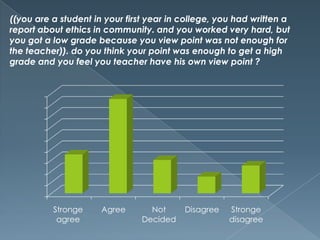
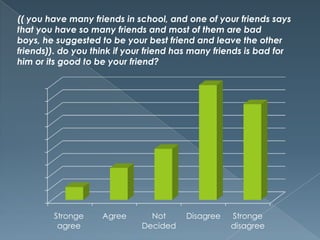
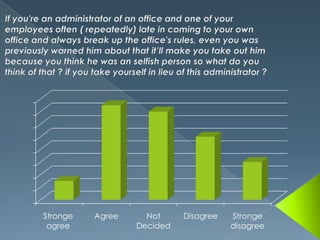
This document defines egocentrism and discusses its characteristics. It begins by defining egocentrism as the inability to differentiate one's own perspective from others' perspectives. It then discusses the developmental stages of egocentrism from infancy through adolescence. Finally, it outlines some characteristics of egocentric thinking such as being selfish, self-interested, and seeing reality as centered on oneself.