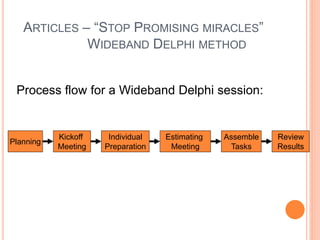
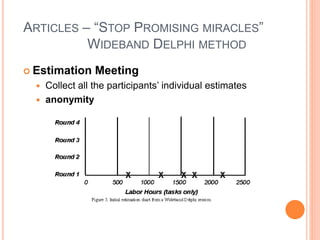
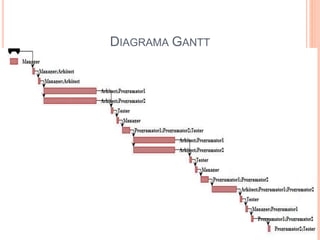
The document outlines a software project management presentation plan that covers software risk management and estimation techniques, particularly the wideband Delphi method. It discusses the importance of identifying and addressing project risks, the process of estimation, and the steps involved in developing a specific vehicle safety system (LCA). Emphasizing effective communication and adaptability to changing client requirements, it concludes that a successful project heavily relies on teamwork and proper management practices.