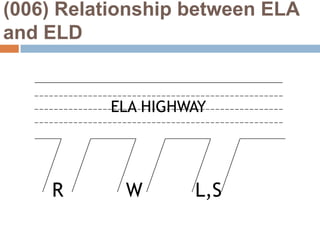
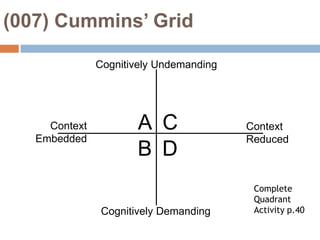
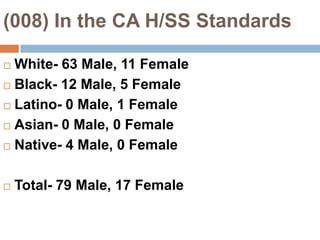
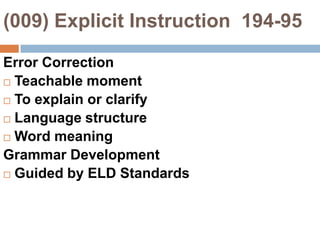
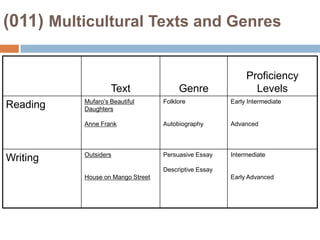
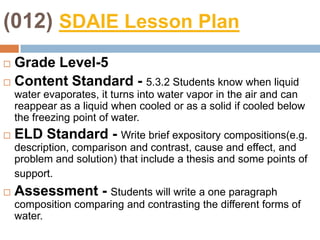
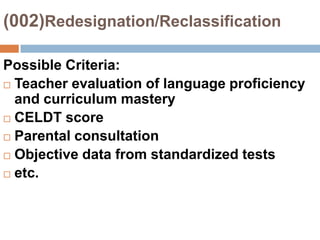
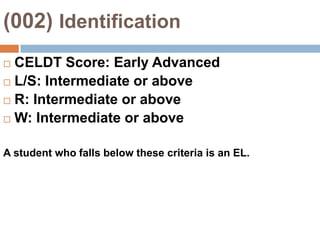
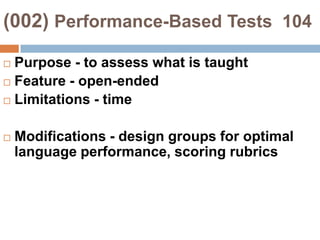
This document provides an overview of Module 2 of a CTEL exam preparation course. It covers several domains related to the foundations of English language development and content instruction for English learners. Some key topics and benchmarks discussed include the history of bilingual education in the US, major laws and court cases affecting English learners, approaches to ELD and SDAIE instruction, and components of effective lesson planning and delivery for English learners. The document also provides examples of strategies and methods that promote the development of English listening, speaking, reading and writing skills in ELD contexts.