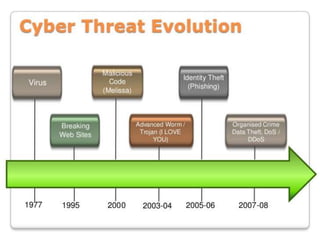
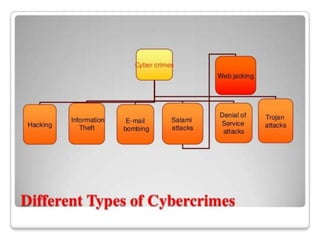
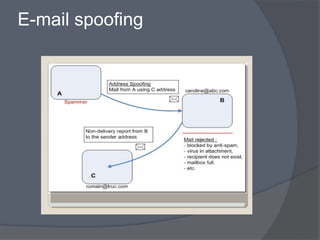
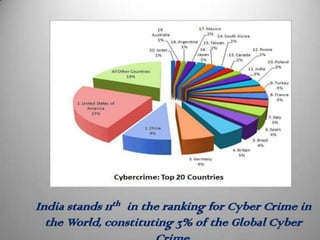
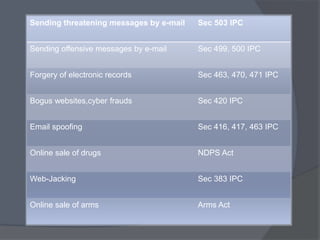
Cyber crime refers to criminal acts involving computers and the internet. The first recorded cyber crime took place in 1820 in France when employees sabotaged a machine that automated textile manufacturing out of fear it would threaten their jobs. Today, cyber crimes are increasingly common and include hacking, financial scams, and spreading computer viruses. While countries have laws against cyber crimes, law enforcement still struggles to deal with the issue due to the evolving nature of technology. Prevention methods include using antivirus software, firewalls, and practicing safe online behavior.