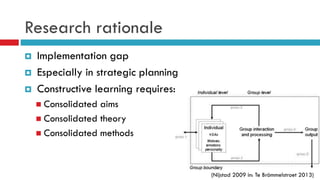
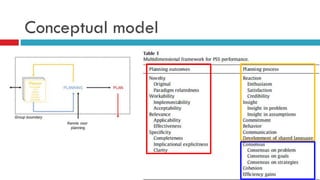
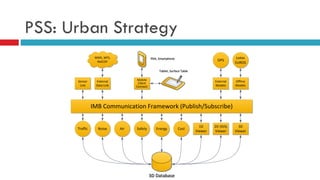
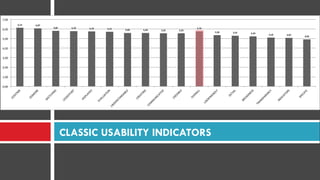
Planning support systems aim to improve planning processes and outcomes, but have not been rigorously tested. This study conducted a controlled experiment using the Urban Strategy planning support system to assess its impacts. Students played the role of planners and used Urban Strategy or traditional methods to develop strategies. Results from usability indicators and observations of the planning process showed Urban Strategy improved the process quality. Metrics also indicated it enhanced outcome quality, though the study design has limitations around external and ecological validity that require further exploration of fundamental improvement mechanisms between participants and planning support systems.