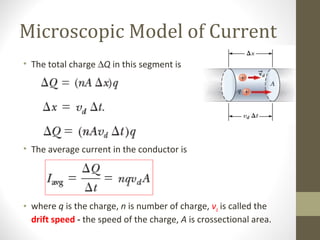
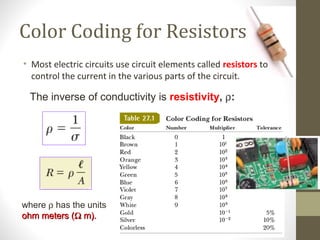
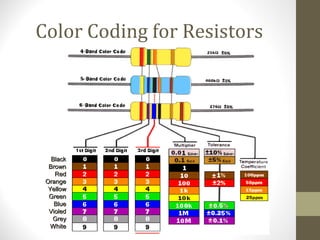
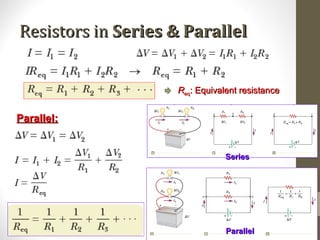
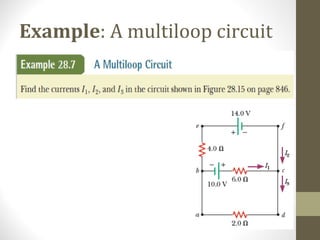
1) The document provides information about physics concepts related to electric current and resistors, including definitions of current, resistance, Ohm's Law, and Kirchhoff's rules.
2) Formulas are given for calculating current, resistance, power, and equivalent resistance for resistors connected in series and parallel.
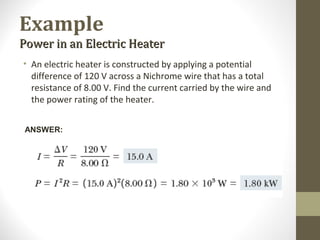
3) Examples are included to demonstrate applying the concepts and formulas to calculate values like current, resistance, and power in electric circuits.