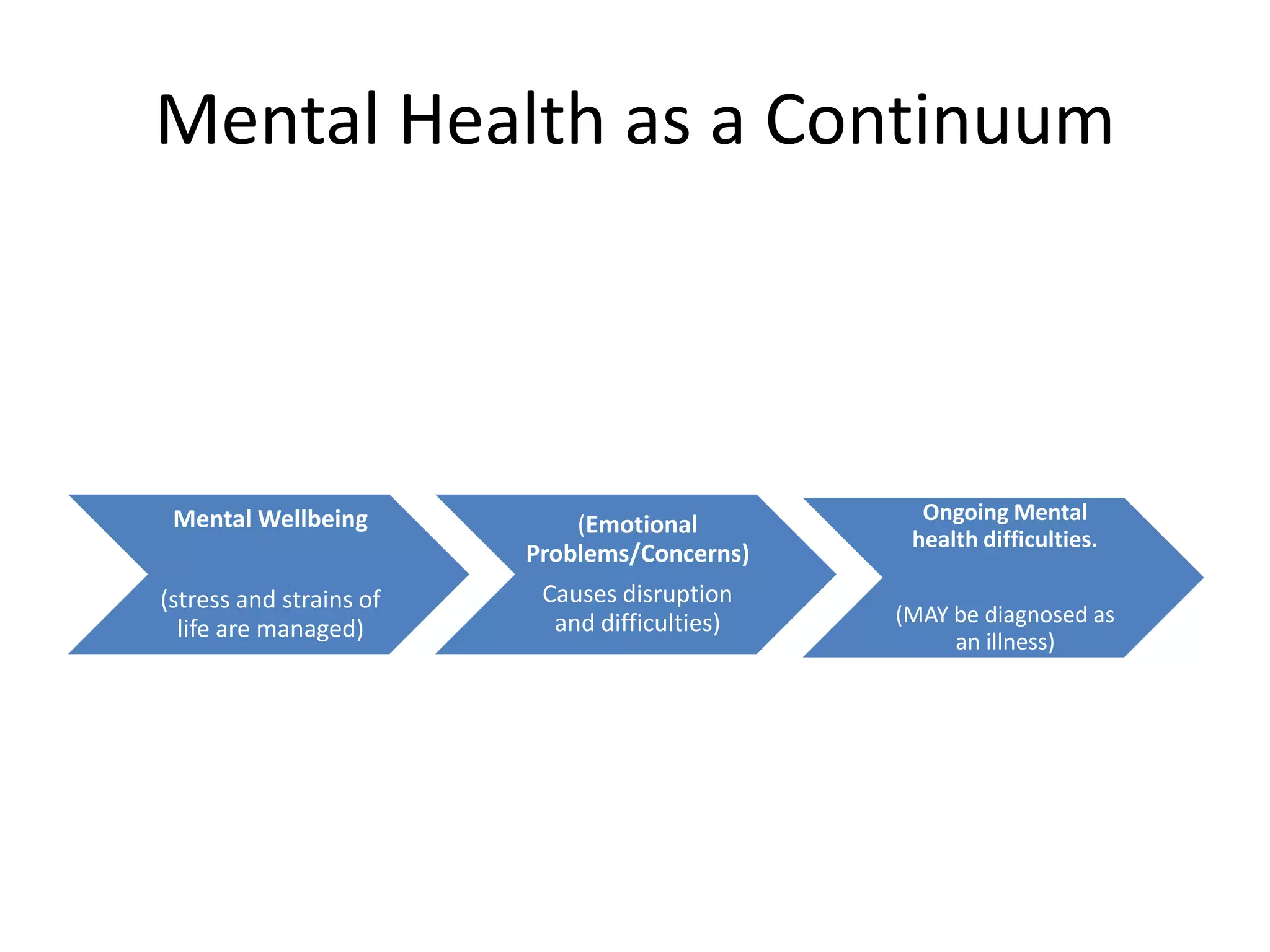
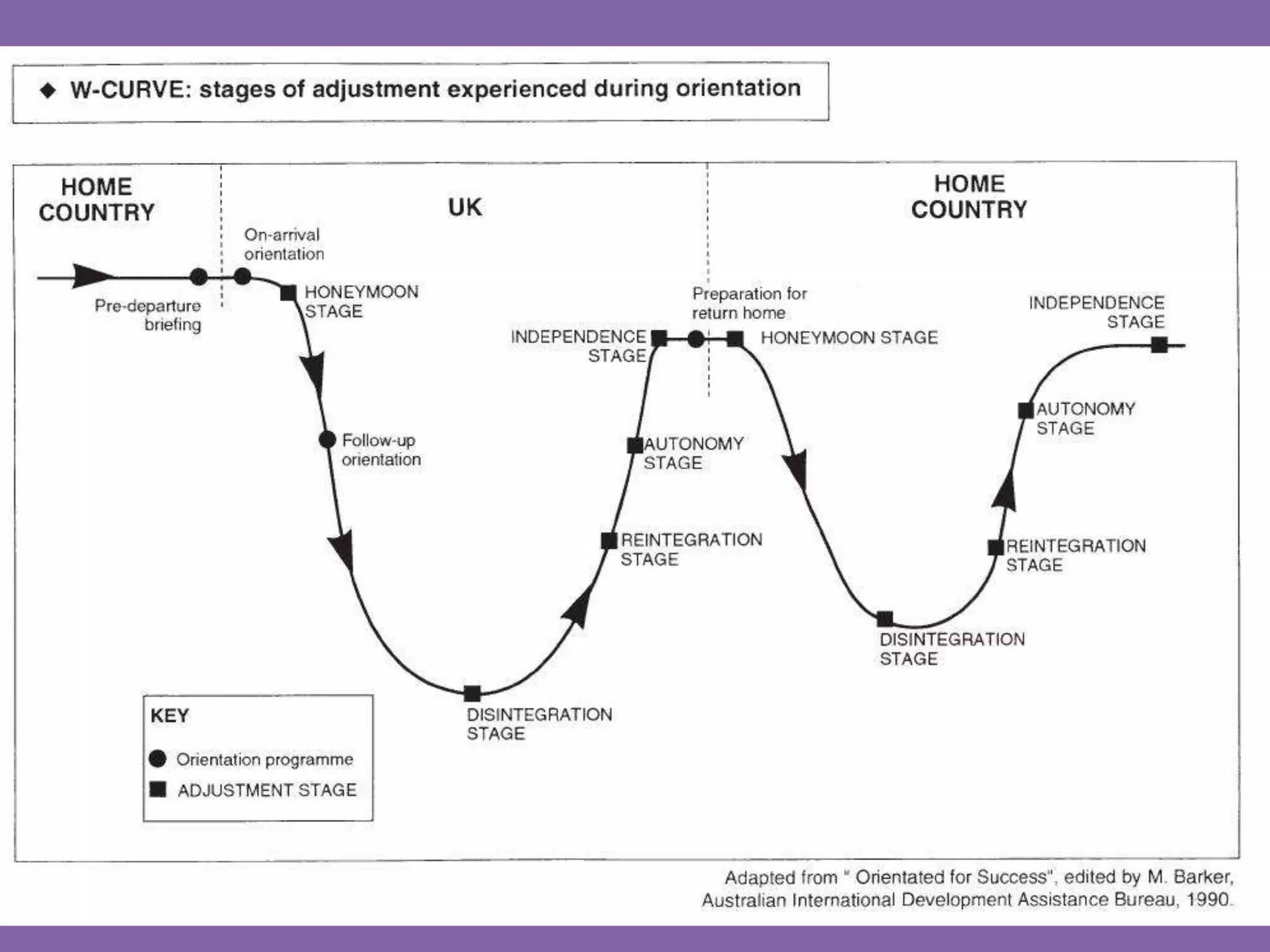
This document discusses cultural and diversity awareness. It defines prejudice and discrimination and encourages sharing experiences of feeling included and excluded. It emphasizes the importance of making people feel included by remembering names, listening, involving everyone, and understanding different abilities, cultures, values and beliefs. It also discusses disability, mental health, well-being, and indicators of mental distress. The document stresses cultural awareness, including different concepts of culture, language barriers, and cultural differences regarding etiquette, socializing, religion, gender, and relationships. It encourages learning names, engaging with other cultures, and focusing on open-minded communication and understanding differences.