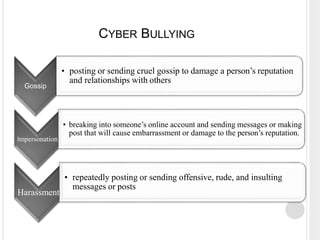
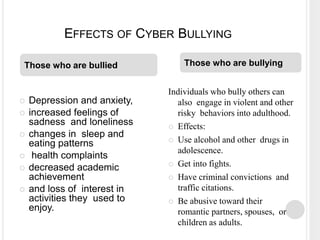
The document discusses cyber bullying, defining it as bullying that occurs through electronic technology and detailing the various forms it takes, such as gossip, harassment, and impersonation. It highlights the negative effects of cyber bullying, including mental health issues and potential long-term consequences for both victims and perpetrators. Additionally, it provides statistics on cyber bullying in Pakistan and offers preventive measures to combat this issue.