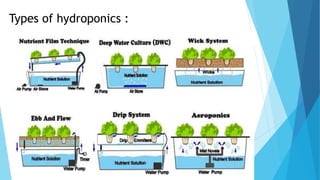
This document discusses current trends in agriculture, including artificial intelligence, vertical farming, hydroponics, and the use of technology. It introduces concepts like using AI to detect pests and diseases early, growing crops vertically with 70-95% less water, and hydroponics which can increase yields 3-4 times in the same space using 90% less water. In conclusion, modern agricultural techniques help farmers better monitor individual crop and animal needs, automate irrigation and harvesting, and use drones to save time spent sowing, while agriculture continues to drive development in rural areas.



![INTRODUCTION:
Agriculture [Ager + cultura = Field + culture]
Agriculture is arts & science of cultivating soil,
producing crops & raising livestock for business.
Traditional agriculture Modern agriculture](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/currenttrendsinagriculture-221102164411-16390057/85/CURRENT-TRENDS-IN-AGRICULTURE-pptx-4-320.jpg)