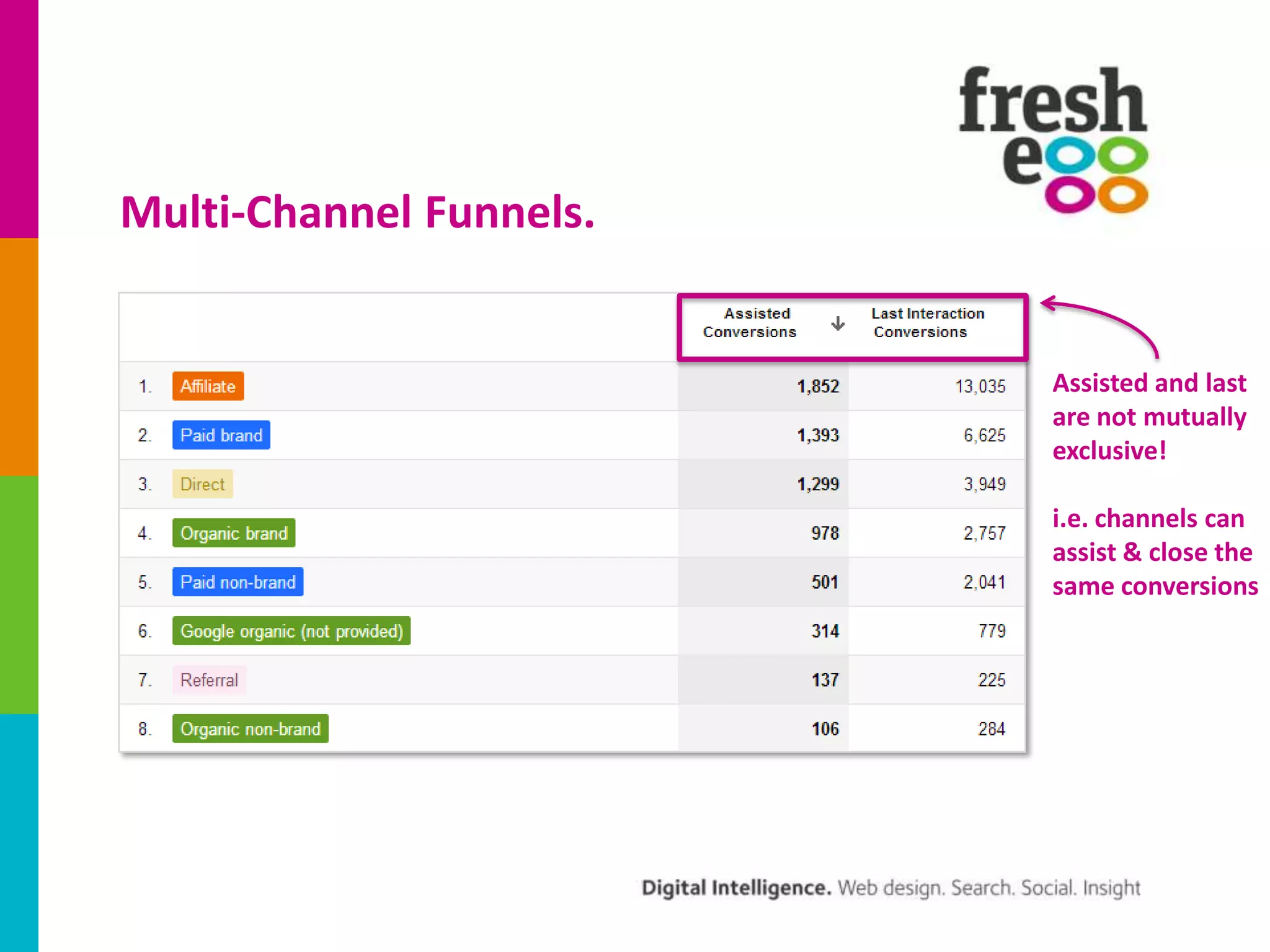
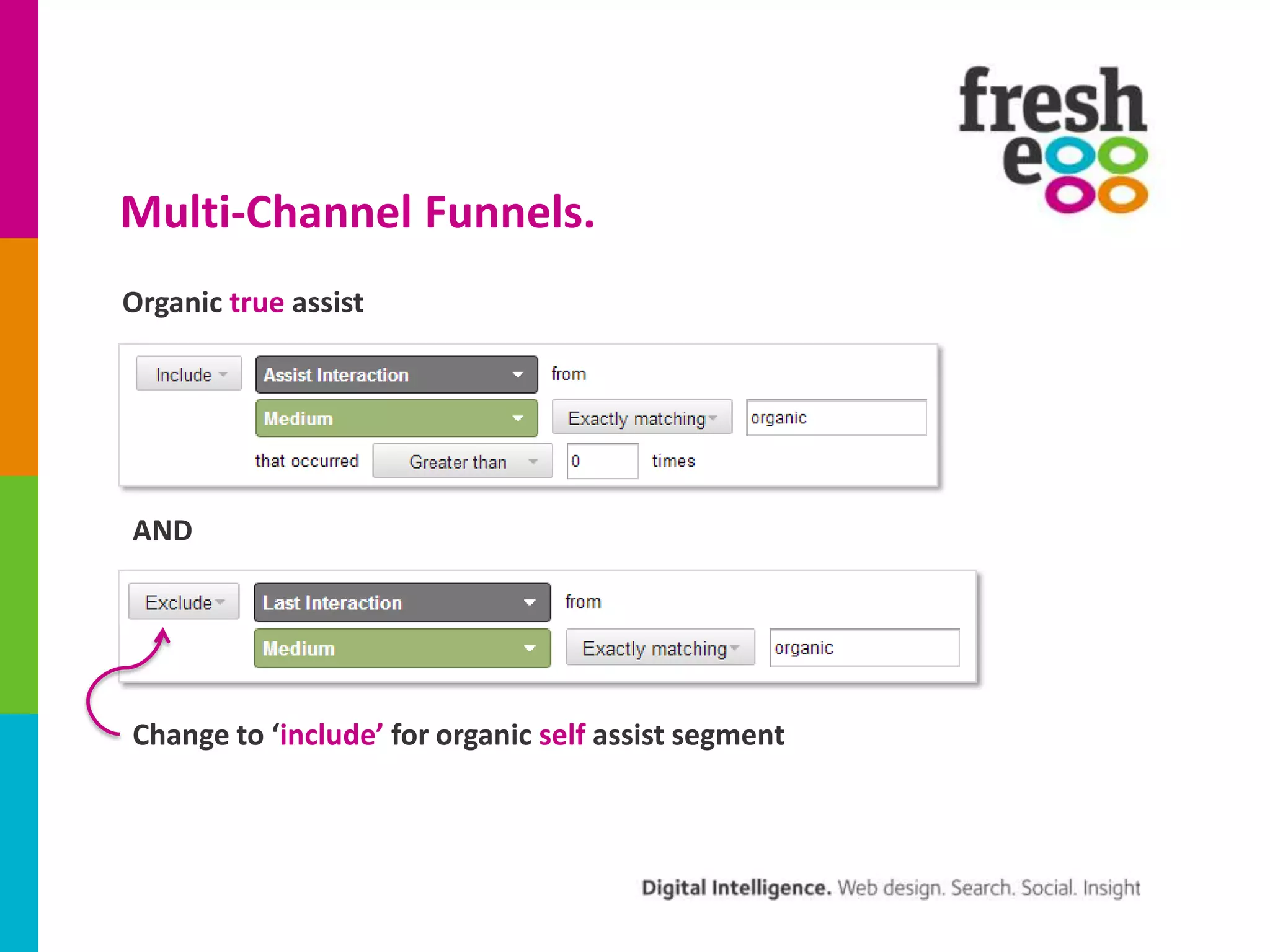
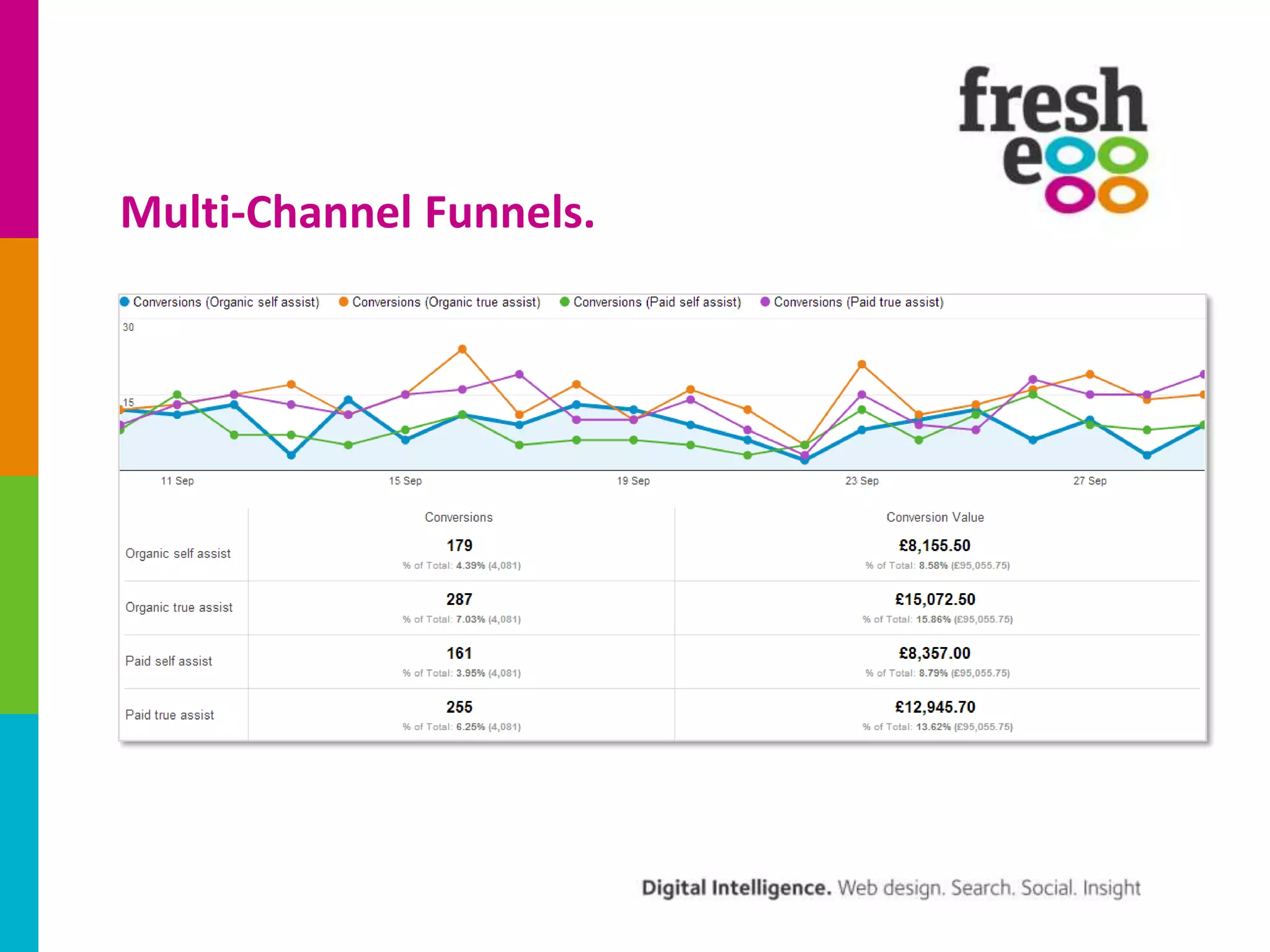
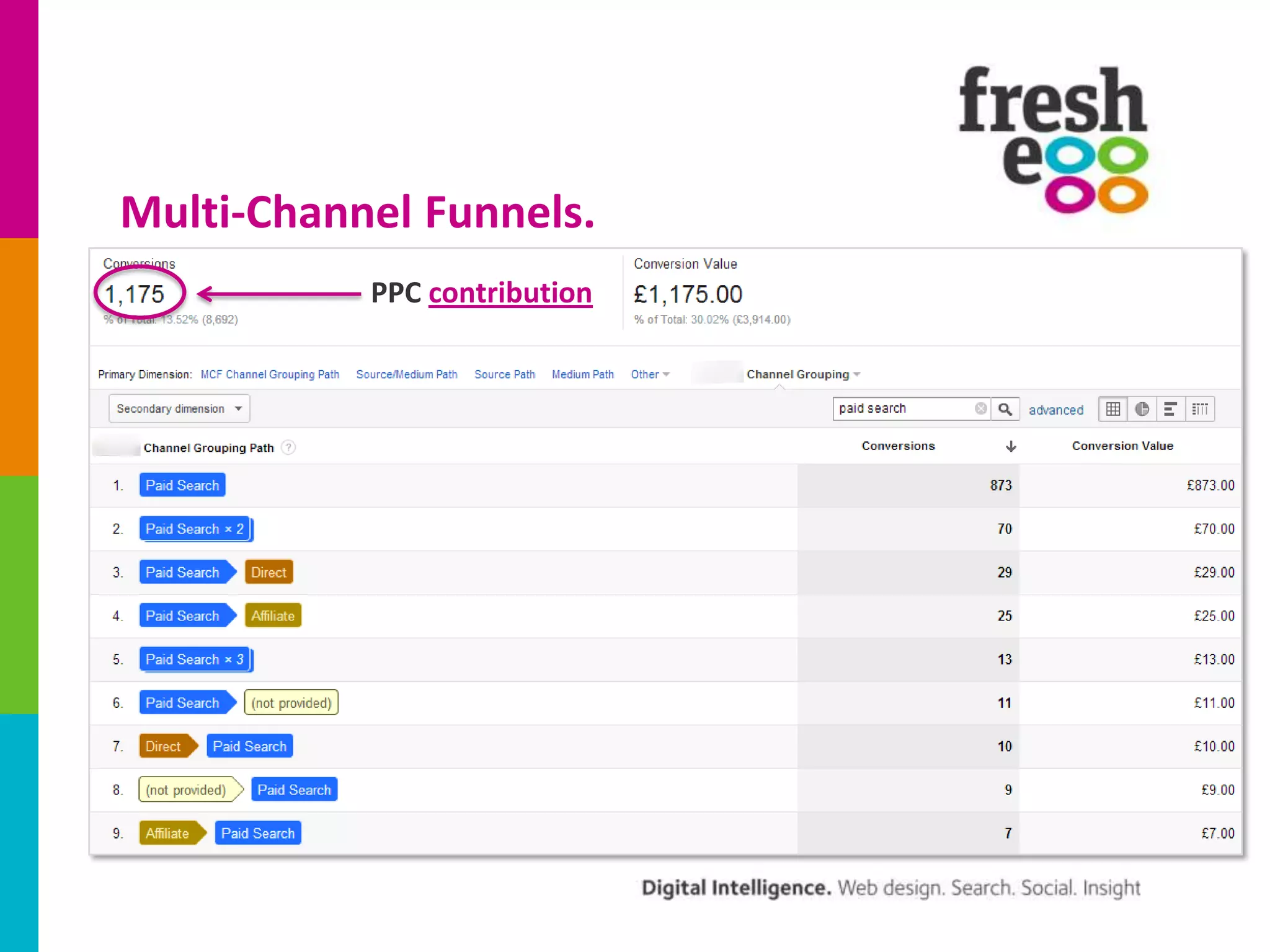
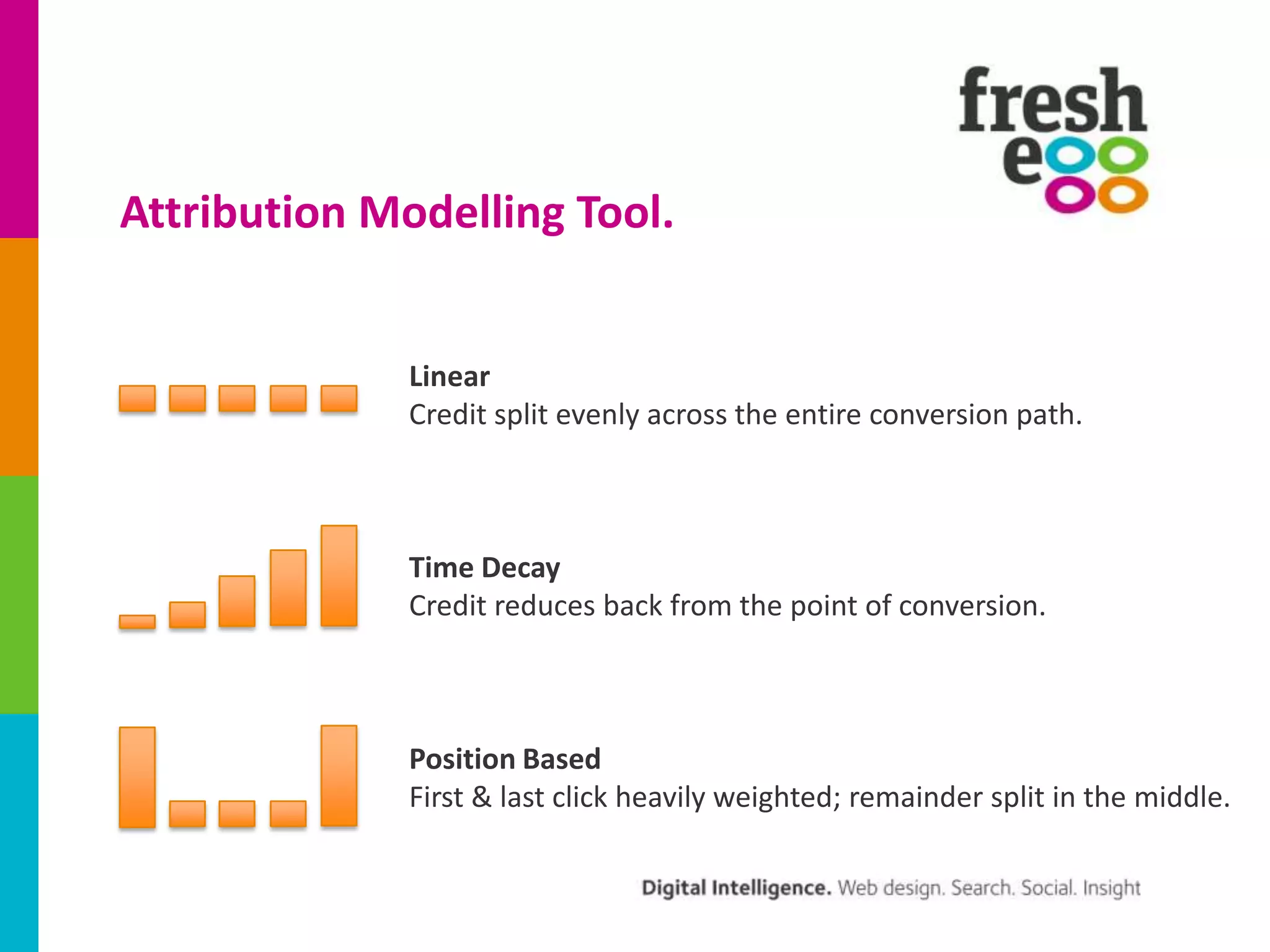
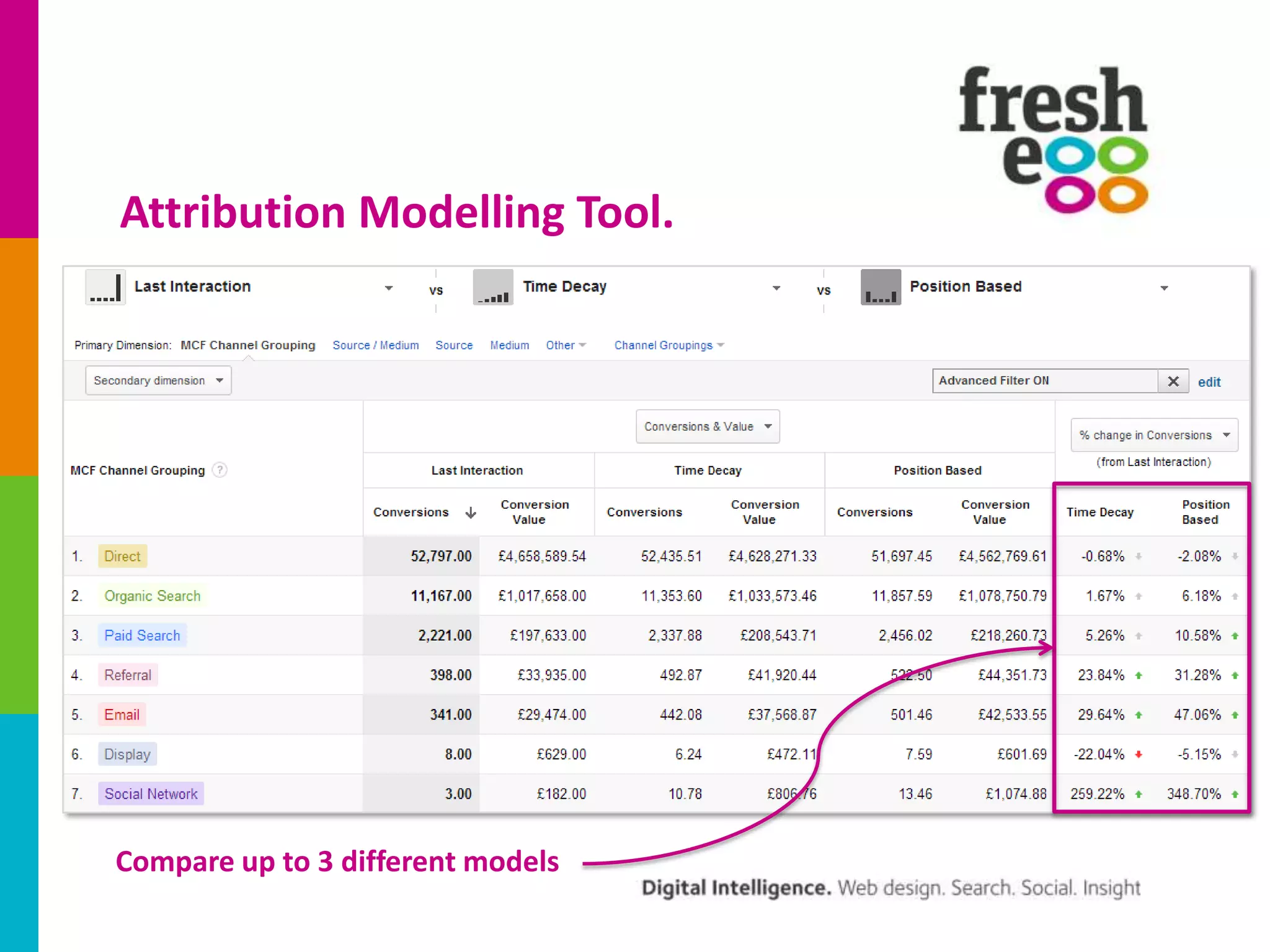
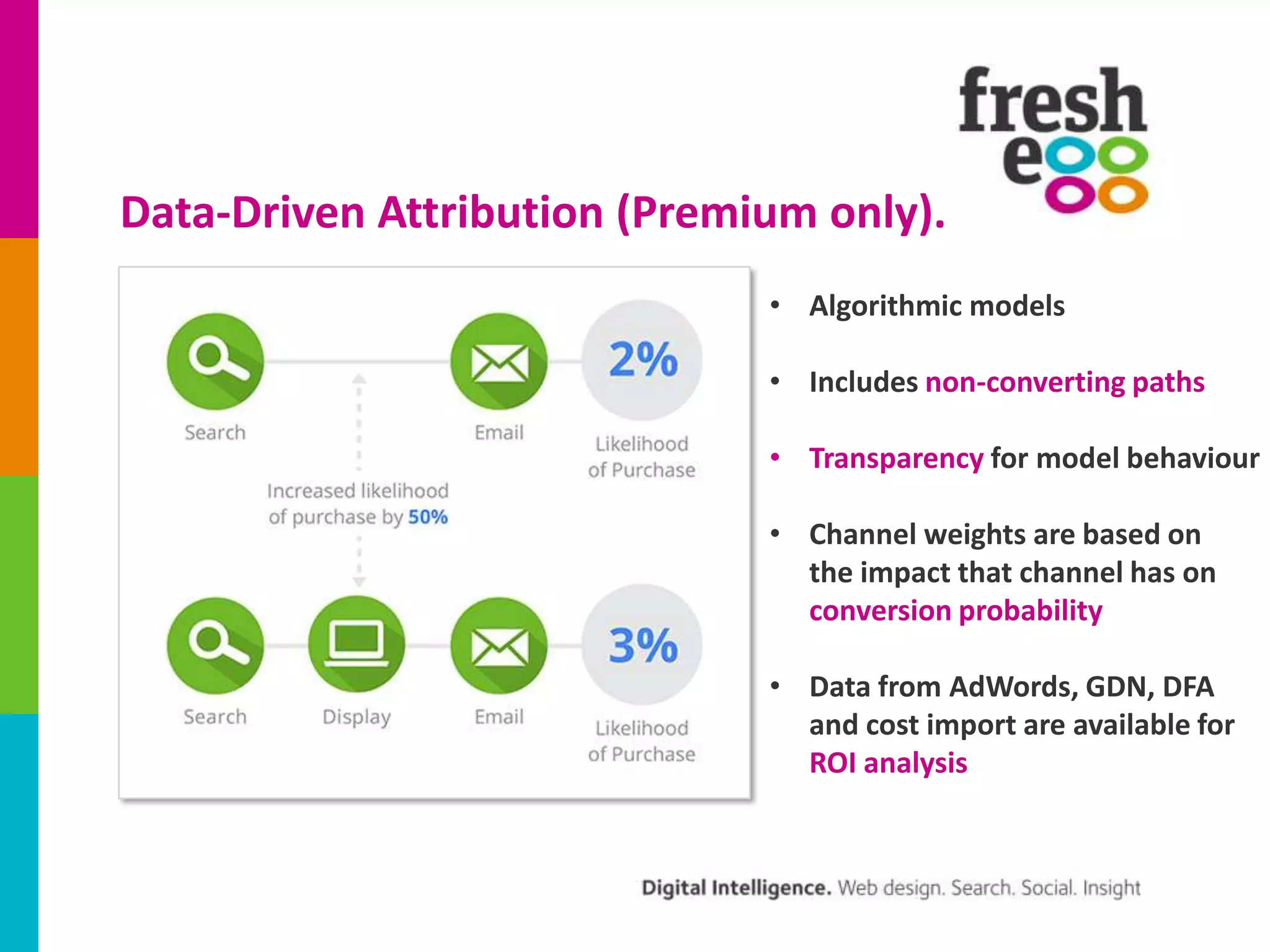
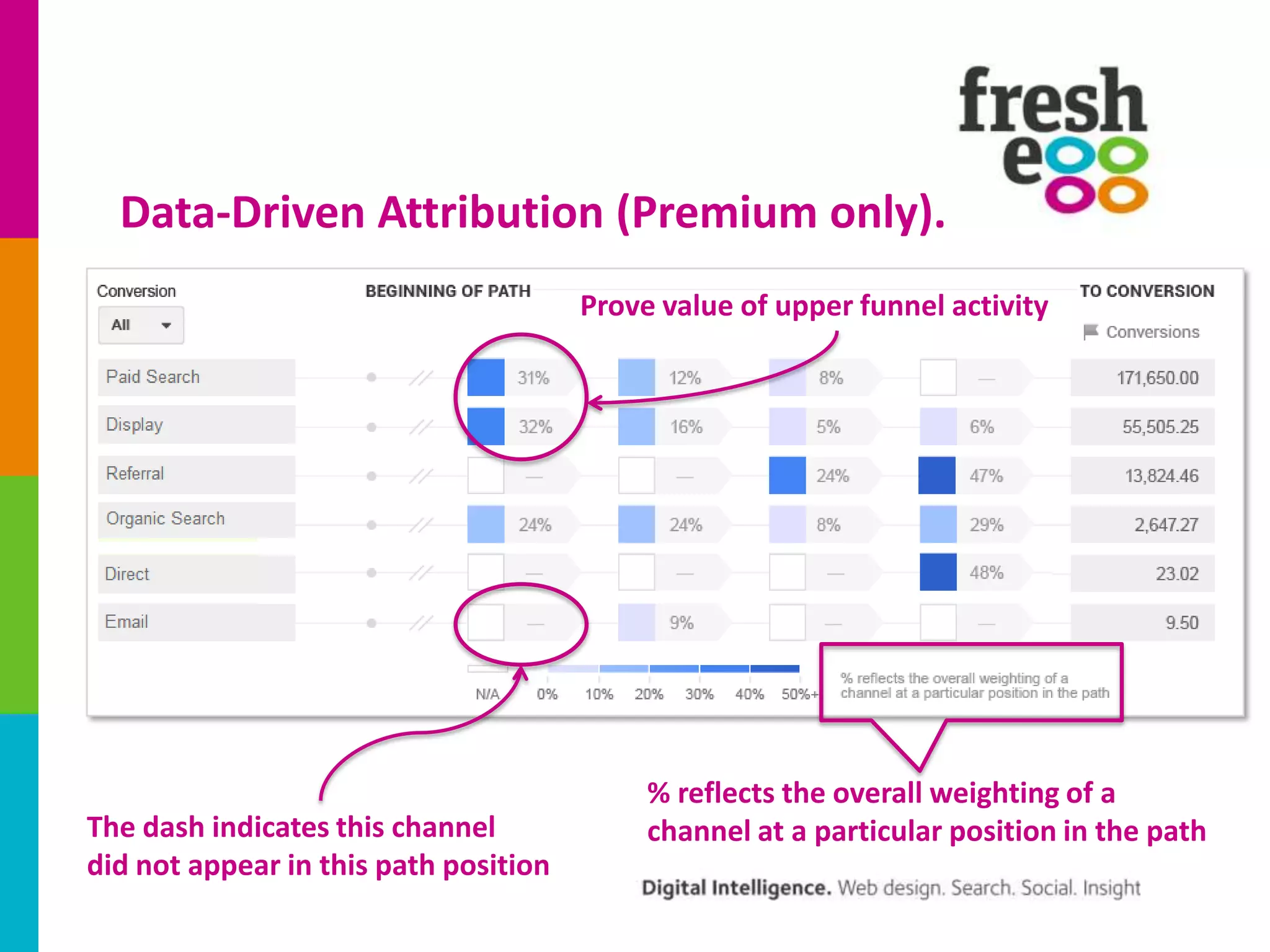
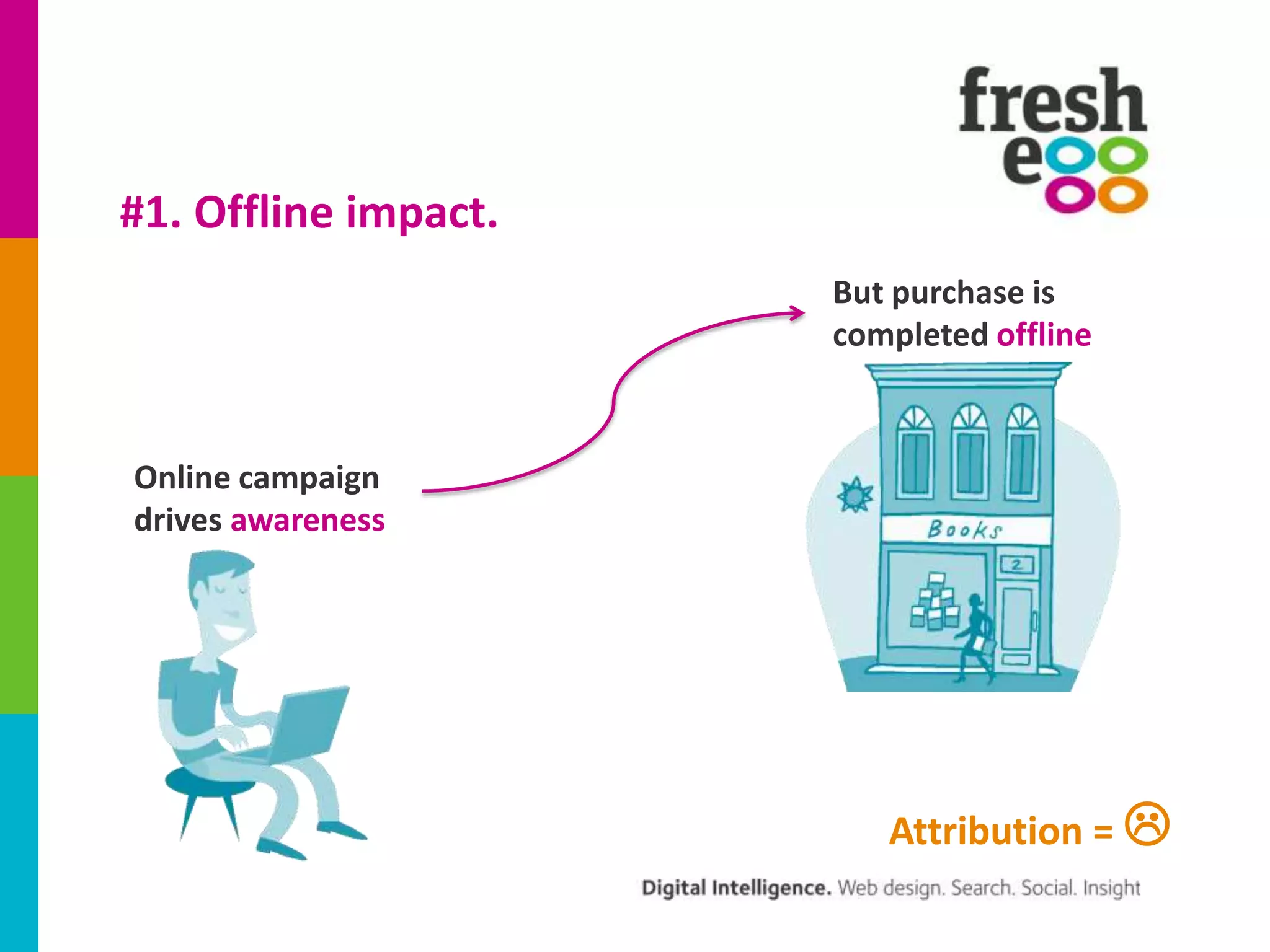
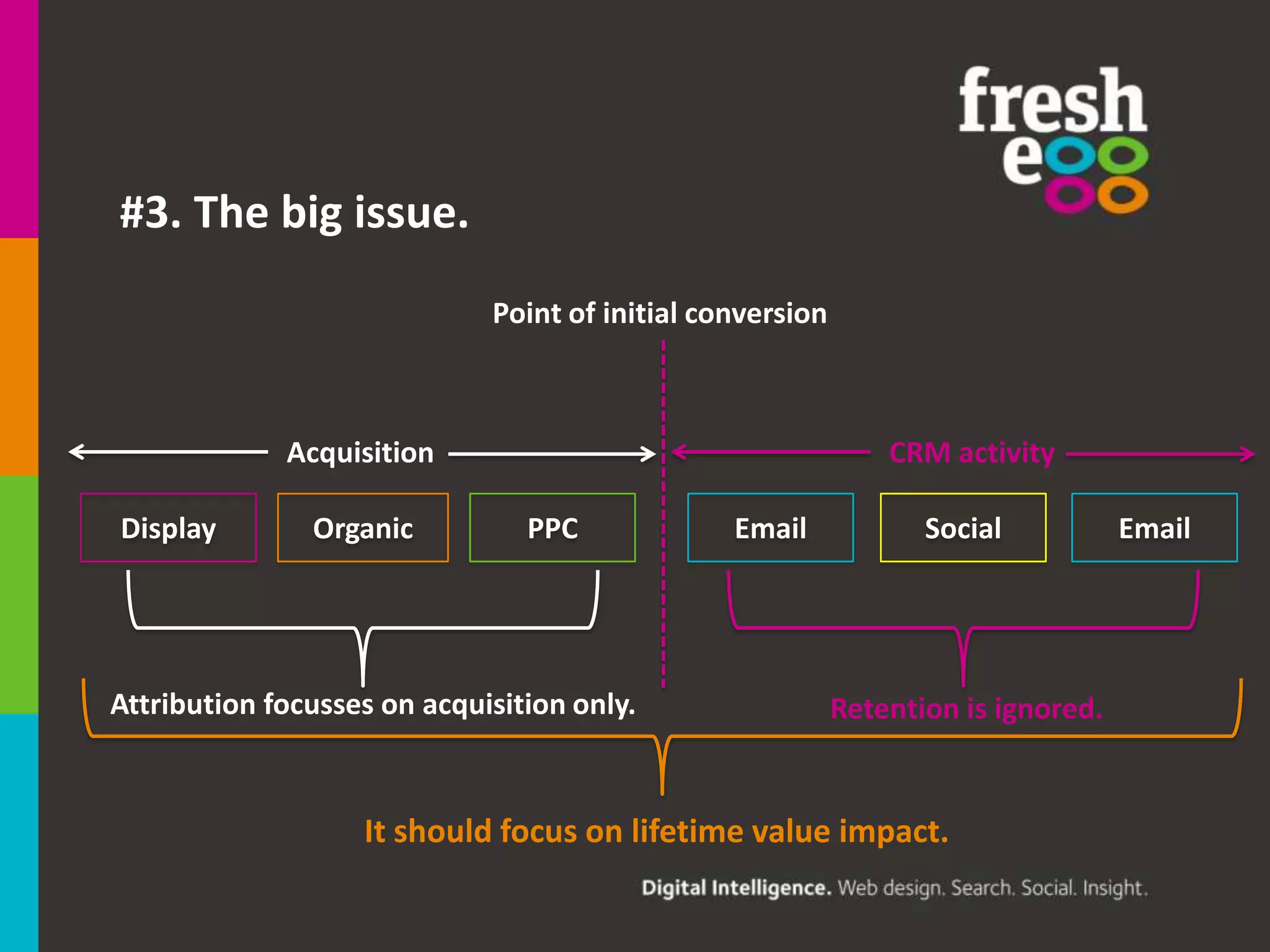
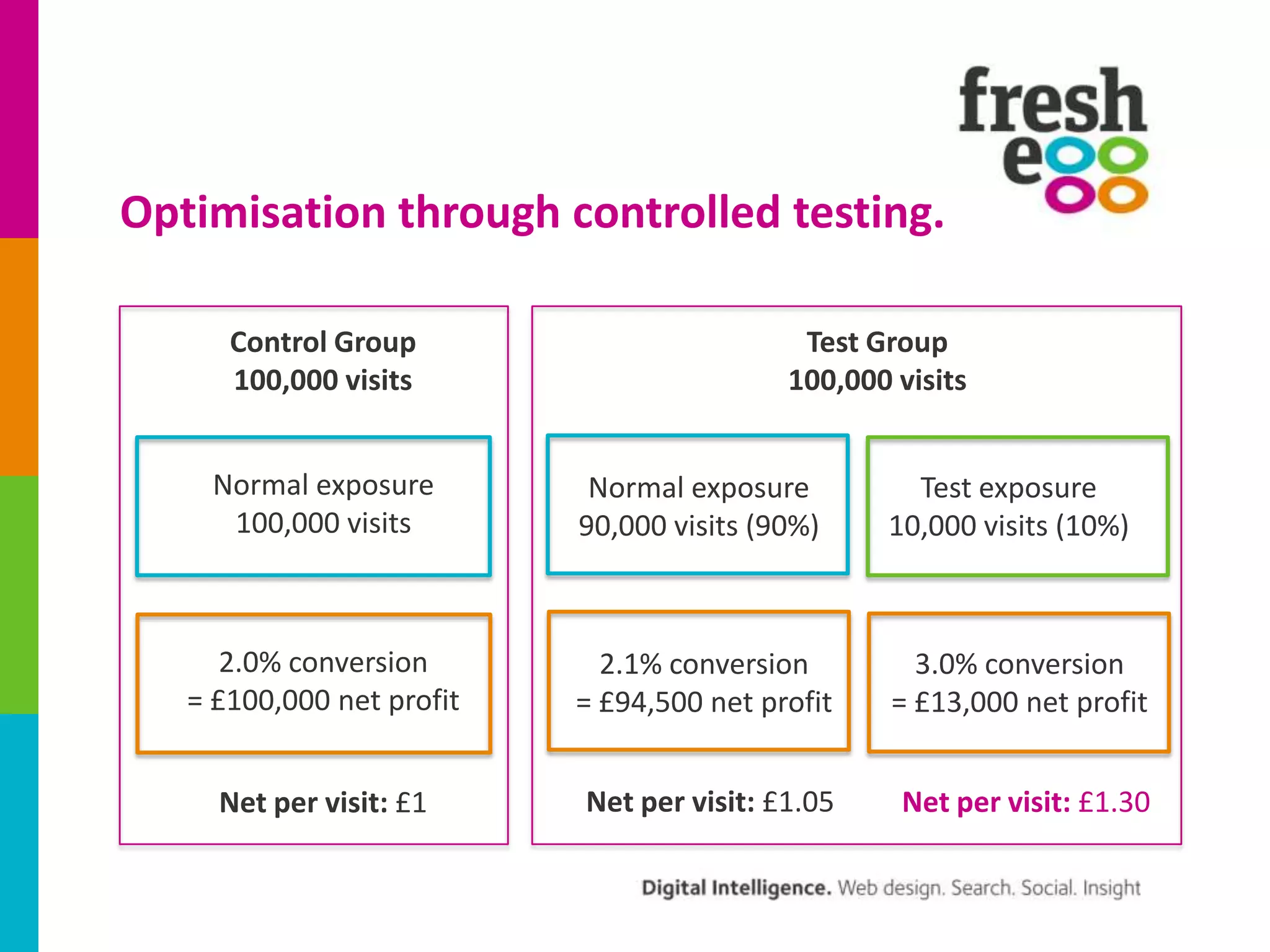
The document discusses how to effectively use Google Analytics for attribution modeling and outlines various tools like multi-channel funnels and data-driven attribution. It highlights the limitations of traditional attribution methods, such as ignoring offline impacts and cross-device behaviors, emphasizing the need for optimization through controlled testing. The author suggests using multi-channel funnels to analyze the role of different channels in conversions and advocates for tailored testing to improve campaign effectiveness.