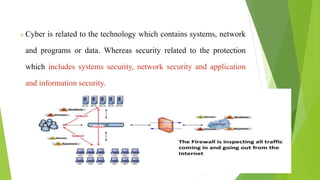
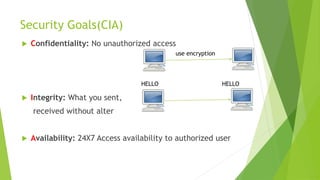
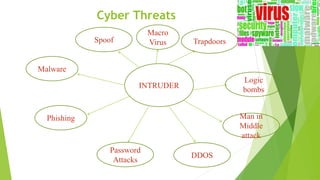
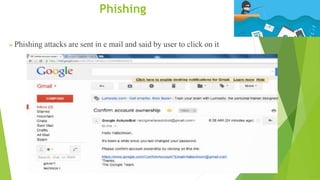
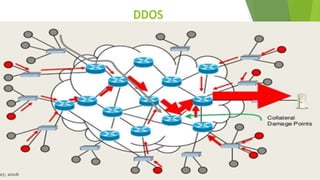
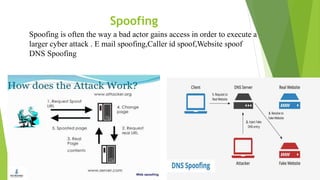
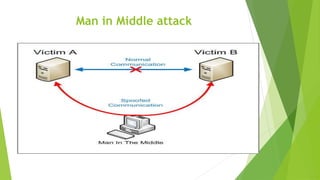
Cyber security and data protection are important in the digital era. Cyber security protects information and data from unauthorized access on the internet. It ensures only authorized people can access data. There are various security threats like malware, phishing, and man-in-the-middle attacks that can compromise data. Cyber laws like the IT Act 2000 and its 2008 amendment provide legal framework for electronic transactions and define cyber crimes and penalties. The Data Protection Act 2018 also governs how personal information is collected and used by organizations.